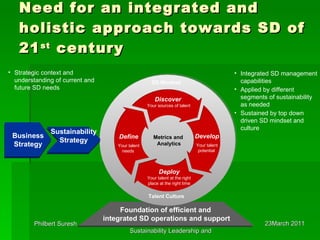
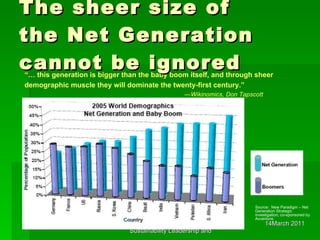
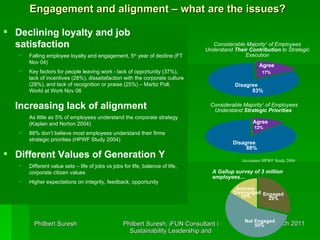
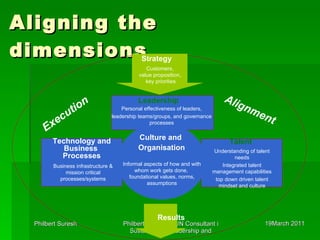
This document discusses sustainability, leadership, and change. It examines drivers of sustainability like consumer demand, stakeholder influence, and resource depletion. It uses Accenture as a case study, highlighting how the company has embedded sustainability into its culture and identified six key drivers. The document outlines challenges of managing a multigenerational workforce and need for strategic and holistic approaches to sustainability for the 21st century.
















![Experience is the best teacher of leadership Organizations can leverage experience and practice to grow more leaders, faster Leadership capability, particularly in managing people and diversity must be developed at all levels These behaviours and practices must be measured and rewarded [coal] [diamond] Leadership Development](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/senecagreensustaiabilitysymposiummarch2011-110206085620-phpapp02/85/Seneca-green-sustaiability-symposium-march-2011-20-320.jpg)