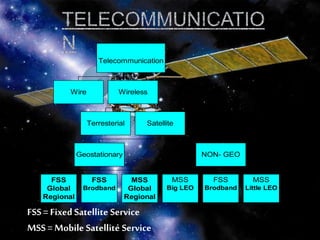
This document discusses satellite communication technology. It provides information on:
1) The types of satellites used including geostationary satellites (GEO) and low earth orbit satellites (LEO). GEO satellites orbit 35,863 km above the earth's surface and remain fixed, while LEO satellites range between 500-1,500 km and do not remain fixed.
2) The advantages and disadvantages of GEO and LEO satellites. GEO satellites provide wide coverage but weaker signals, while LEO satellites provide stronger signals but require a network to maintain coverage.
3) The multiple access techniques used in satellite communications, including Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA), Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), and Code Division