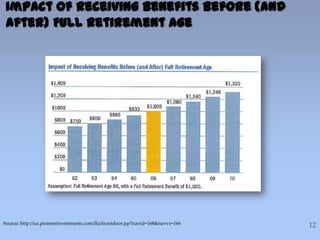
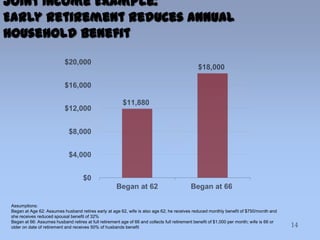
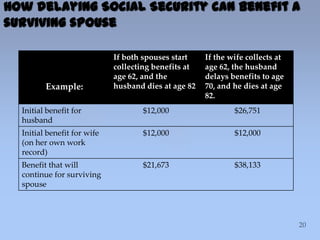
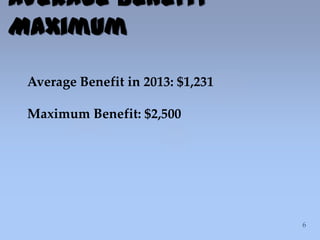This document summarizes information about Social Security benefits. It covers the different types of benefits including spousal, survivor, divorce, and disability benefits. It provides details on eligibility, how benefits are calculated based on earnings history, and the impact of claiming benefits at different ages. Examples are given showing how a married couple's total household benefit changes based on one spouse claiming early versus at full retirement age. The document also discusses options for divorced spouses and surviving spouses. Tools for learning more about benefits and applying are listed at the end.