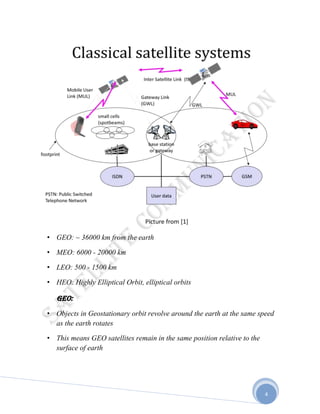
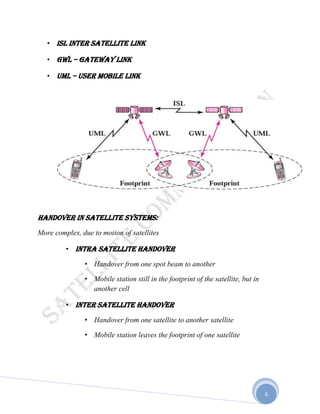
Satellites are used for telecommunication by acting as relay stations in space. A communication satellite receives radio signals from an earth station and retransmits them to another earth station. There are over 750 communication satellites currently in orbit. Satellites allow communication over greater distances than terrestrial methods by transmitting signals between earth stations via the satellite. While satellites provide broader coverage than terrestrial systems, they also have higher launch costs and greater signal delays. Different types of orbits, such as low earth orbit (LEO), medium earth orbit (MEO), and geostationary orbit (GEO), determine factors like coverage area, signal strength, and number of satellites required.