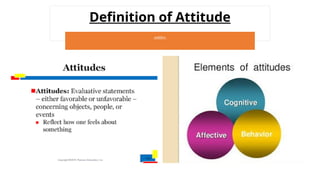
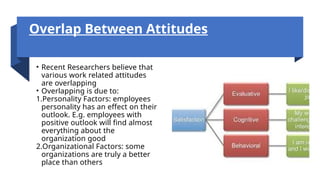
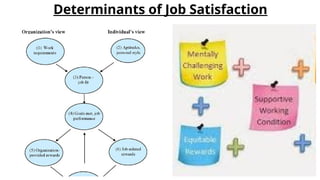
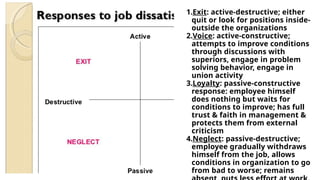
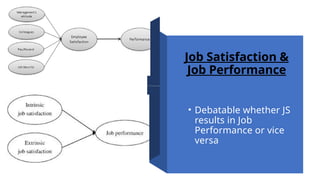
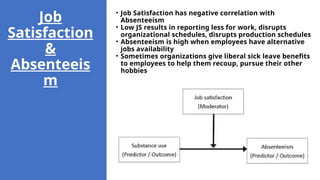
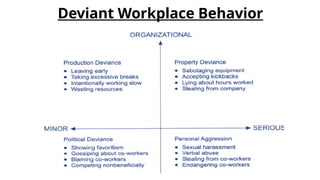
The document discusses attitudes and job satisfaction within organizational behavior, emphasizing the components of attitudes, methods for measuring job satisfaction, and its determinants such as work itself, pay, and personality. It explores the relationship between job satisfaction and job performance, organizational citizenship behavior, and implications for absenteeism and employee turnover. Additionally, it highlights the negative impacts of dissatisfaction, including workplace deviance and suggestions for enhancing job satisfaction.