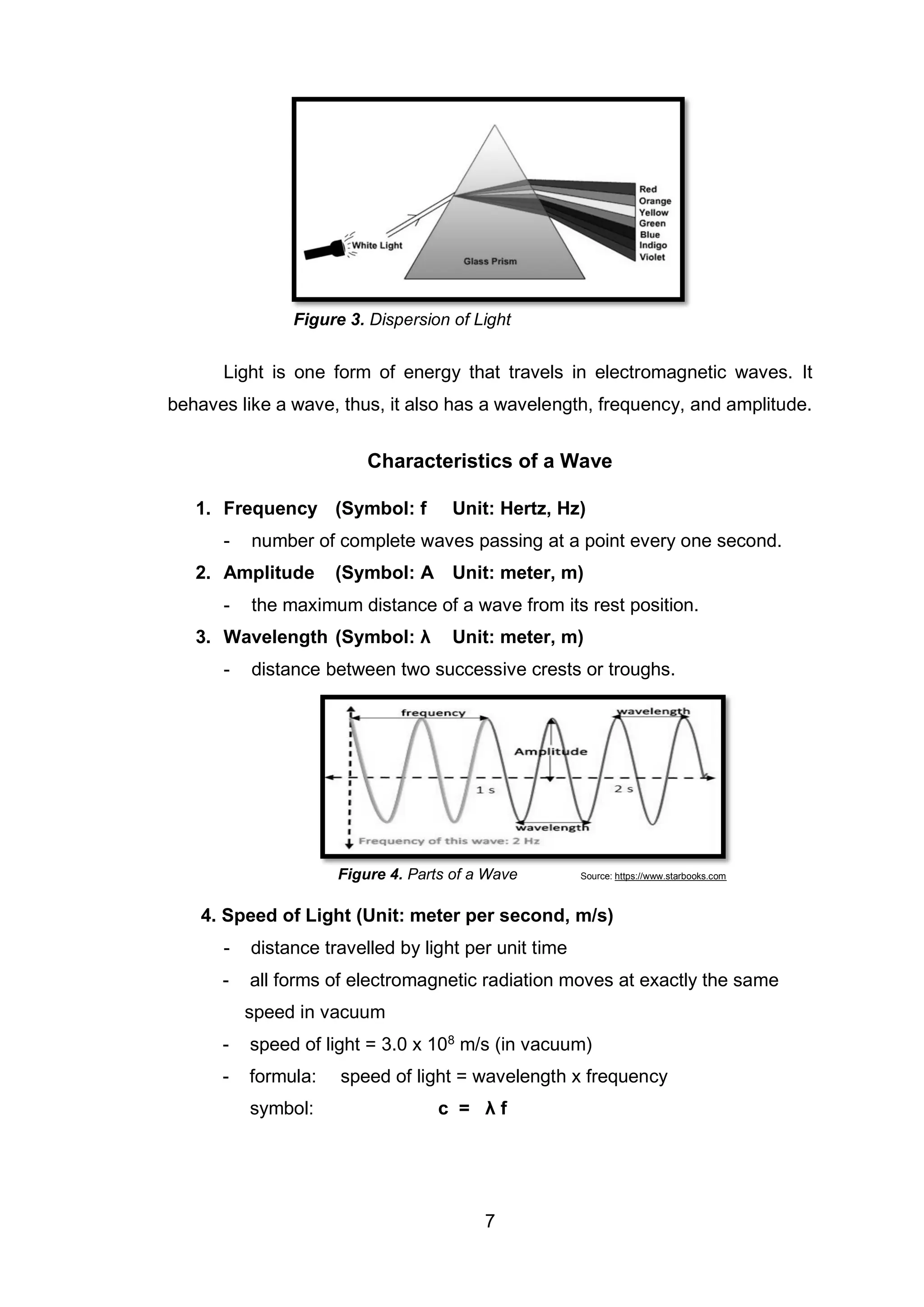
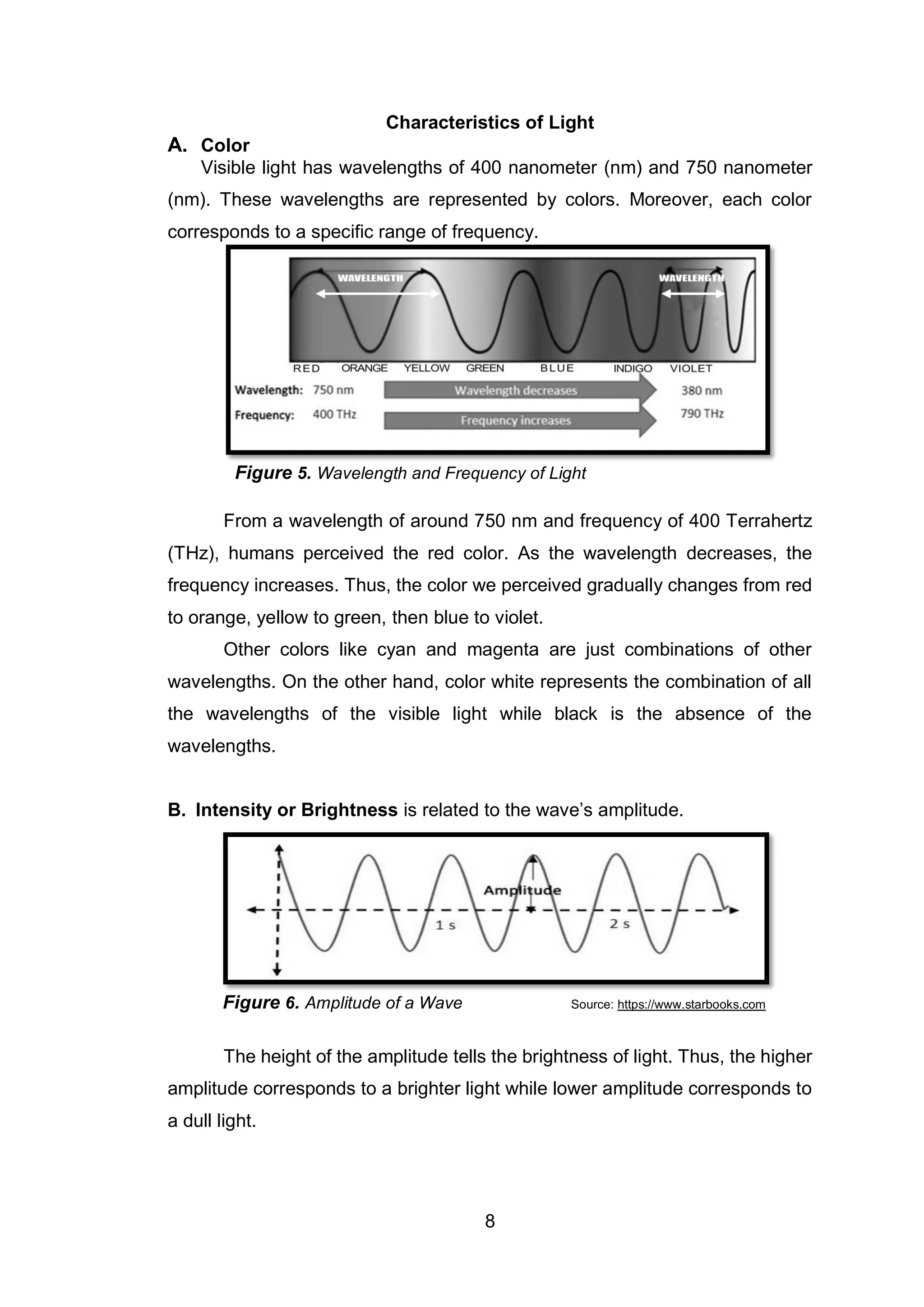
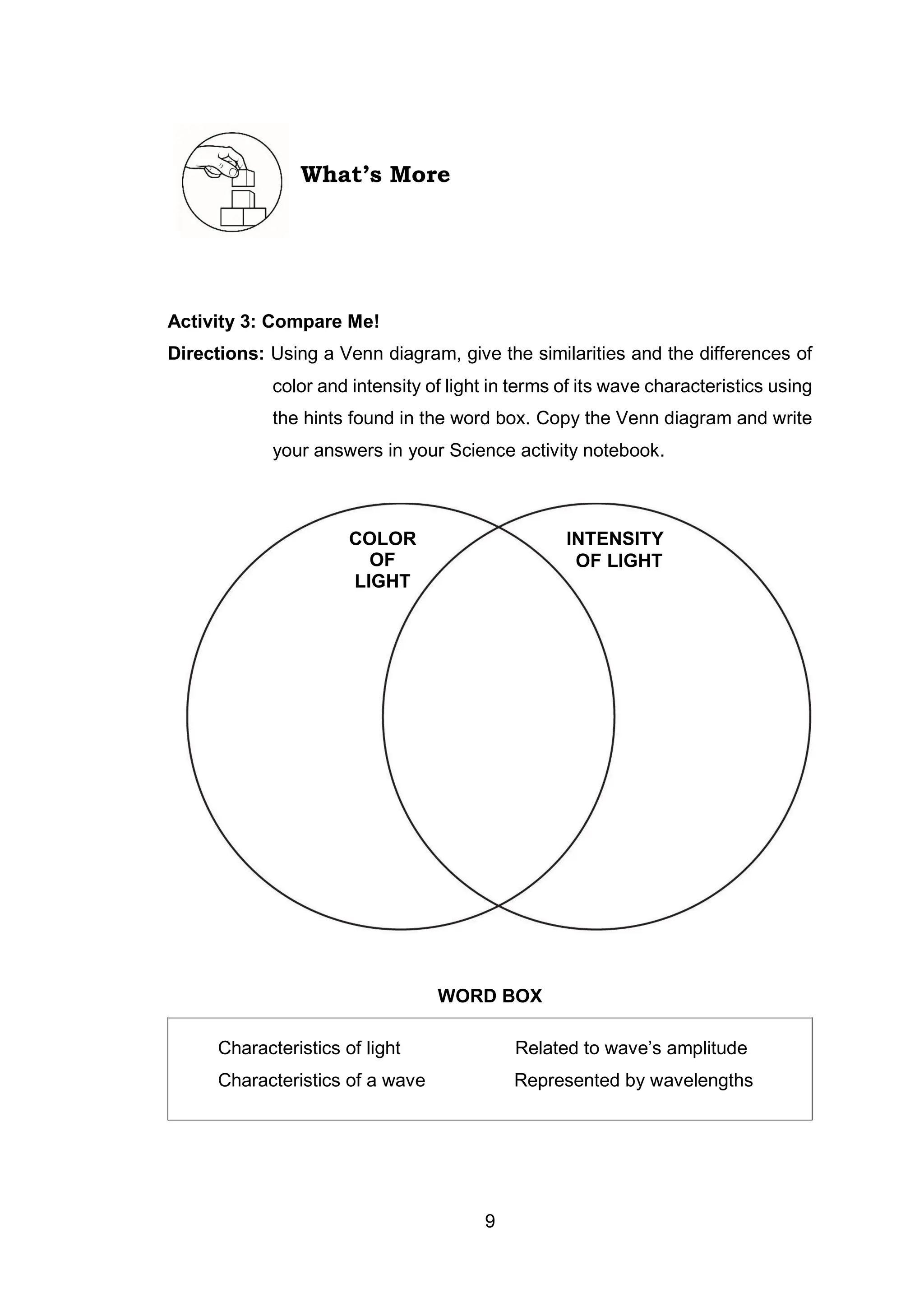
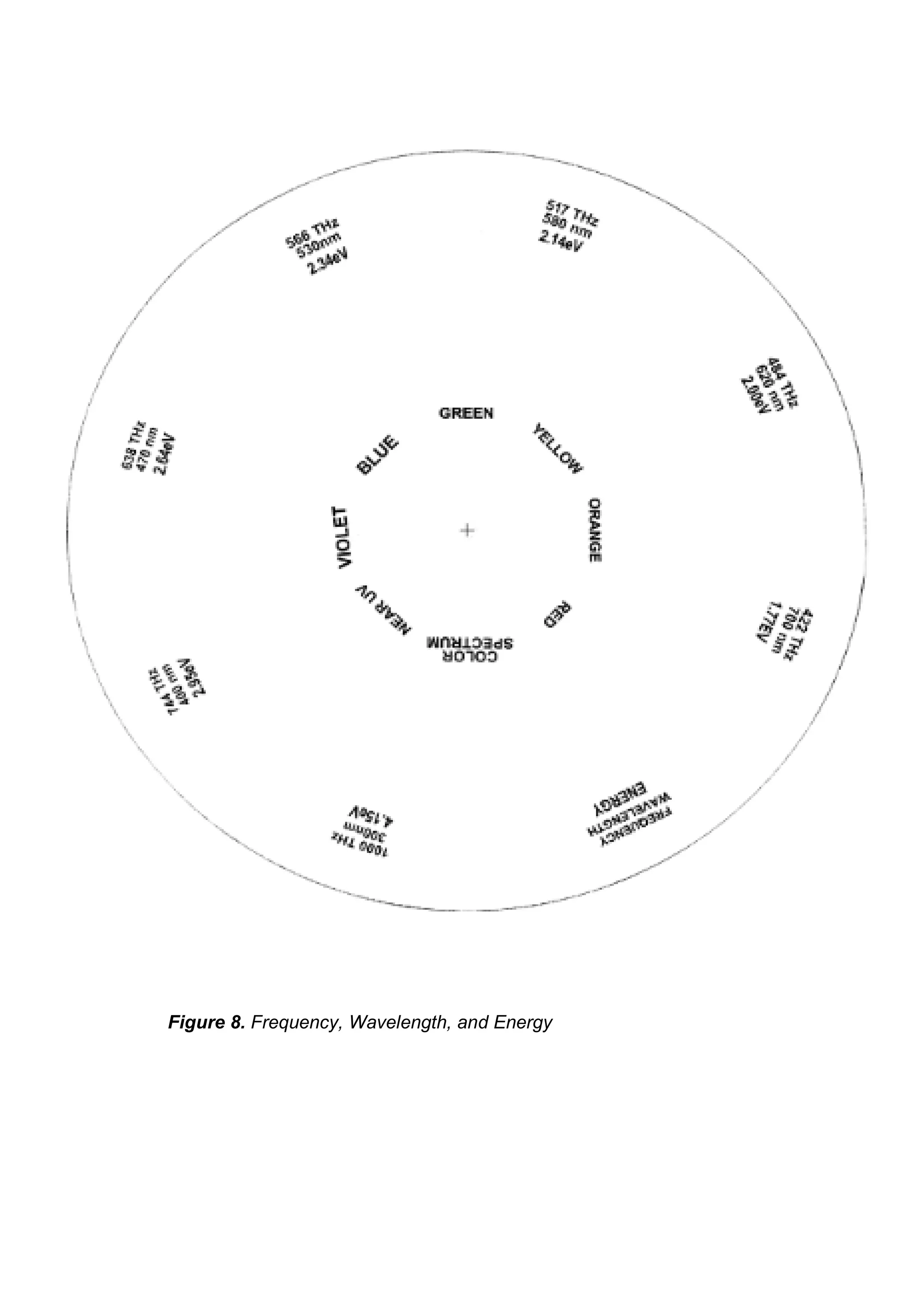
This document is a science educational module for Grade 7 students in the Philippines, focusing on the characteristics of light. It outlines the structure of the module, the importance of light, and various activities designed for independent learning about light's properties, such as wavelength, frequency, and brightness. The module emphasizes guided learning and includes assessments to evaluate understanding of the topics covered.