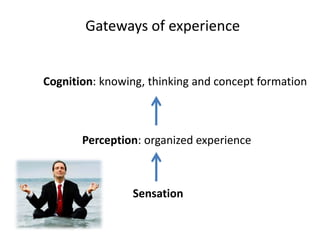
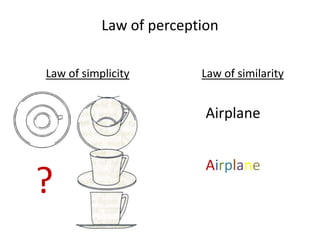
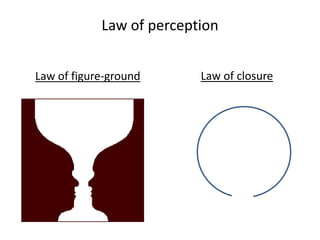
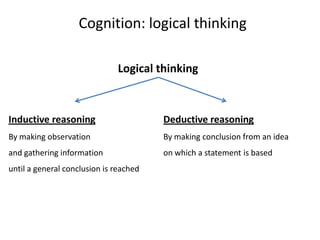
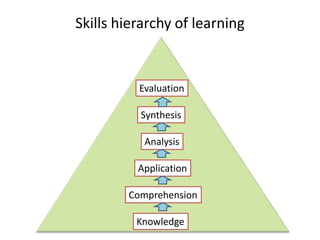
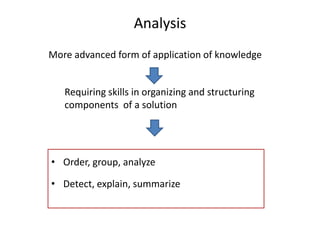
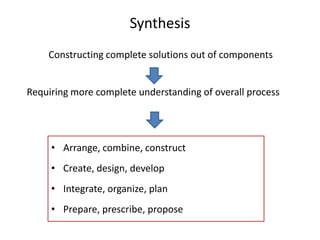
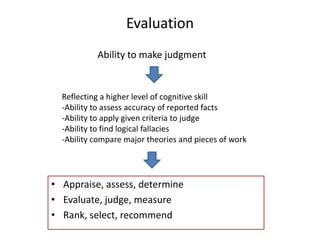
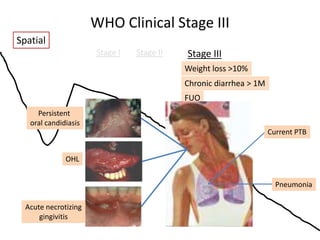
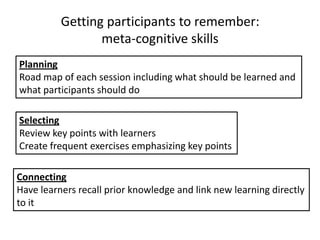
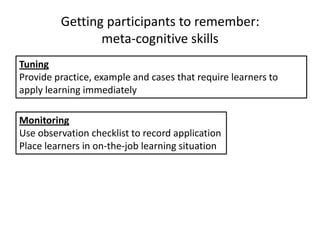
The document outlines cognitive learning frameworks, emphasizing the hierarchy of learning, skills development, and strategies for memory retention and application. It discusses various types of cognition such as logical and creative thinking and highlights the key factors influencing learning, including motivation and prior knowledge. Additionally, it covers adult learning principles focused on autonomy, experience, and the practical application of skills in real-world scenarios.