Embed presentation
Download to read offline








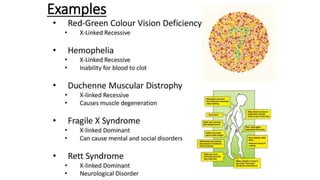




1. Sex linked traits are traits determined by genes on the X or Y chromosomes, mostly on the X chromosome as it contains more genes. 2. Sex linked traits are expressed differently in males and females since females have two X chromosomes and males have one X and one Y chromosome. 3. For X-linked conditions, only females can be carriers as males either express the trait or not, inherit the trait from their mother, and females cannot inherit an X-linked recessive trait from an unaffected father.












