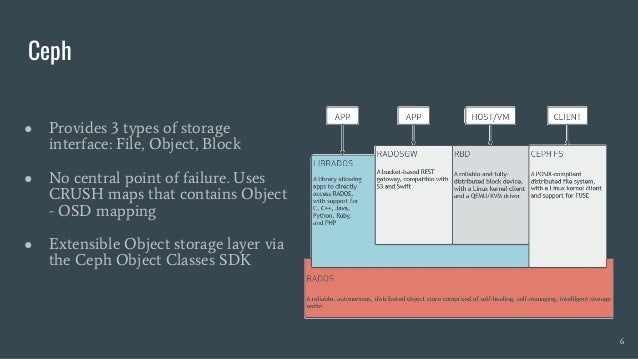
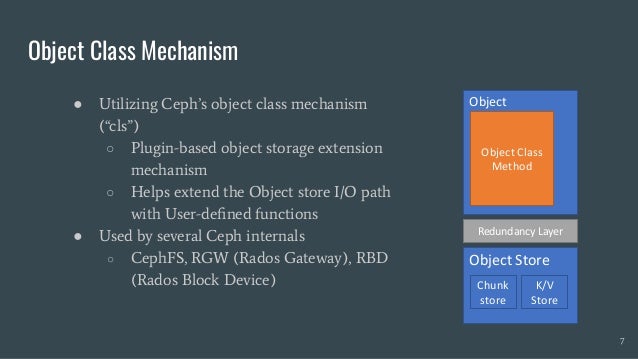
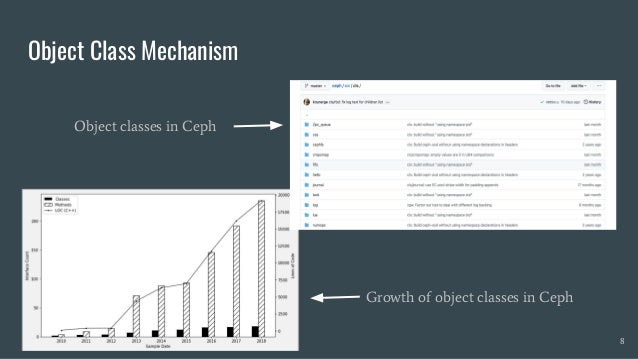
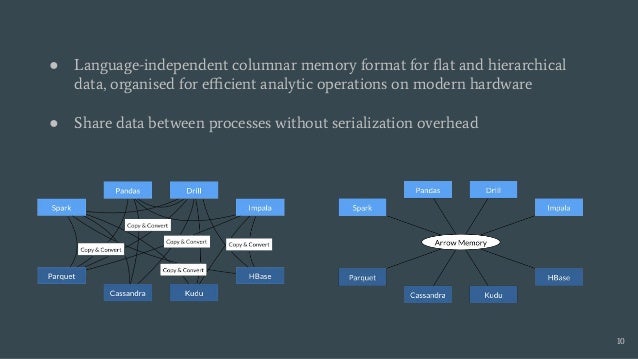
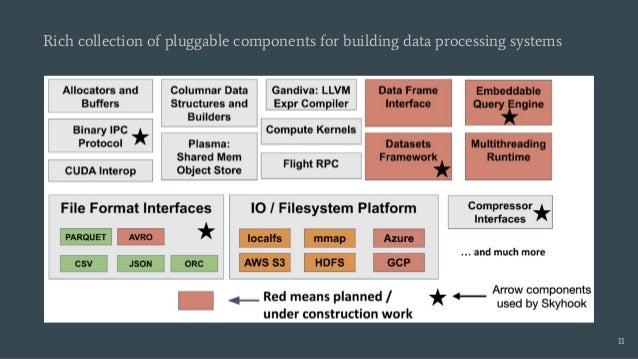
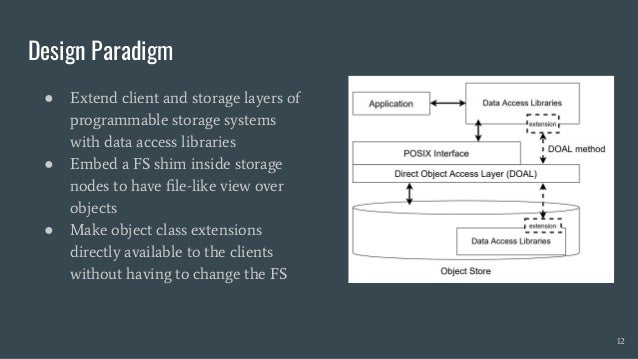
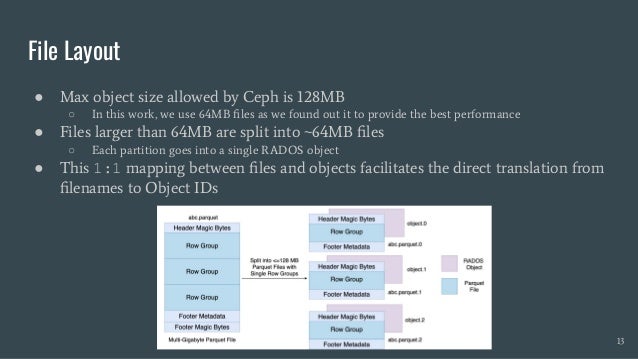
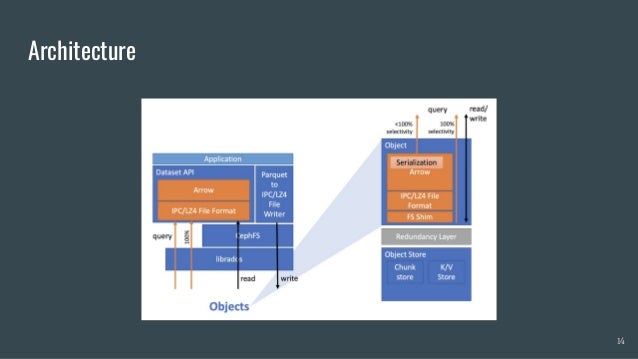
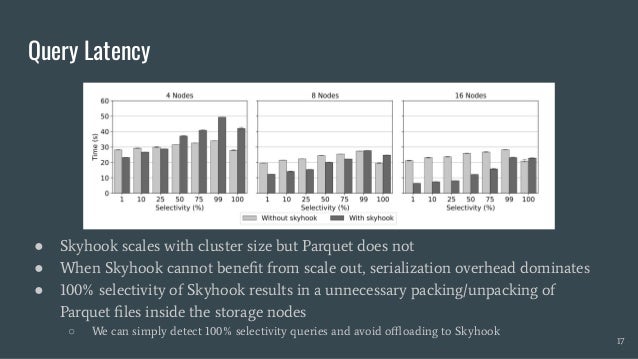
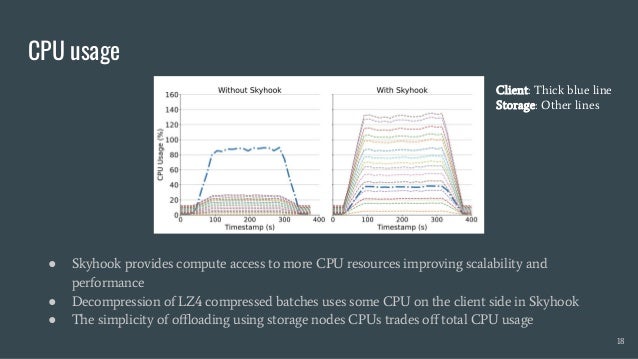
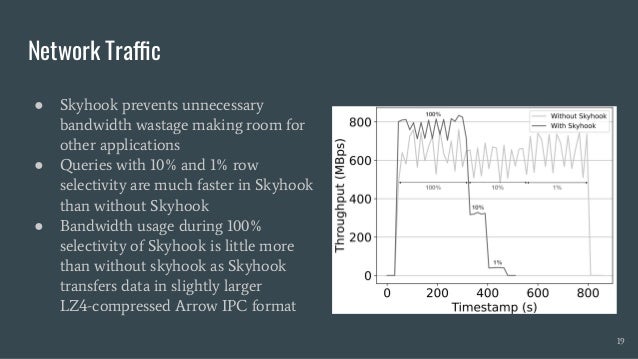
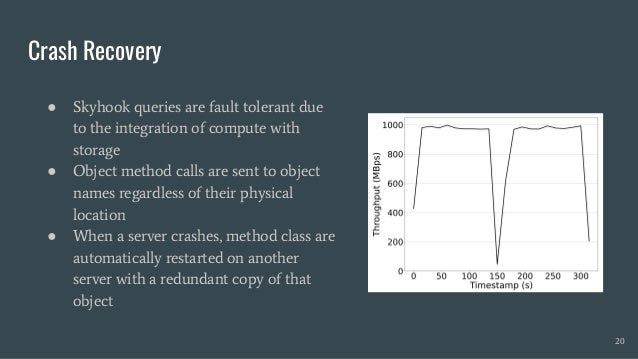
Skyhook is a storage system designed to offload computation to storage nodes, alleviating CPU bottlenecks caused by high-speed storage and networks. It enables seamless integration with existing storage systems without requiring additional hardware and supports various interfaces like file, object, and block storage. Evaluations demonstrate improvements in query latency and CPU resource utilization, with features like fault tolerance and plans for future enhancements including RDMA support and advanced query processing.