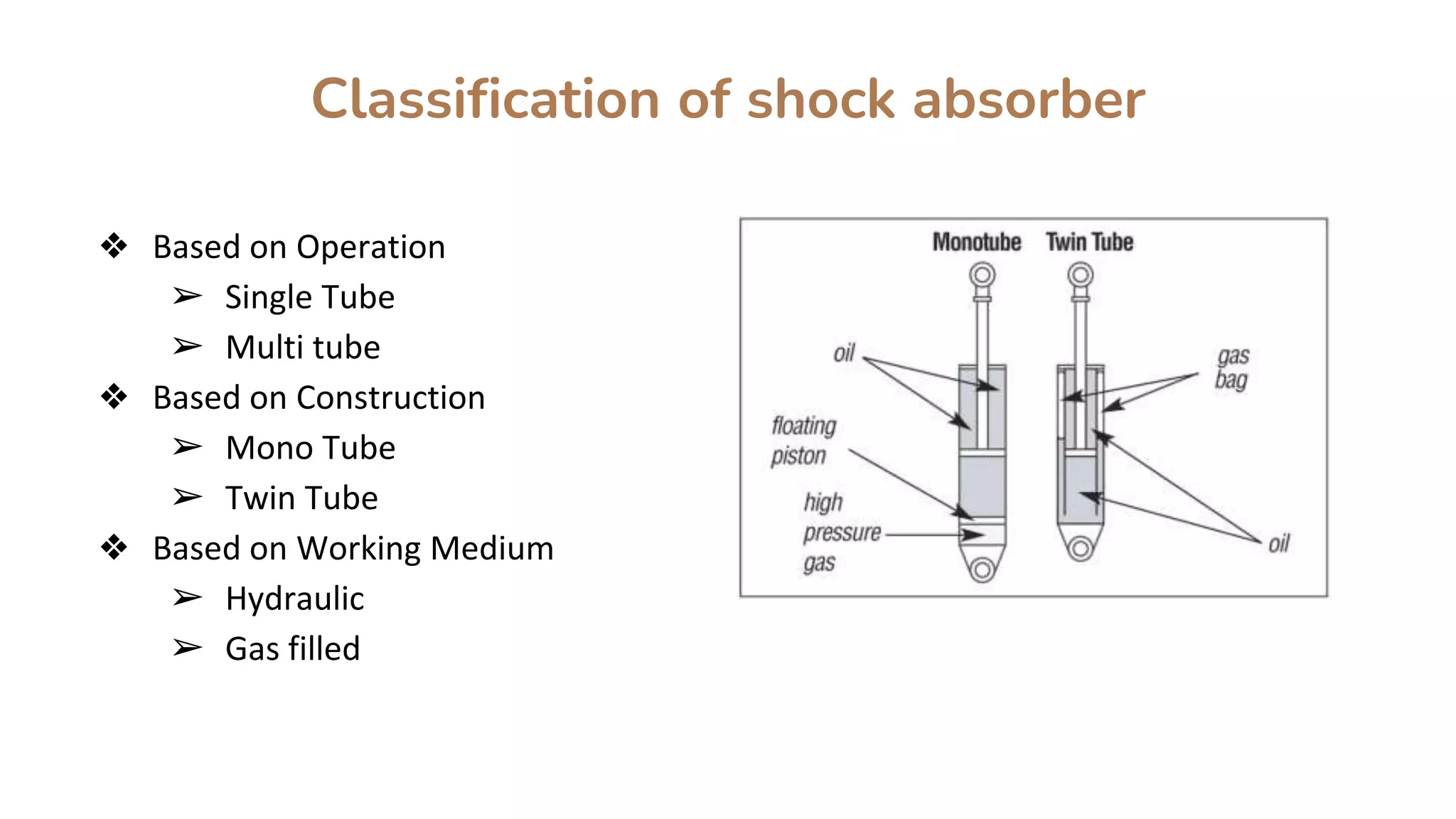
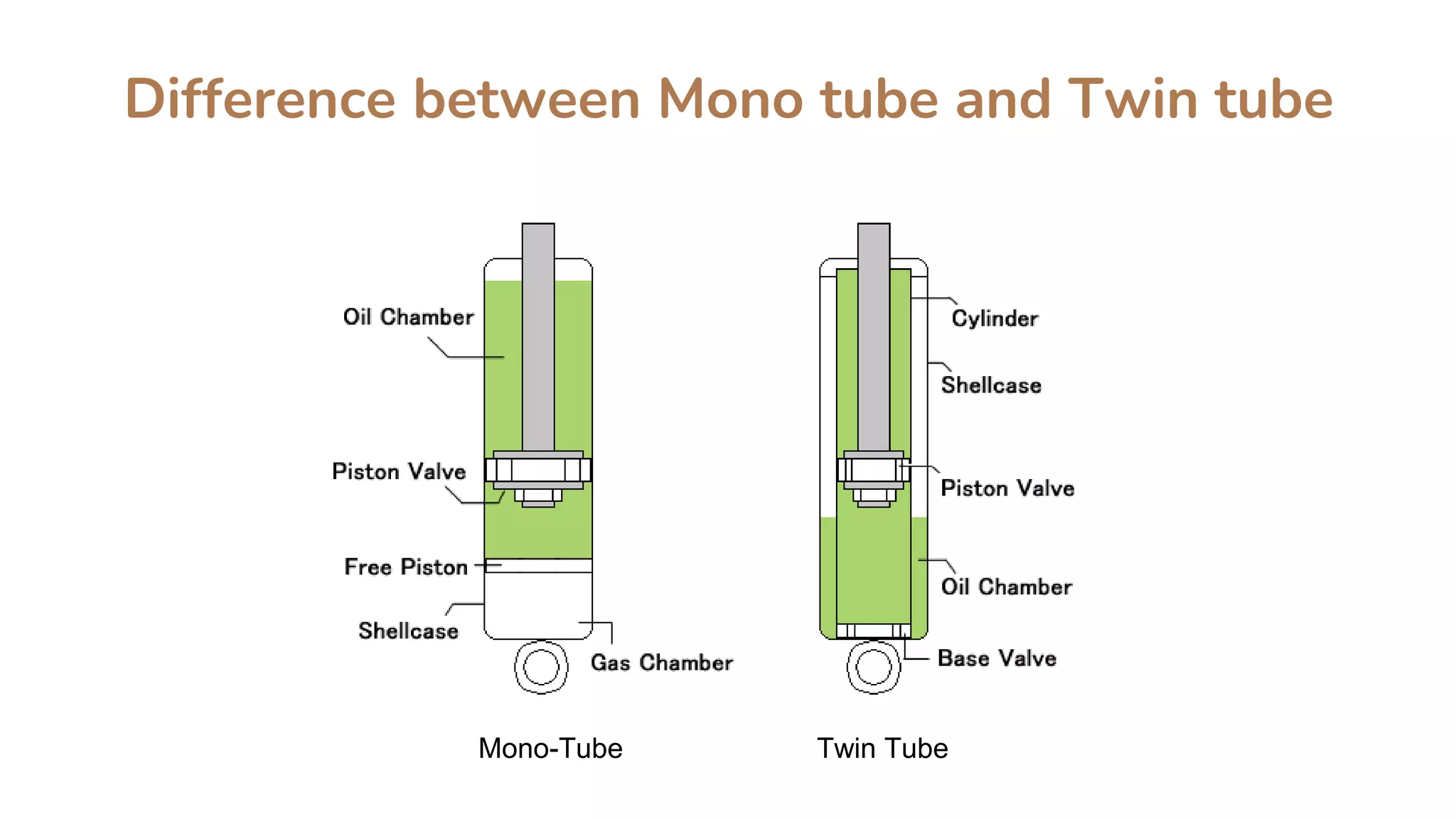
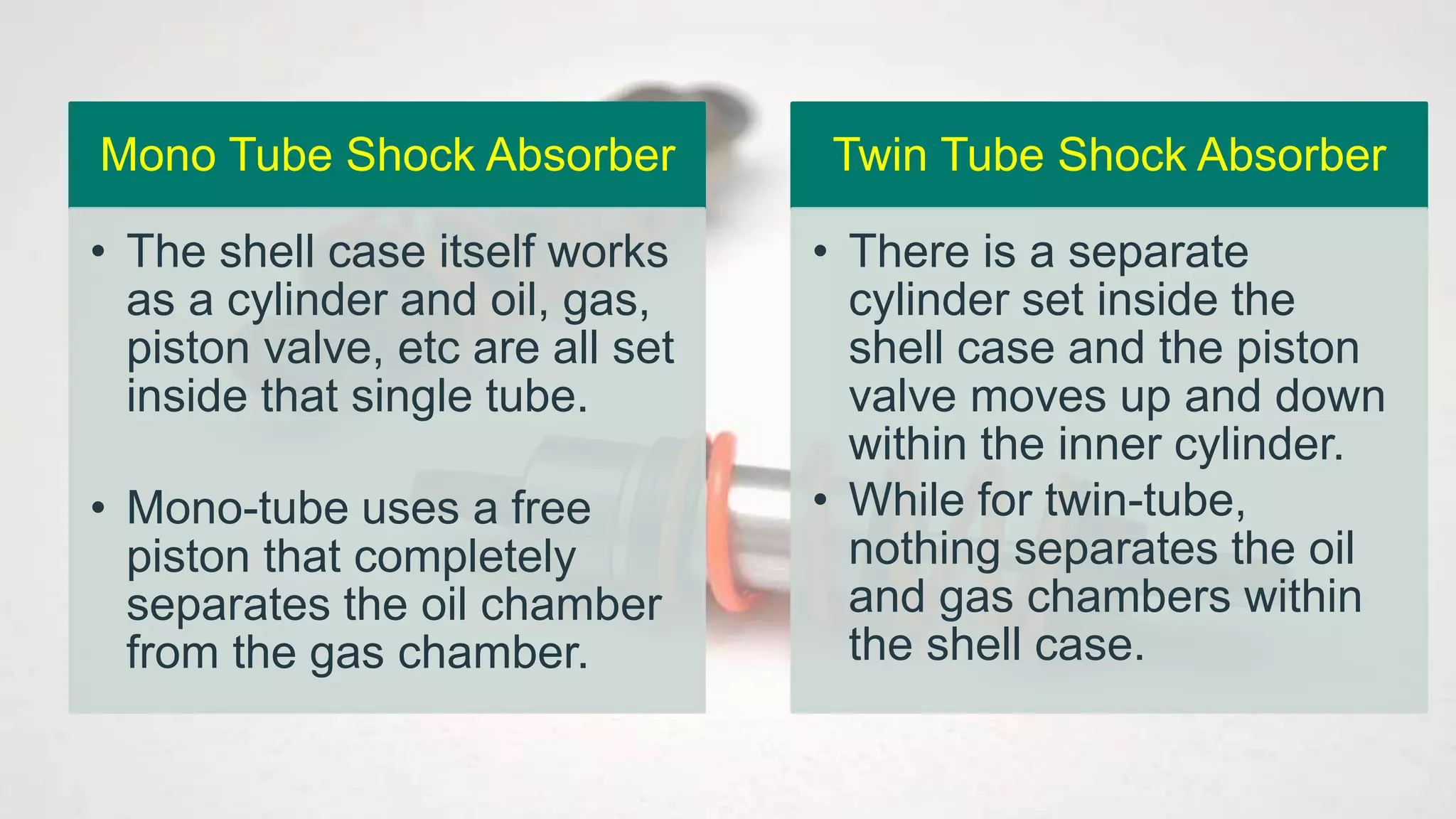
Shock absorbers are mechanical or hydraulic devices that absorb shock impulses by converting kinetic energy into heat. There are different types of shock absorbers classified by operation, construction, and working medium, including twin tube shock absorbers which consist of two nested cylindrical tubes that allow hydraulic fluid to move between chambers via small holes or orifices in the piston and compression valve. The key difference between mono tube and twin tube shock absorbers is that mono tubes use a free piston to separate the oil and gas chambers within a single tube, while twin tubes do not separate the chambers within the outer shell case.