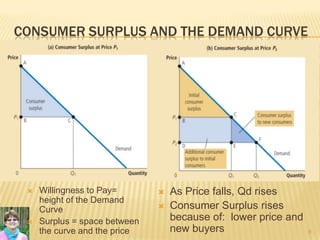
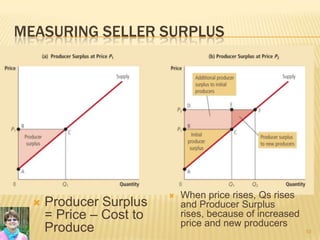
This document provides an overview of key economic concepts related to consumers, producers, and the efficiency of markets. It defines willingness to pay, consumer surplus, cost, and producer surplus. It explains that consumer surplus is the difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good and what they actually pay. Producer surplus is the difference between the price received and the cost of producing a good. The document states that market efficiency is achieved when total surplus, the sum of consumer and producer surplus, is maximized. This maximizes the overall benefit to society.