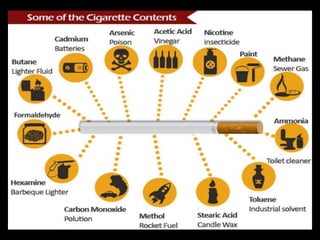
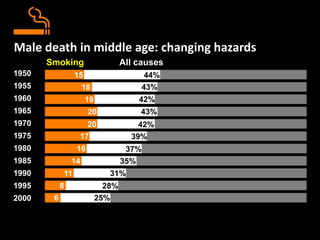
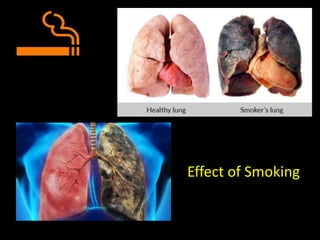
The document summarizes the hazards of smoking and benefits of quitting. It discusses what smoking is, the harmful chemicals in cigarettes, smoking statistics globally and in India, short-term and long-term health effects of smoking, reasons some people smoke, case studies of people who have quit smoking, and why smoking is difficult to quit due to nicotine withdrawal symptoms and addiction. The conclusion emphasizes it is easy to become a smoker but difficult to quit, and encourages not starting smoking or quitting for good if currently a smoker.