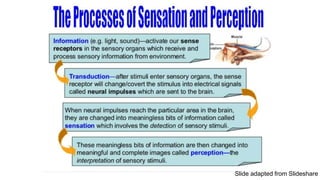
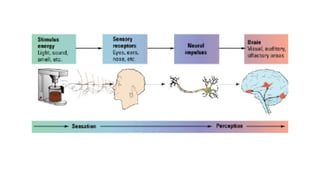
This document discusses key concepts related to sensory perception thresholds. It defines the difference threshold as the smallest detectable change between two stimuli. The absolute threshold is the lowest level at which a single stimulus can be detected. Sensory adaptation is described as decreased sensitivity to a stimulus with repeated exposure. Weber's Law states that for a difference to be perceived, the stimuli must differ by a constant proportion rather than a constant amount. Examples are provided to illustrate these concepts related to detecting changes in stimuli.