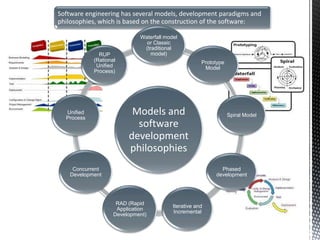
Software engineering is the systematic and quantifiable approach to developing software through principles of computer science and mathematics. It involves analyzing requirements, specifying and designing the architecture, programming and developing the software, testing it, documenting it, and maintaining it. The software engineering process aims to develop cost-effective solutions to software problems through various models and approaches.