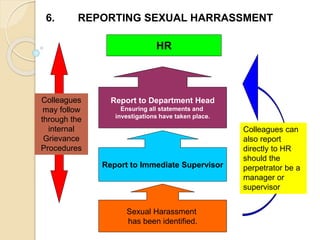
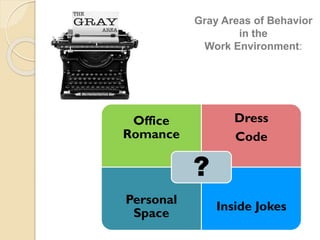
The document discusses sexual harassment in the workplace and provides guidance for managers. It defines sexual harassment and outlines behaviors that constitute it, such as unwelcome physical, verbal, and non-verbal conduct of a sexual nature. Sexual harassment can occur between any combination of colleagues, customers, and visitors in various locations at work. The document advises managers to prevent sexual harassment, address complaints confidentially, and understand the serious psychological and organizational effects it can cause like decreased productivity. It stresses the responsibility of managers to ensure a safe work environment and handle issues properly according to company policy.