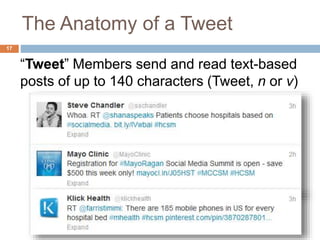
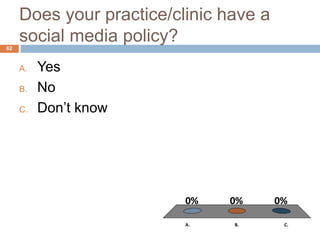
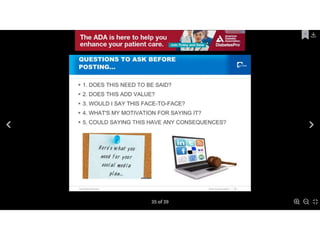
This document discusses social networking and medicine. It begins with a warning that social media is disruptive technology. It then lists objectives for the session such as defining social media, listing ways patients and clinicians use social media, and identifying guidelines for physician use of social media. The document discusses major social media sites and how physicians can use them to connect with patients and other doctors. It also addresses managing your online reputation as a physician and providing strategies for appropriate social media use.