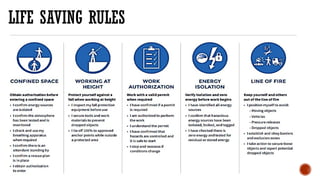
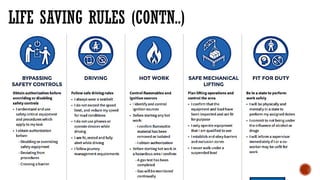
The document outlines essential safety protocols and behaviors necessary for maintaining a safe working environment, emphasizing the importance of positive safety attitudes among employees. It addresses common hazards like slips, trips, falls, and musculoskeletal disorders, offering preventive measures and proper techniques for lifting and carrying. Additionally, it covers fire safety procedures, the proper handling of hazardous chemicals, electrical safety, and first aid fundamentals.