The document discusses key concepts in server configuration, including the implications of single points of failure, round-robin scheduling, and the importance of caching for performance. It highlights the benefits of database caching and configurations for various operating systems, including recommendations for server setup based on available RAM. The article concludes with a note on the challenges of maintaining system packages and the use of external repositories for updates.




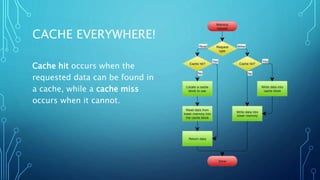


![TWO CACHING SOFTWARE
• Key / Value
• Up to 512MiB per Key
• Support data types
• Not only a cache mechanism
• Can perform persistence
• Simple Key / Value [String]
• Up to 1MiB per Key
• Faster than Redis
• Non-persistence
Use case:
User sessions caching
Use case:
Database caching](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/servelikeaboss-160822181038/85/Serve-like-a-boss-part-one-8-320.jpg)
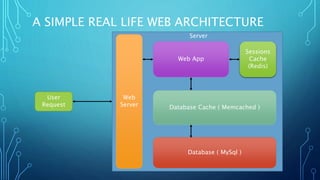



![OPERATING SYSTEM CHALLENGES
Challenge: Distribution support
has finished and packages are
not maintained any more, so
you can not find a package or
the package is out dated
Solution: Use an external
repository to get the latest [or
your preferred] version of the
package (Like Remi and EPEL
for CentOS).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/servelikeaboss-160822181038/85/Serve-like-a-boss-part-one-13-320.jpg)

