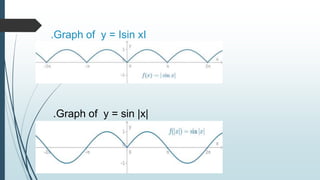
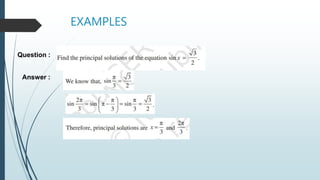
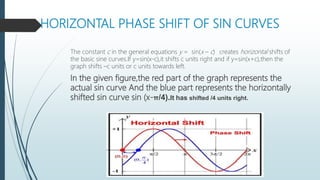
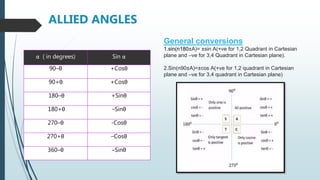
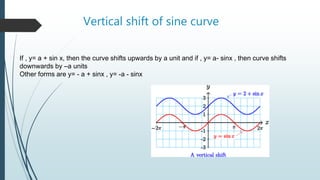
The document discusses the basic properties and transformations of the sine curve. It defines sine as the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse in a right triangle. The sine curve has a period of 2π and is an odd function. The domain is all real numbers and the range is [-1,1]. Horizontal phase shifts move the sine curve left or right. Allied angles use trigonometric identities to relate sine and cosine values for angles in all four quadrants. Examples demonstrate finding sine values for specific angles. Vertical shifts, amplitude changes, and absolute value functions are shown to transform the basic sine curve. Applications of trigonometry include astronomy, construction, and satellite navigation.
![BASIC PROPERTIES OF SINE FUNCTION
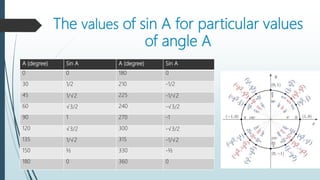
Sine is a trigonometric function. It is defined as p/h in a right angle triangle, where p is the
perpendicular and h is the hypotenuse.In triangle ABC,sin A=BC/AB.
Sin A is a periodic function, with period 2 π
Sin A is an odd function. Sin (-A)= -Sin A
Domain of Sin x : ( -∞ , +∞ )
Range of Sin x : [ -1 , 1 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sinecurvesfinalppt-220906170452-0dbec277/85/Sine_curves_-final-ppt-pptx-2-320.jpg)
![GRAPH OF SINX
If, sin θ = sin α
Then, General Solution of sine function :
θ = nπ + (-1)
n
α, where α ∈ [-π/2, π/2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sinecurvesfinalppt-220906170452-0dbec277/85/Sine_curves_-final-ppt-pptx-3-320.jpg)

![Sine curve with f(x)= k sin x transformation
Y= a sin x form changes the amplitude of sin x to from 1 to k.The
range of ksinx is [-k,k].The crest and trough changes as k times -1
or 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sinecurvesfinalppt-220906170452-0dbec277/85/Sine_curves_-final-ppt-pptx-9-320.jpg)