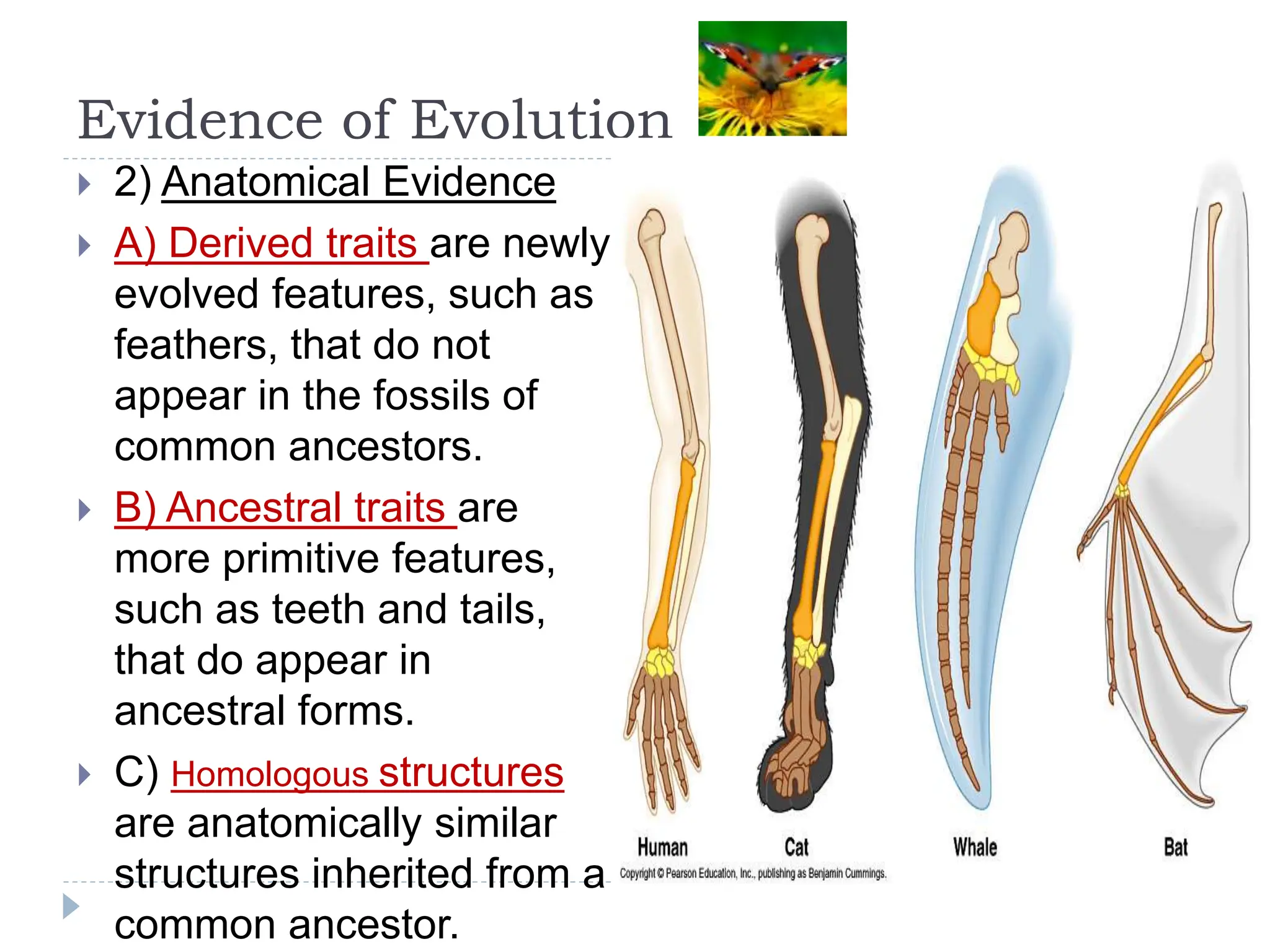
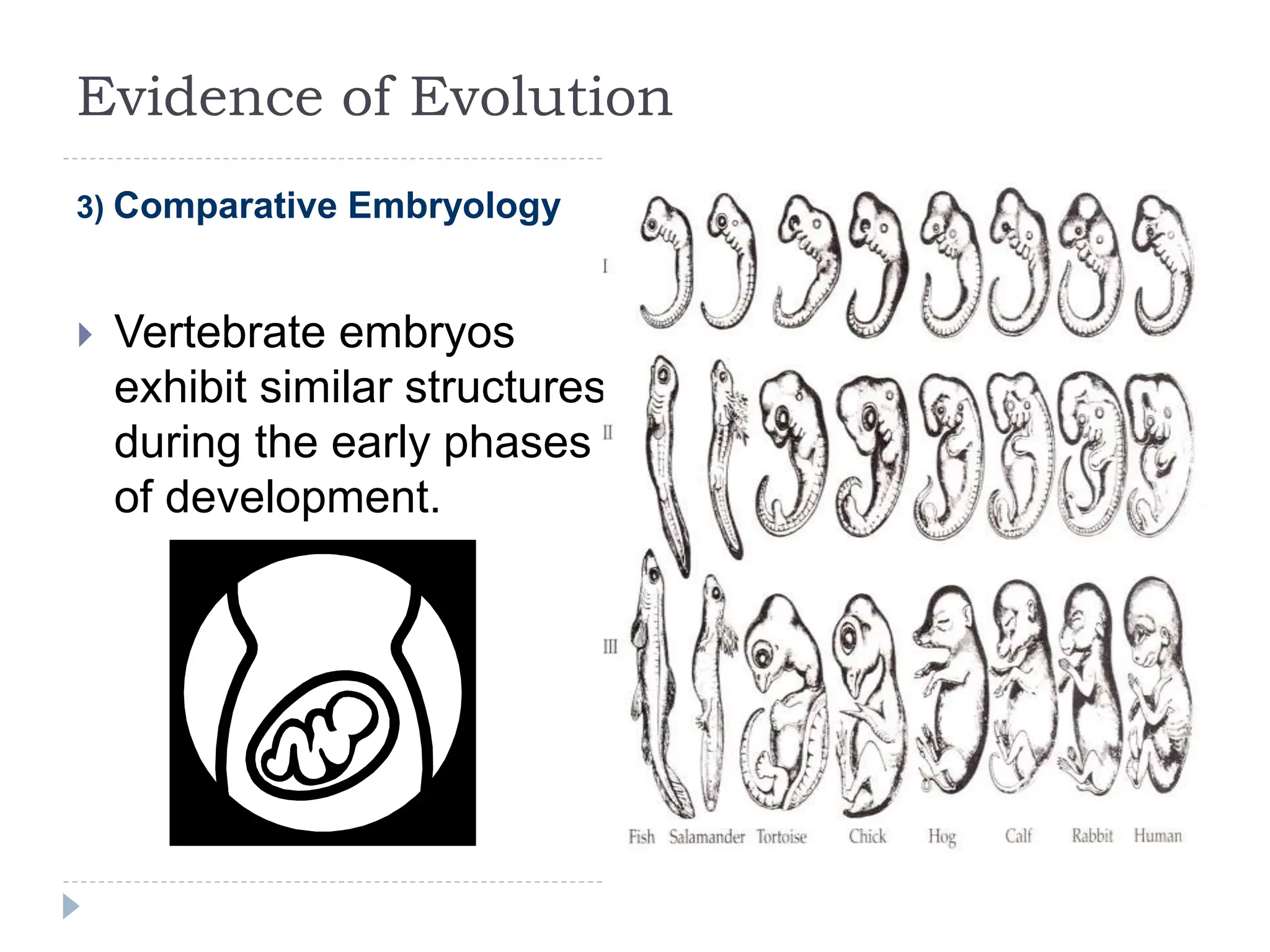
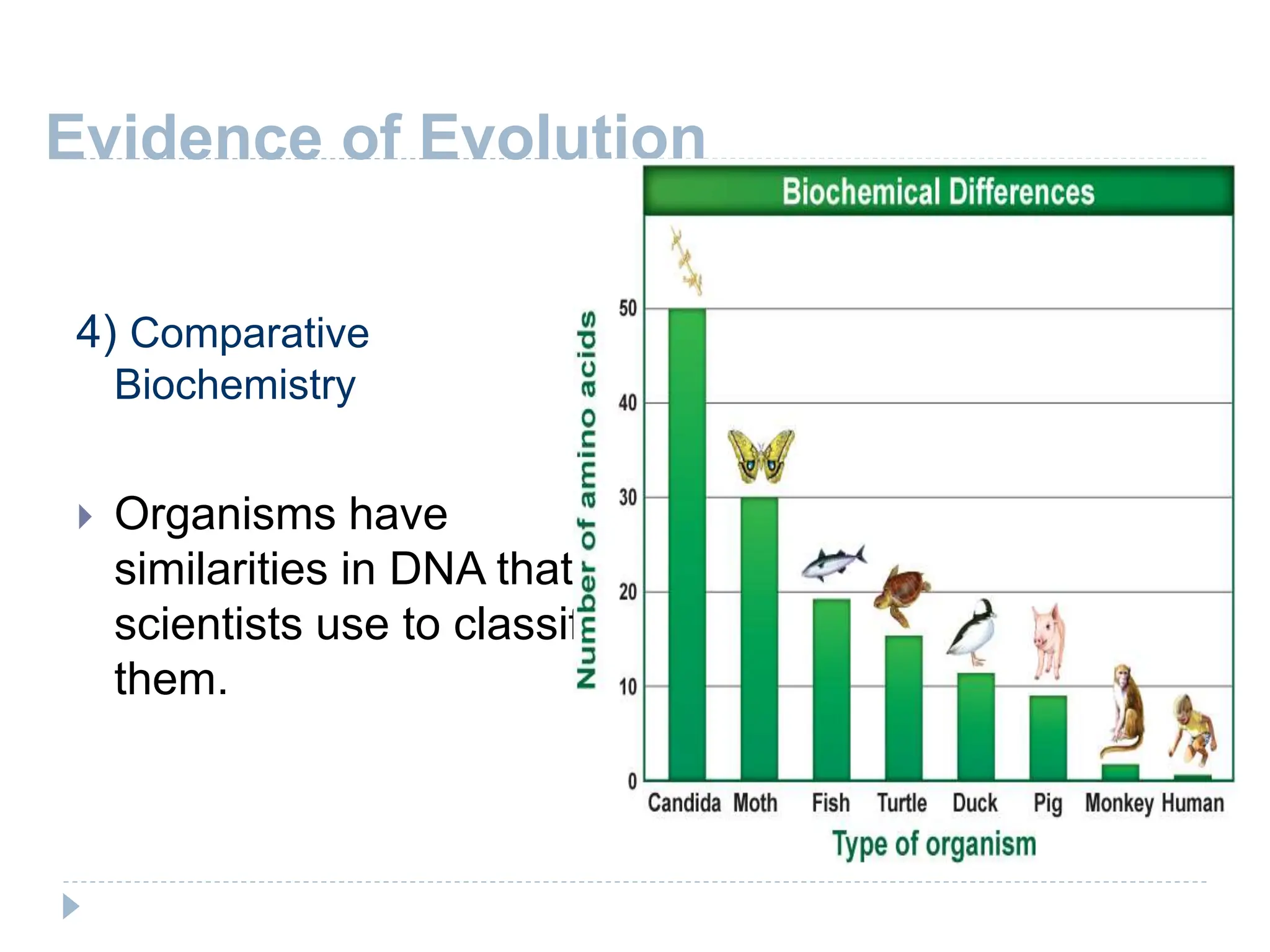
This document outlines the five evidences that support the theory of evolution: 1) The fossil record shows similarities between ancient and modern species. 2) Anatomical evidence like homologous and vestigial structures provide evidence of common ancestry. 3) Comparative embryology shows that vertebrate embryos share similar early structures. 4) Comparative biochemistry finds similarities in DNA that are used to classify organisms. 5) Geographic distribution of related species on islands first suggested evolution to Darwin as island species evolved similar traits.