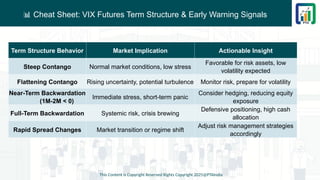
Section 6 - Chapter 3 - Volatility Indexes and VIX Complex - Presented by Rohan Sharma - The CMT Coach - Chartered Market Technician CMT Level 2 Study Material - CMT Level 2 Chapter Wise Short Notes - CMT Level 2 Course Content - CMT Level 2 2025 Exam Syllabus Visit Site : www.learn.ptaindia.com and www.ptaindia.com