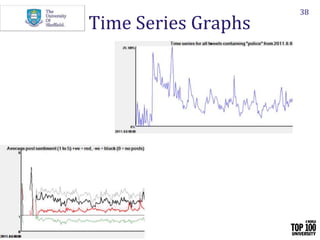
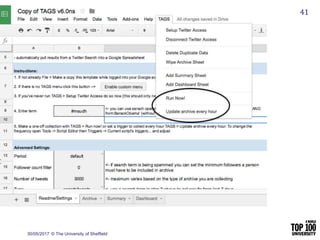
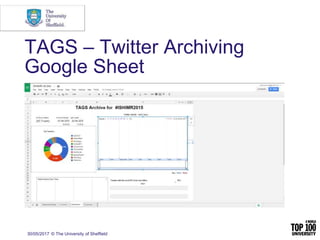
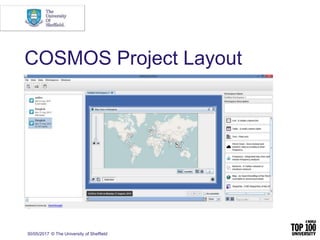
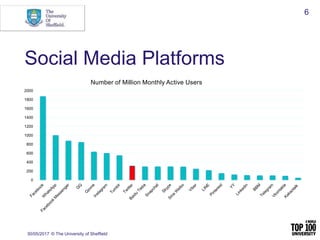
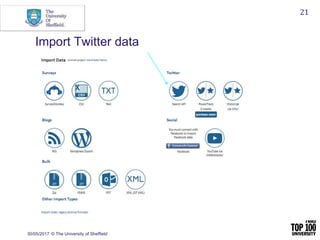
The document provides an overview of social media research, focusing on the use of Twitter for academic purposes. It highlights various tools for capturing and analyzing Twitter data, such as DiscoverText, Mozdeh, and NodeXL, along with their respective features and pricing. Additionally, it discusses the potential applications of social media analytics in various fields and emphasizes the importance of social network analysis for understanding user interactions.




















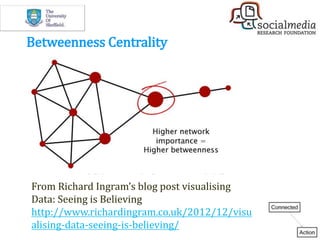
![[Divided]
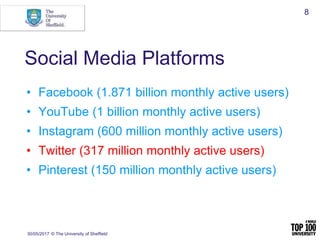
Polarized Crowds
[Unified]
Tight Crowd
[Fragmented]
Brand Clusters
[Clustered]
Community Clusters
[In-Hub & Spoke]
Broadcast Network
[Out-Hub & Spoke]
Support Network
6 kinds of Twitter networks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop-practicaltoolsoverview30may-170530182726/85/Social-Media-A-Practical-Approach-26-320.jpg)
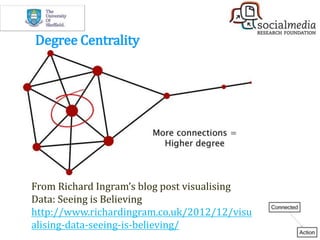
![[Divided]
Polarized Crowds
[Unified]
Tight Crowd
[Fragmented]
Brand Clusters
[Clustered]
Community Clusters
[In-Hub & Spoke]
Broadcast Network
[Out-Hub & Spoke]
Support Network
6 kinds of Twitter networks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop-practicaltoolsoverview30may-170530182726/85/Social-Media-A-Practical-Approach-27-320.jpg)