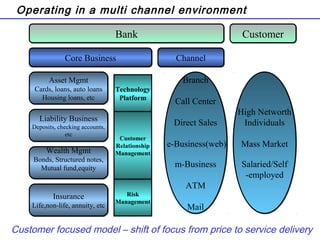
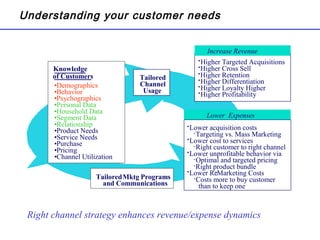
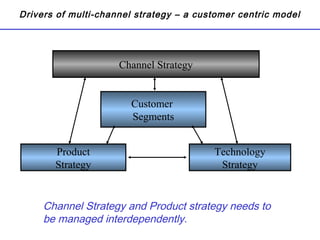
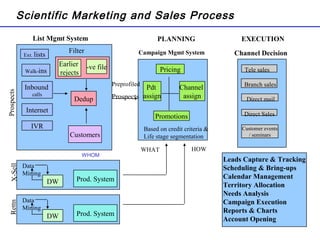
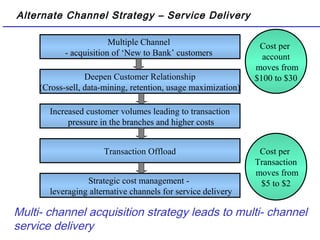
The document summarizes the future of retail banking in China and strategies for multi-channel operations. It notes that retail banking profits in China are expected to surpass corporate banking by 2013. It also describes opportunities in various retail banking products and challenges in China, including regulatory restrictions and risk assessment. The document advocates for a customer-focused, multi-channel approach using branches, call centers, online and mobile banking, ATMs, and more to acquire and service customers across segments. Tailoring marketing and product offerings to customer needs through data analysis and channel management is highlighted as important for driving revenue and reducing expenses in China's growing retail banking industry.