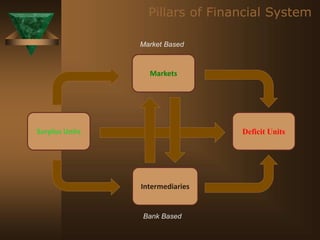
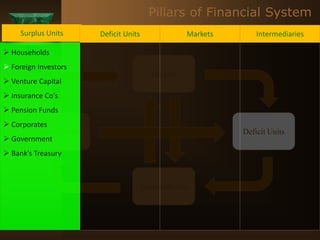
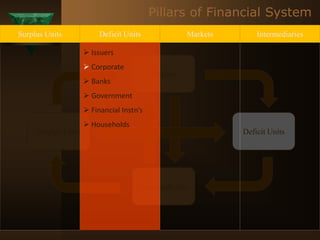
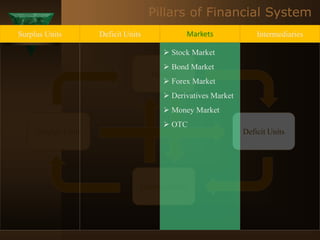
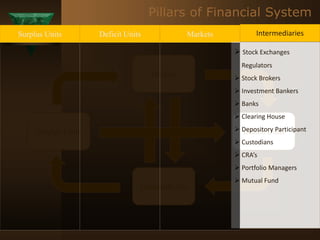
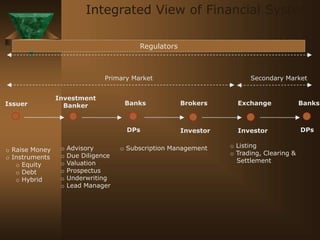
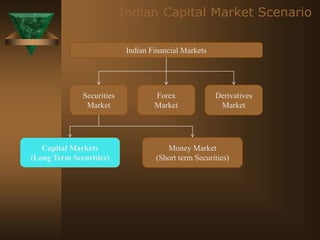
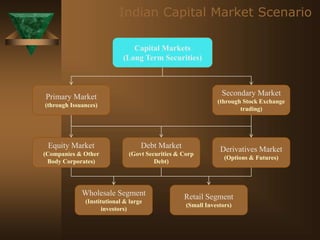
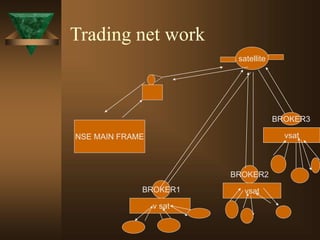
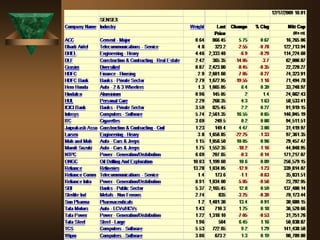
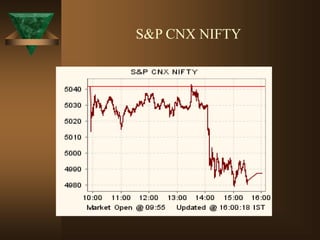
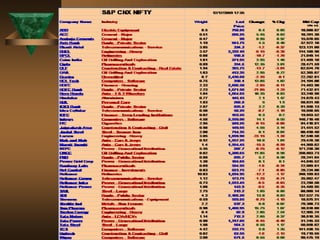
The document discusses the key elements of securities markets in India. It identifies the main participants as investors (surplus units), issuers (deficit units), intermediaries like stock exchanges and brokers, and regulators. Households and foreign investors are typically surplus units, while corporates, governments, and banks are deficit units. The securities markets allow surplus units to invest in financial claims issued by deficit units. Together with intermediaries and a regulatory framework, these form the four main pillars of securities markets in India.