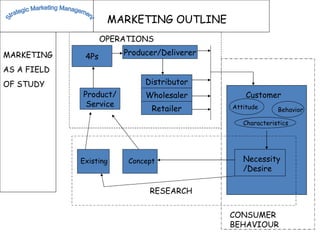
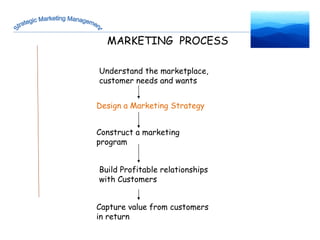
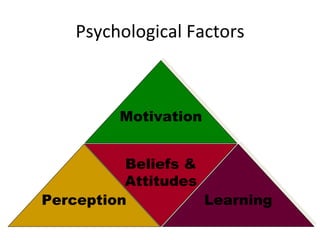
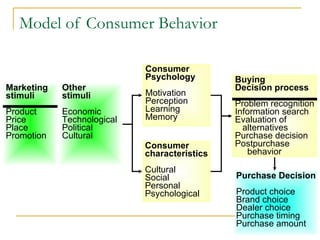
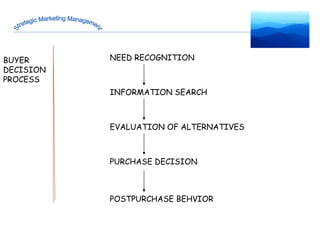
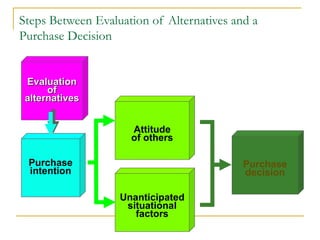
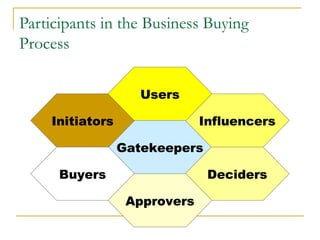
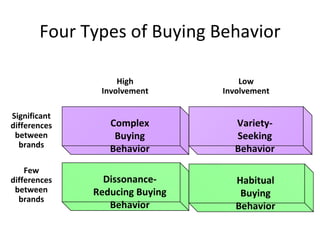
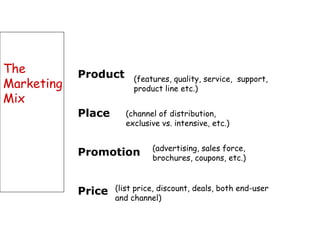
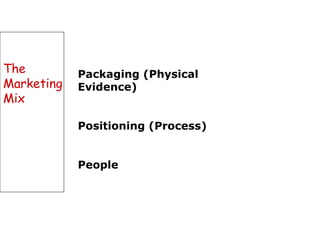
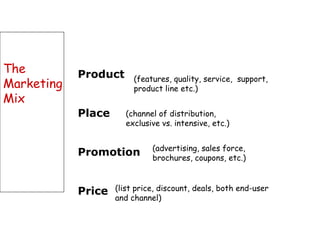
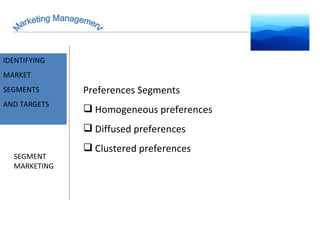
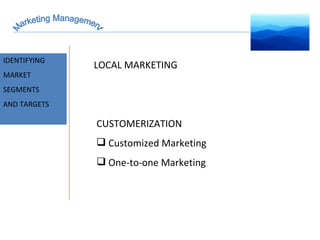
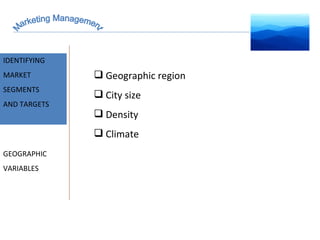
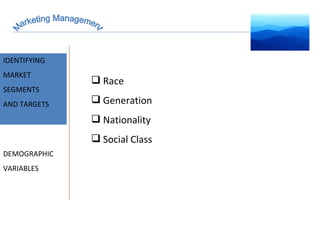
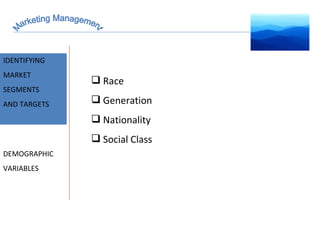
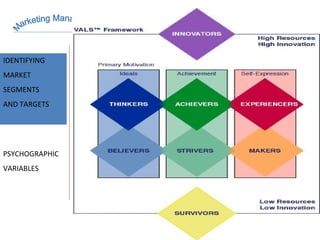
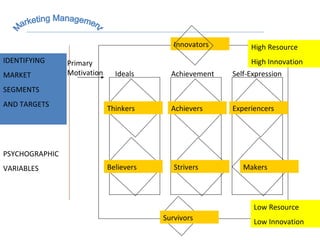
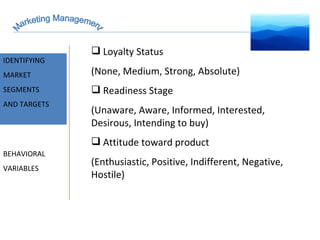
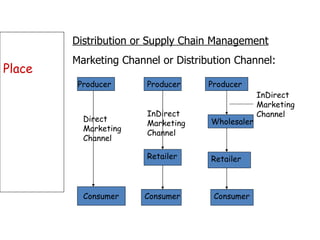
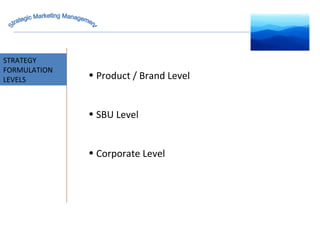
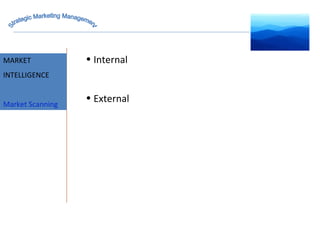
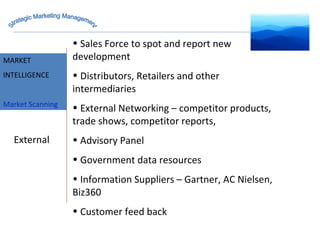
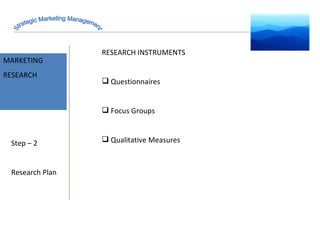
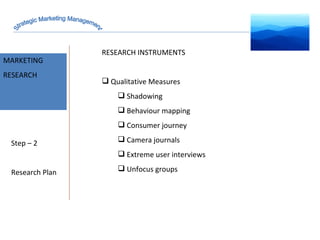
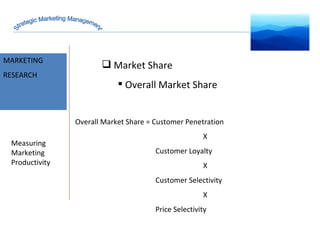
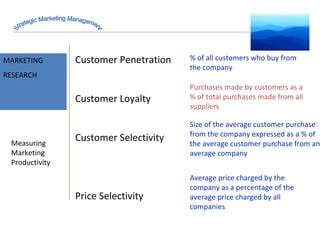
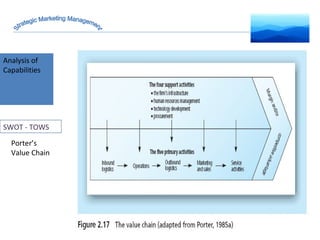
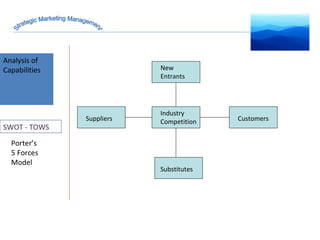
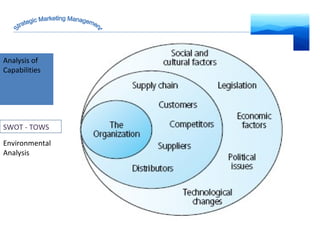
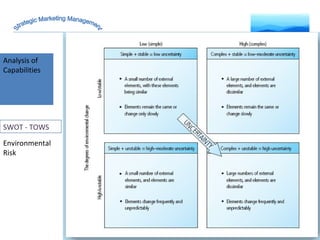
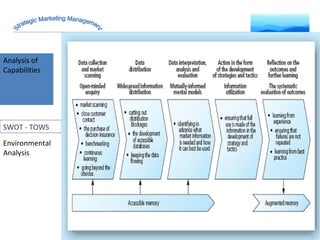
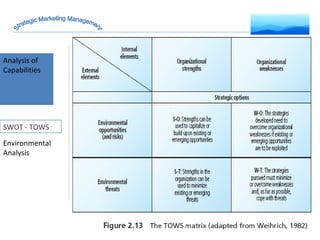
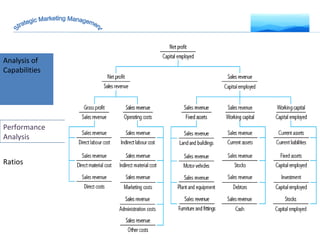
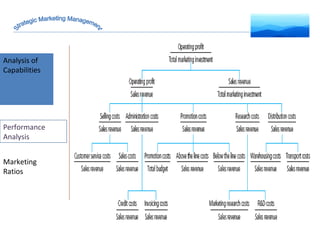
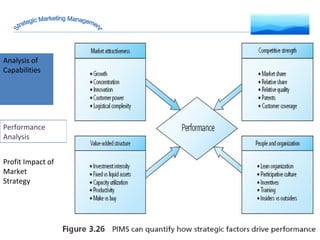
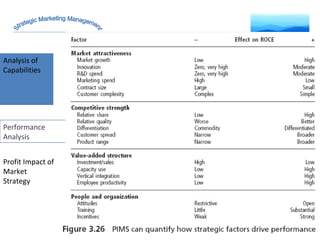
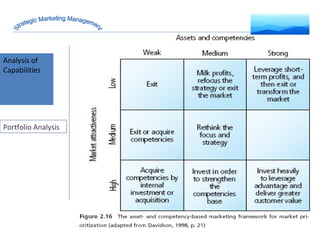
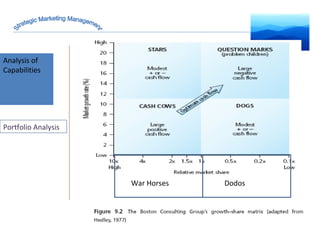
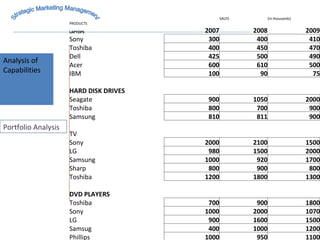
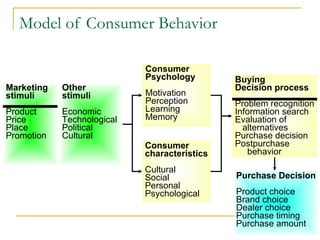
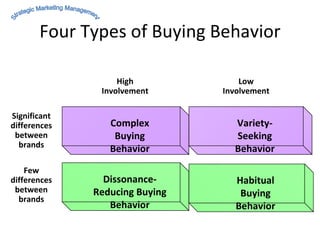
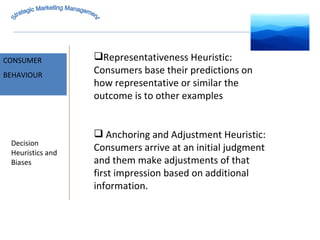
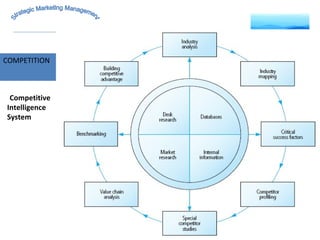
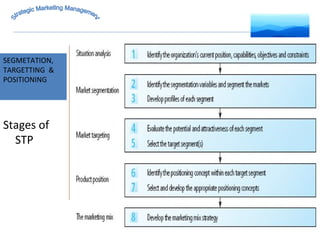
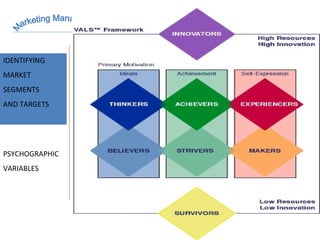
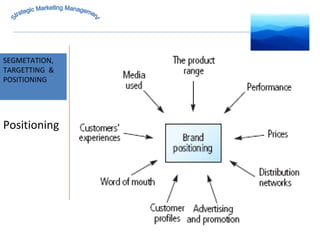
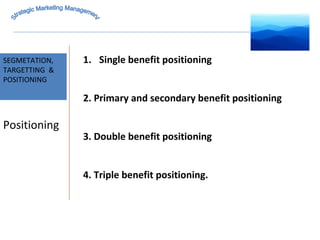
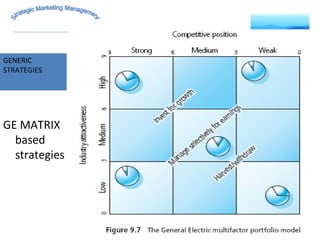
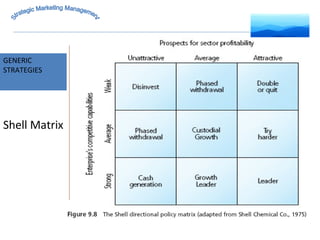
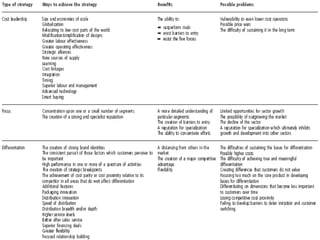
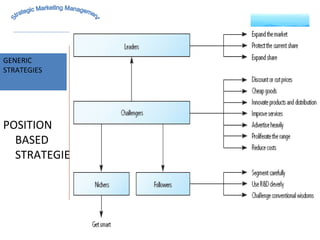
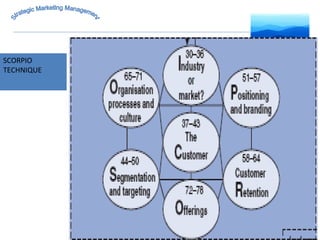
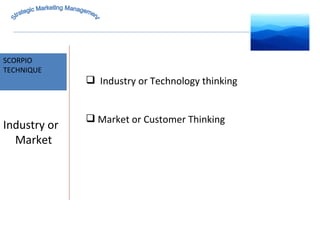
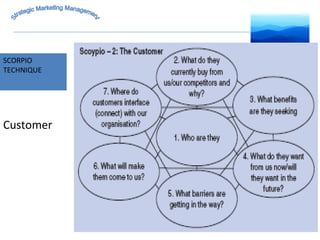
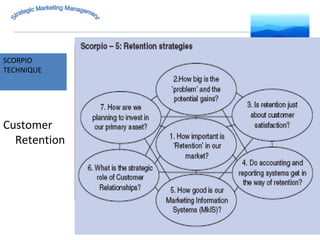
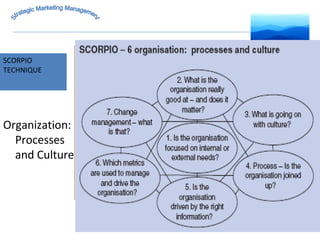
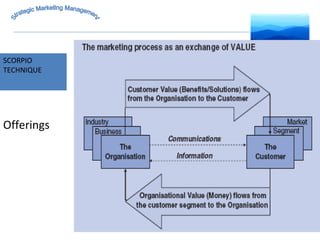
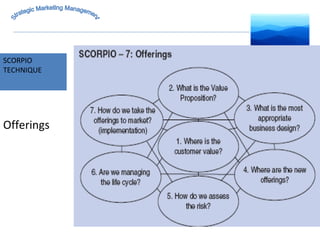
The document discusses strategic marketing management and defines marketing. It states that marketing is the process of creating value for customers to build relationships and capture value in return. It also provides the American Marketing Association's definition of marketing as the activity of creating and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, partners, and society. Finally, it discusses the marketing process as understanding customer needs, designing a strategy, and building profitable relationships to capture value from customers.