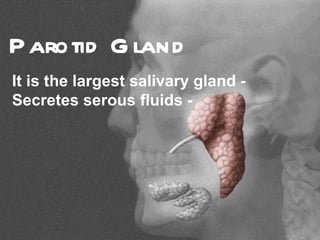
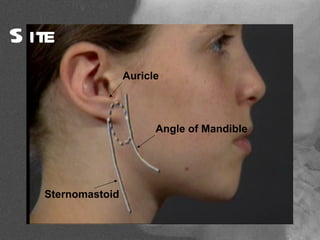
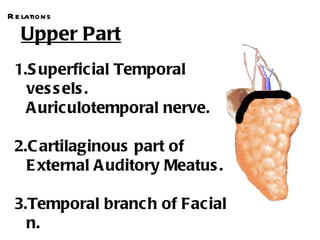
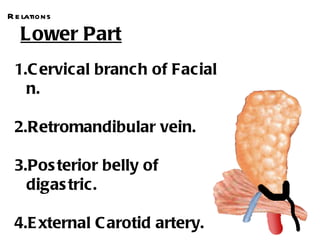
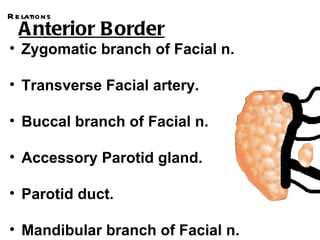
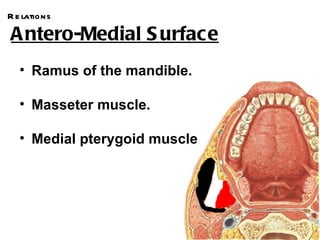
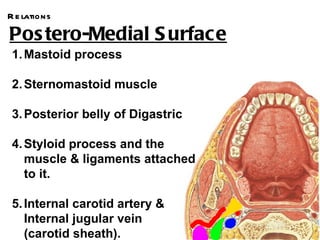
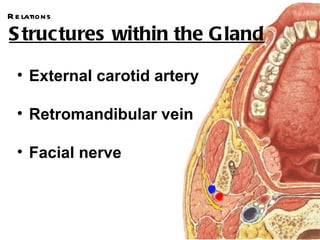
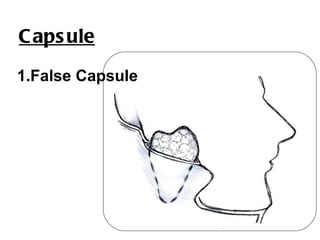
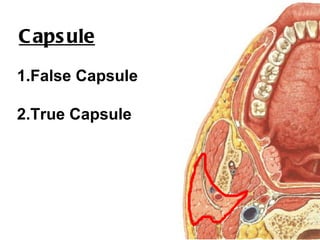
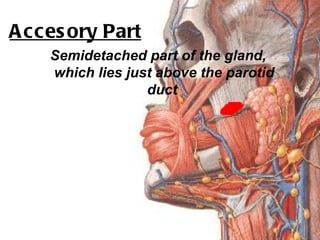
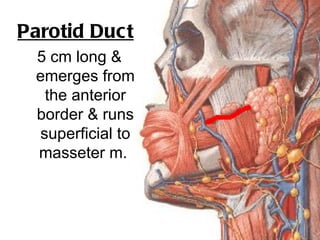
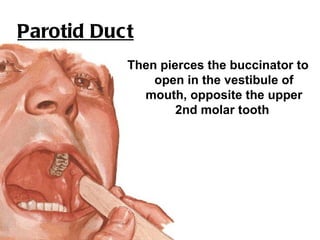
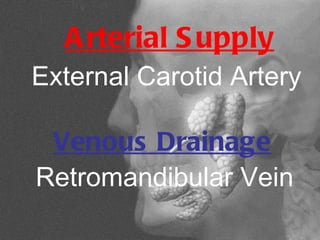
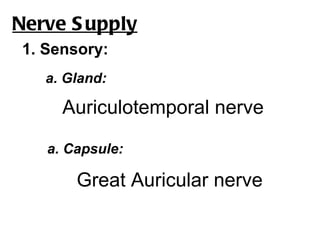
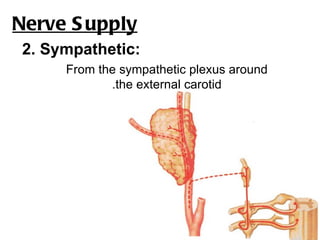
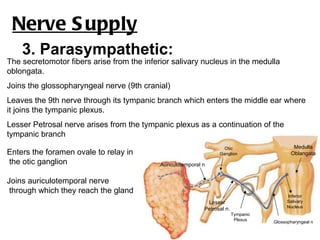
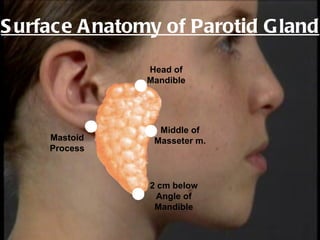
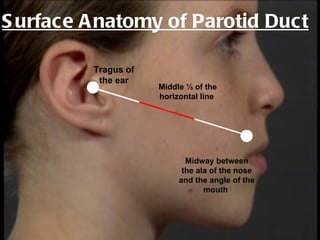
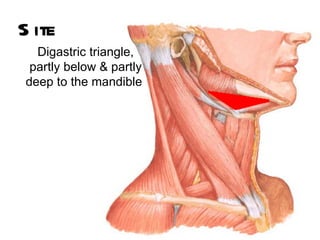
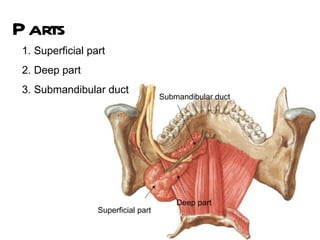
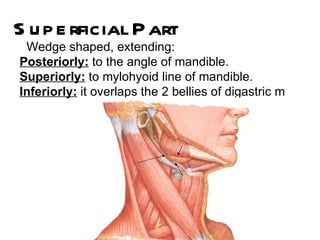
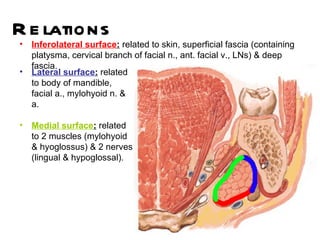
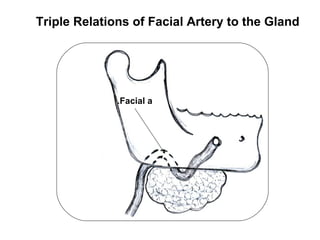
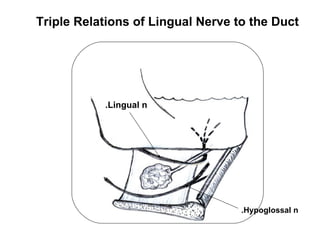
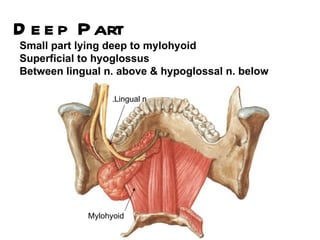
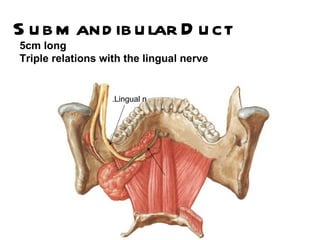
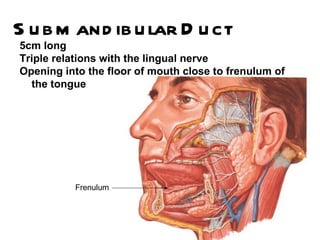
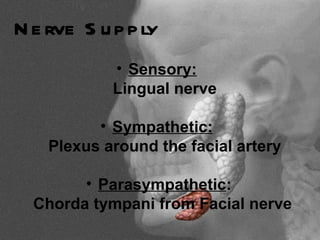
The parotid gland is the largest salivary gland. It secretes serous fluid and is located below and in front of the ear. The submandibular gland is partly below and deep to the mandible. It has superficial and deep parts and secretes both serous and mucous fluids. The parotid and submandibular glands receive parasympathetic innervation from the facial and glossopharyngeal nerves respectively to stimulate secretion. Both glands have multiple anatomical relationships with surrounding structures.