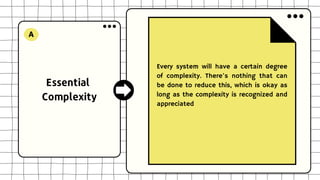
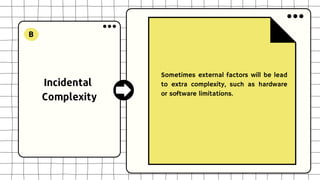
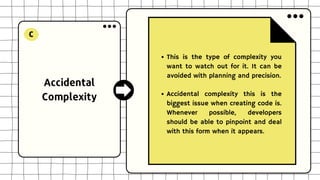
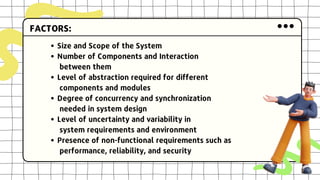
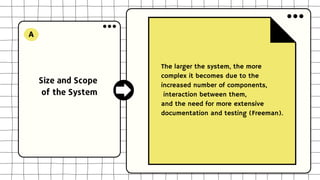
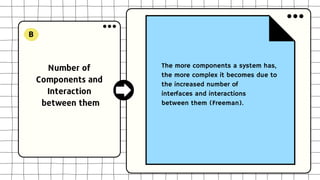
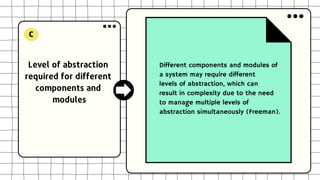
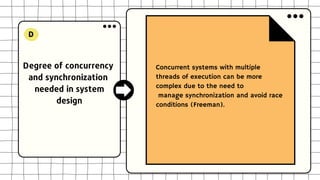
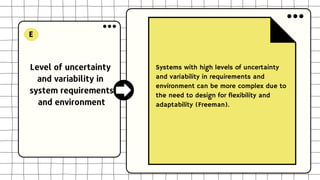
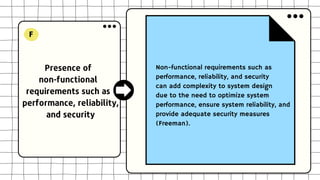
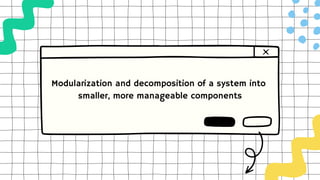
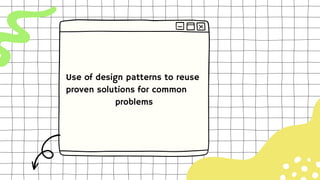
This document discusses software design complexity, including its types (essential, incidental, accidental), ways to measure it, and factors that contribute to it such as system size and scope, number of components, levels of abstraction, concurrency needs, and non-functional requirements. Understanding software design complexity is important because it affects time, cost, and quality. Techniques for managing complexity include modularization, design patterns, formal methods, visualization tools, agile development, and automated testing.