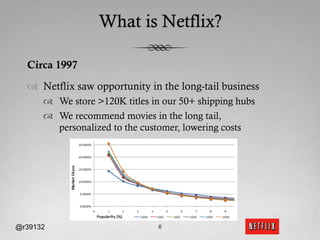
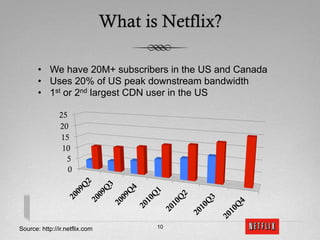
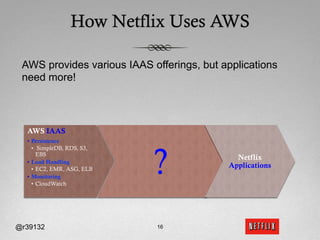
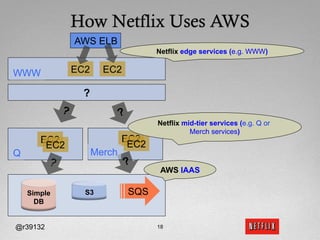
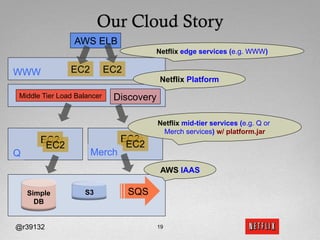
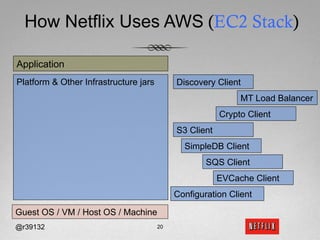
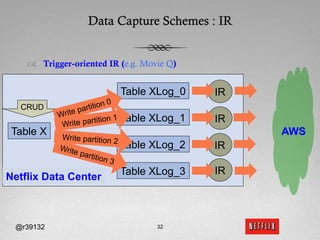
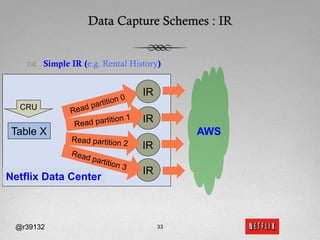
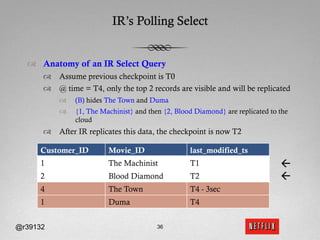
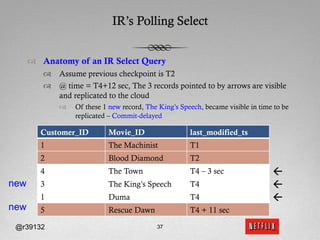
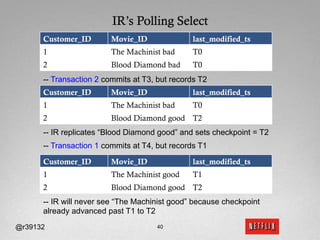
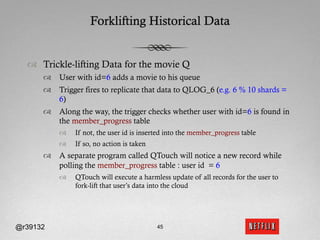
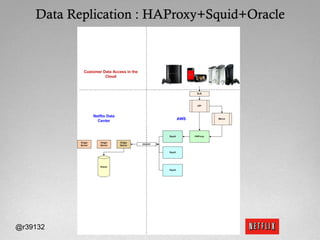
The document discusses Netflix's transition to cloud computing with Amazon Web Services, including how they use various AWS services like SimpleDB, S3, EC2, and ELB. It describes how Netflix built their own platform on top of AWS to provide additional functionality for their applications. The document also covers how Netflix uses SimpleDB and S3 for data persistence and storage in the cloud.