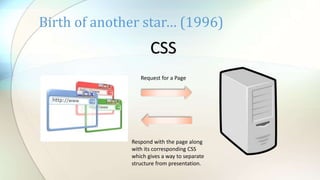
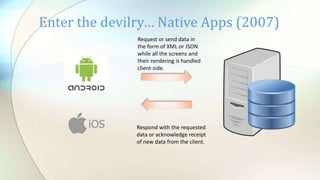
This document discusses the evolution of web applications from static HTML pages to single page applications (SPAs). Early web applications used static HTML pages that loaded entirely when requested, while dynamic pages loaded content from a database. JavaScript added interactivity but required page reloads to update. AJAX allowed updating parts of a page without reloading via XML/JSON. Native apps communicated with servers via APIs for new data. SPAs combine JavaScript, DOM manipulation, and AJAX to allow web browsers to behave like native apps, loading initial content and then updating dynamically without reloads. This avoids maintaining separate web and API code.