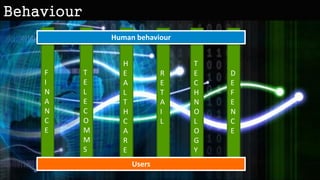
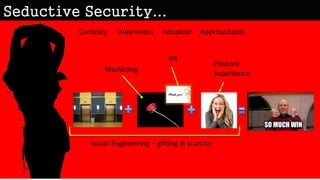
The document discusses the importance of human behavior and psychology in information security, emphasizing that 85% of success relies on interpersonal skills rather than technical knowledge. It highlights the need for security practices to evolve and engage users positively, making information security relatable and less intimidating. Additionally, it explores social engineering tactics and principles that exploit human tendencies, emphasizing the significance of understanding user behavior to minimize risk and enhance security awareness.