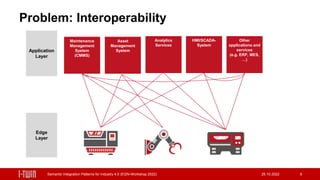
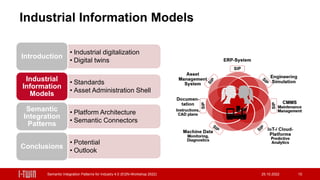
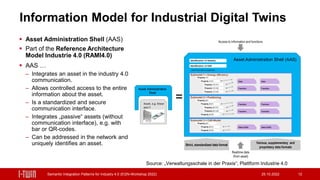
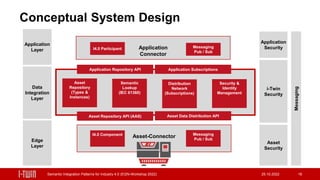
The document presents semantic integration patterns for data-driven digital twins in the manufacturing industry, highlighting their role in enhancing interoperability in Industry 4.0. The i-twin project aims to develop an open source middleware for integrating operational management systems and connected assets, thus reducing integration efforts and facilitating master and operational data exchange. The research is sponsored by Austrian federal entities and focuses on creating a standardized approach to asset data integration in manufacturing environments.