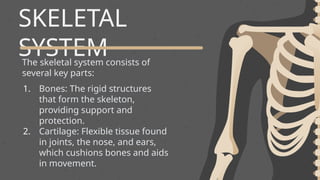
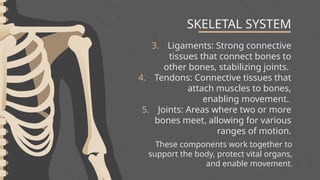
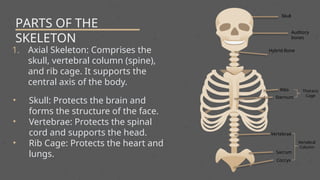
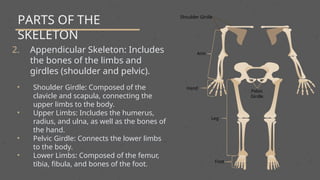
The skeletal system is the internal framework of bones in vertebrates and includes bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and joints. It consists of the axial skeleton, which supports the central axis of the body, and the appendicular skeleton, which includes the limbs and girdles. The primary functions of the skeleton are to provide support, protection, facilitate movement, store minerals, and produce blood cells.