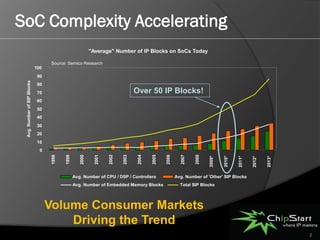
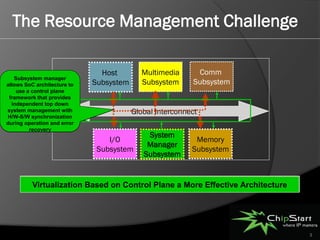
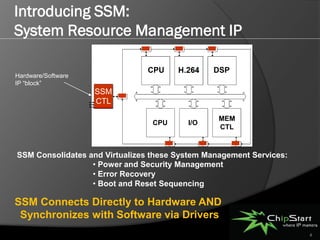
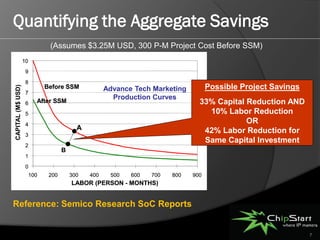
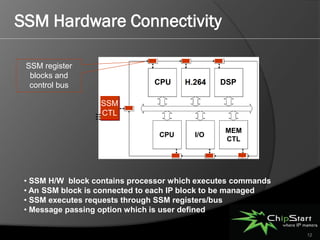
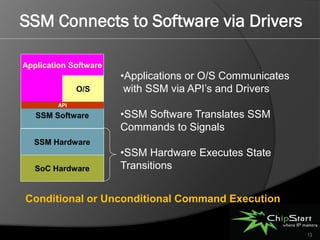
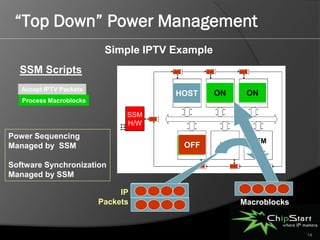
The document introduces the System Manager (SSM), the first SOC IP subsystem designed for efficient system resource management, addressing challenges in SOC architecture complexity. It highlights the advantages of SSM, including reduced development costs, enhanced software control, and improved hardware-software integration through high-level management governance. SSM also features capabilities for power and error management, streamlining development processes and enabling better coordination between hardware and software.