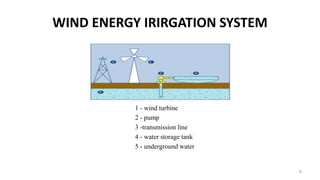
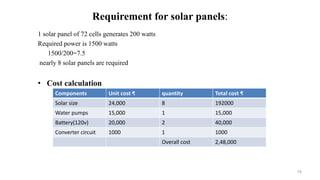
The document details a seminar presentation on the application of wind and solar energy for irrigation, highlighting the challenges faced by farmers due to electric supply constraints. It outlines the objectives, benefits, and drawbacks of utilizing these renewable energy sources, as well as a case study demonstrating their effectiveness in Bihar, India. The conclusion emphasizes the economic and environmental advantages of implementing renewable energy irrigation systems.