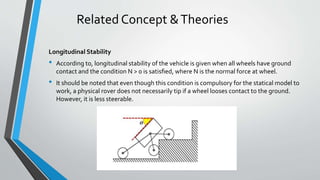
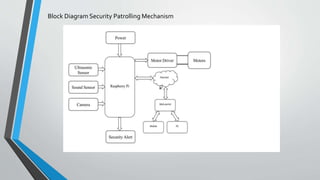
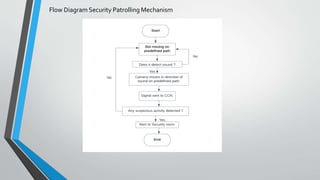
This presentation summarizes a final year project on designing a stairs climbing bot based on a rocker bogie mechanism and IoT. It introduces the motivation for the project, provides an overview of the literature survey conducted. It describes the methodology adopted, including concepts related to traction, stability, and applications of IoT. It shows the block and flow diagrams of the security patrolling mechanism. It presents the timeline and work done so far on the project. In conclusion, the presentation outlines a final year project on developing a stairs climbing robot for security patrolling applications using a rocker bogie mechanism.