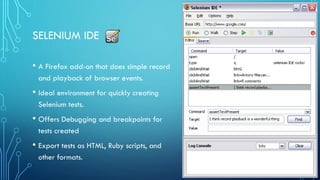
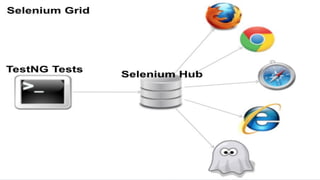
This document provides an overview of Selenium, an open source tool used for automating web browser testing. It discusses the main components of Selenium, including the Selenium IDE for recording and playback of tests in Firefox, the Selenium WebDriver for controlling browsers programmatically, and Selenium Grid for distributed testing across multiple environments. It also introduces TestNG as a testing framework and Maven for build management in the Selenium test environment configuration.