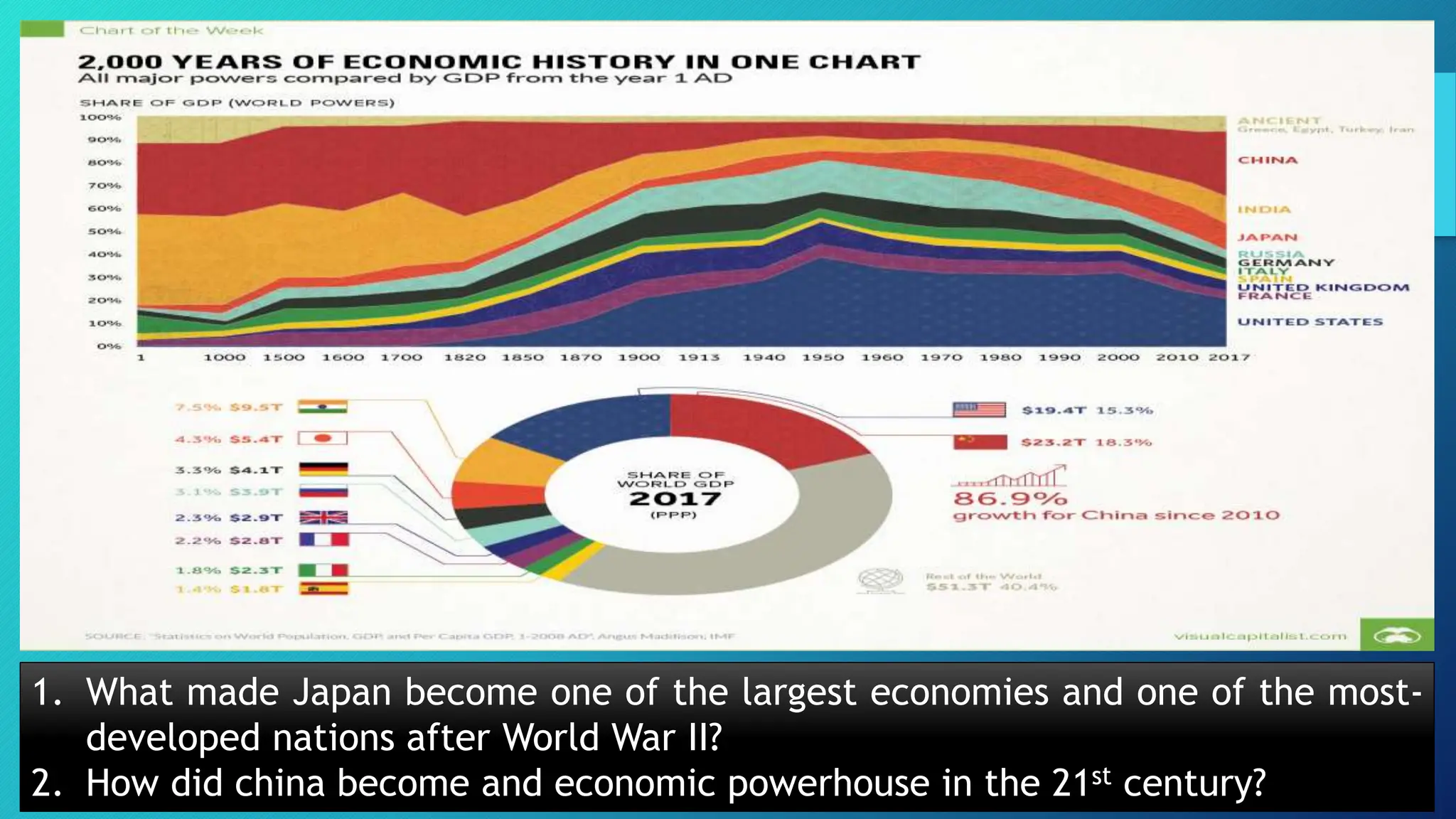
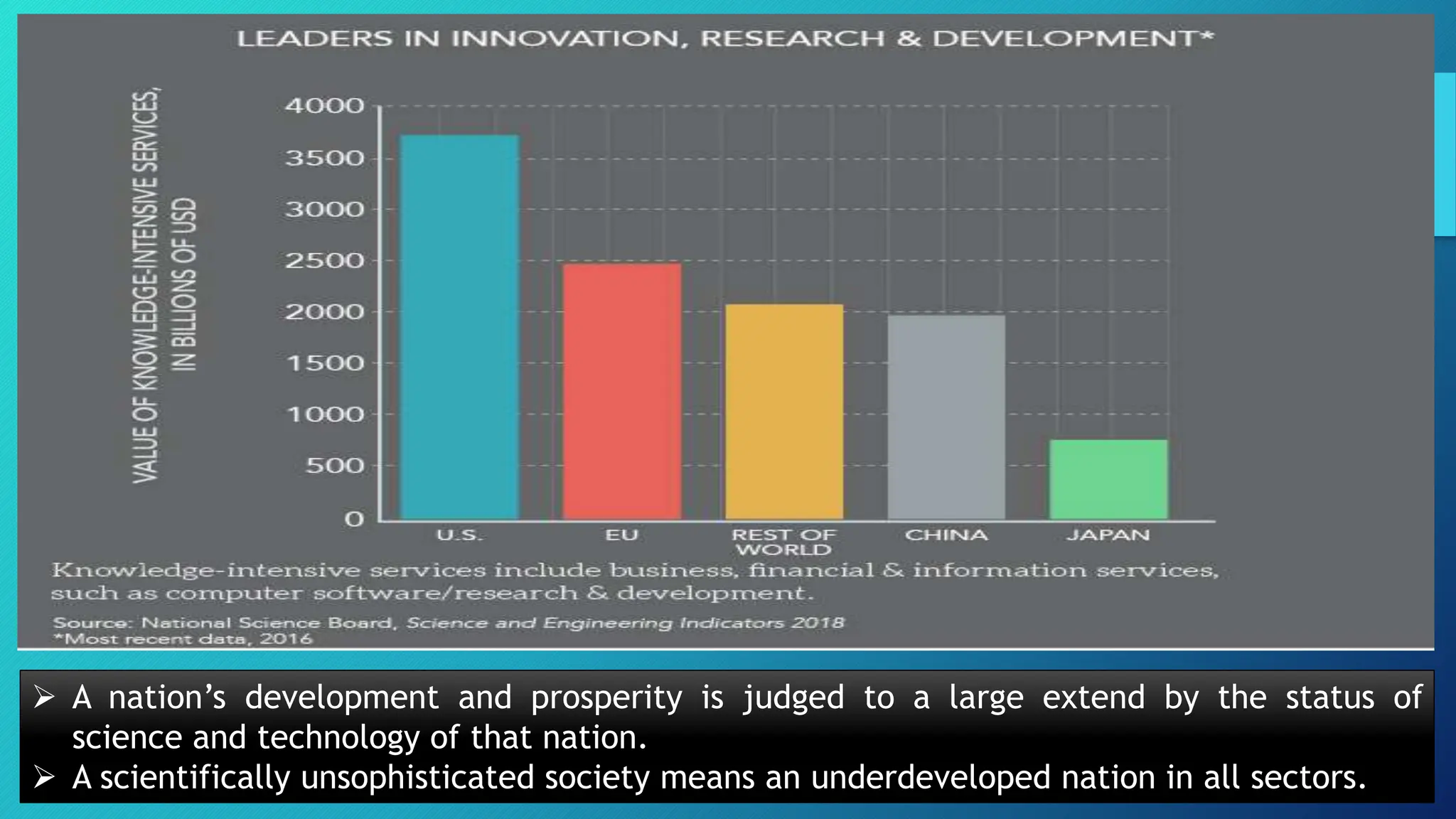
The document discusses the critical role of science and technology in the Philippines' nation-building efforts, highlighting its contributions to economic growth, healthcare, environmental protection, and disaster management. It outlines government policies aimed at promoting scientific innovation and technological adoption, emphasizing the significance of these initiatives for national development. Various programs and research agendas are established to align with national goals, aiming to enhance societal progress and competitiveness.