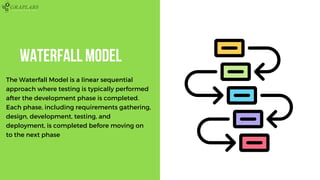
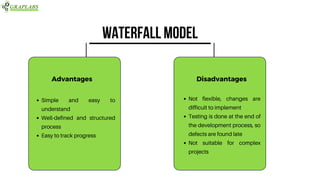
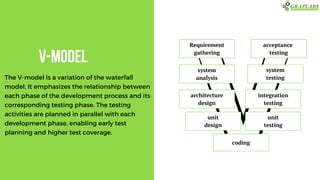
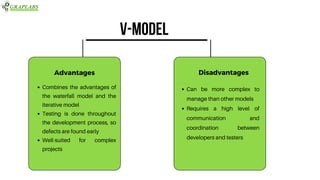
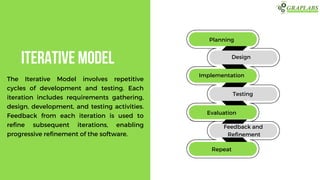
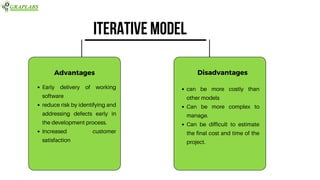
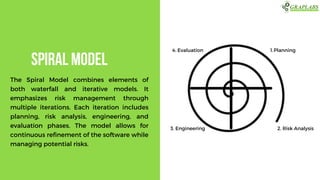
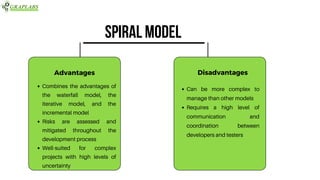
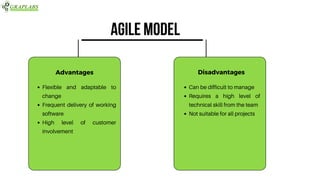
The document outlines various software testing models, including Waterfall, V-Model, Iterative, Spiral, and Agile models. Each model is described with its advantages and disadvantages, focusing on aspects like flexibility, risk management, and early defect identification. The document serves as a guide for understanding these testing methodologies and their application in software development.