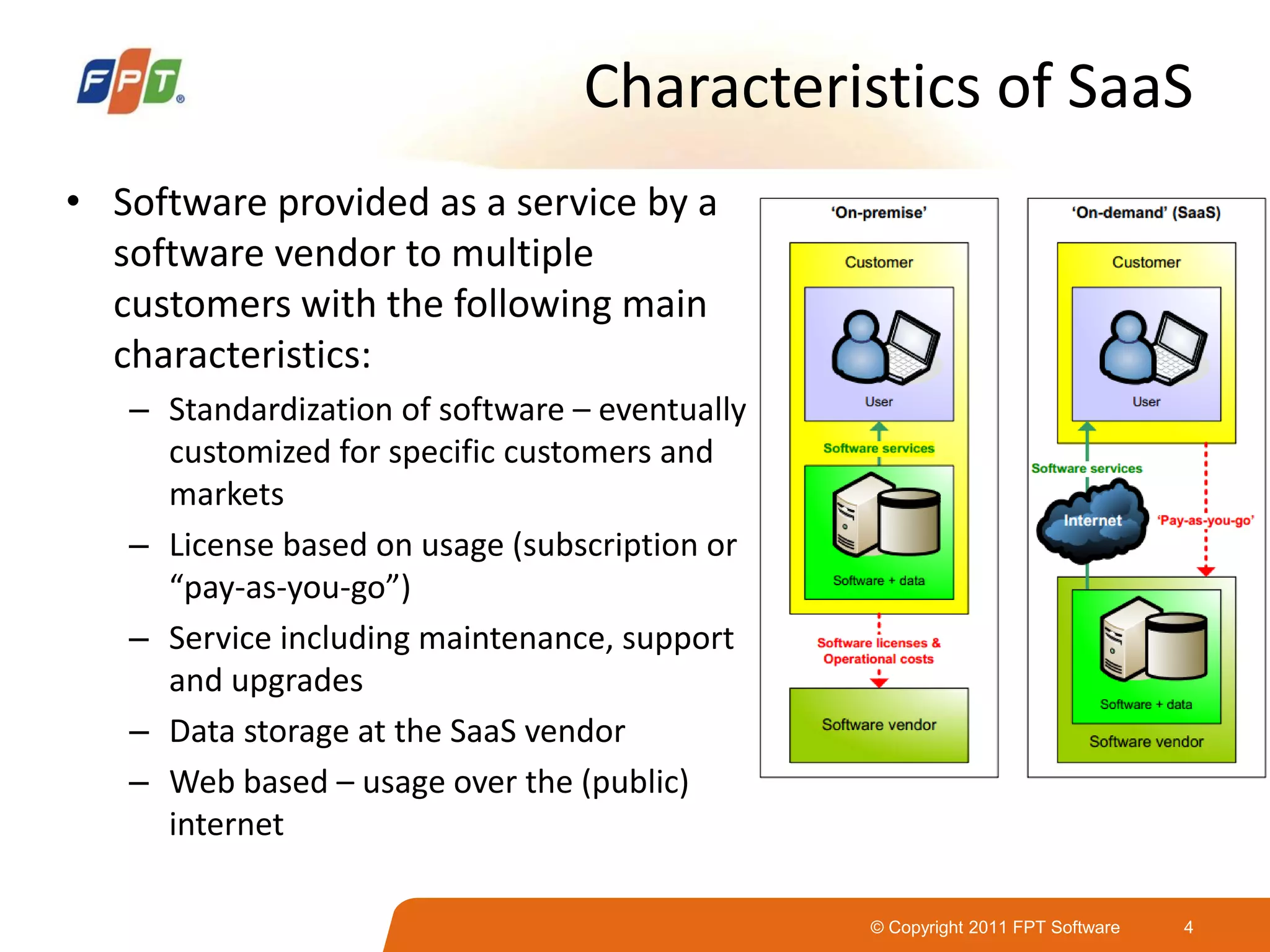
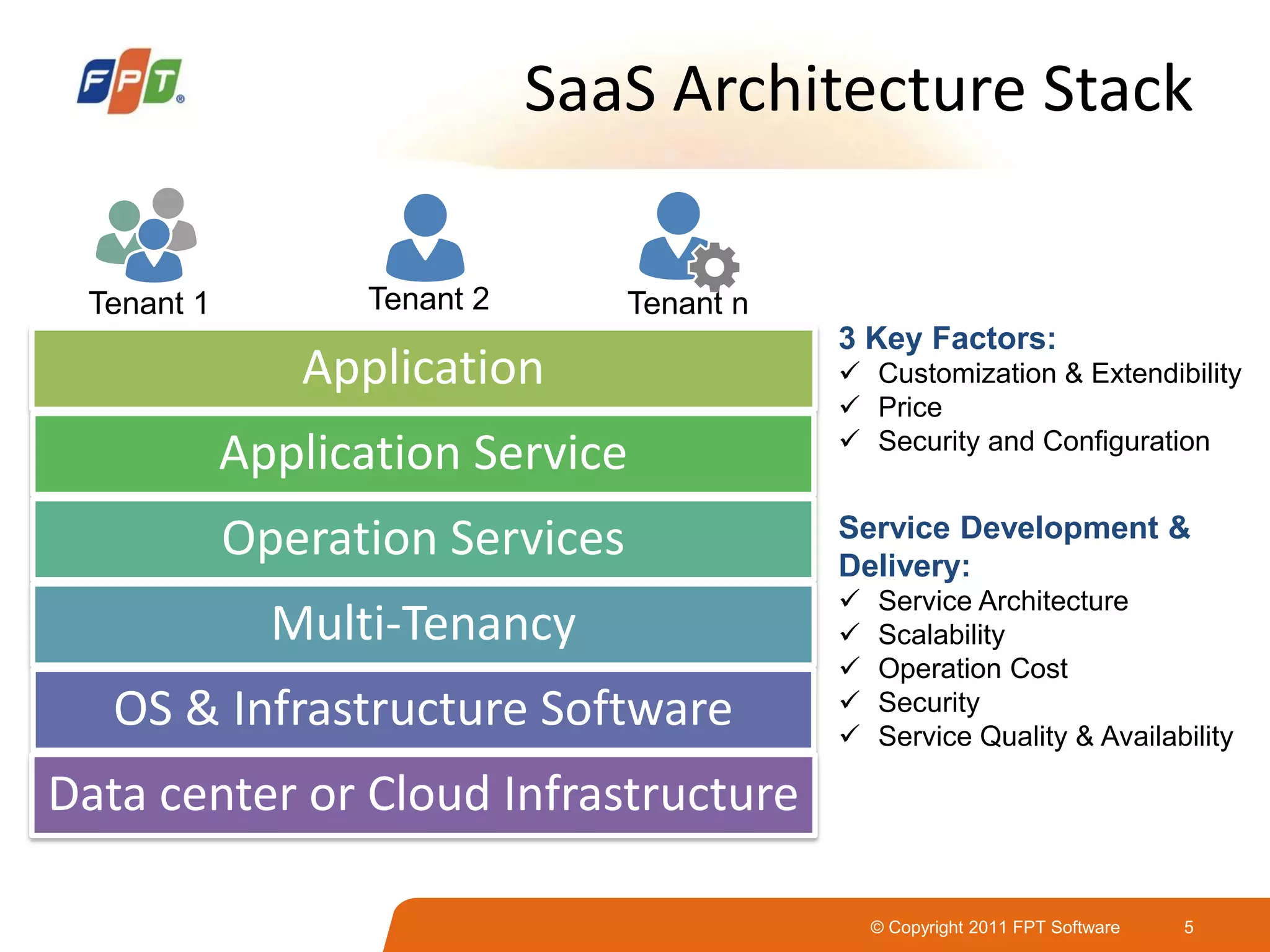
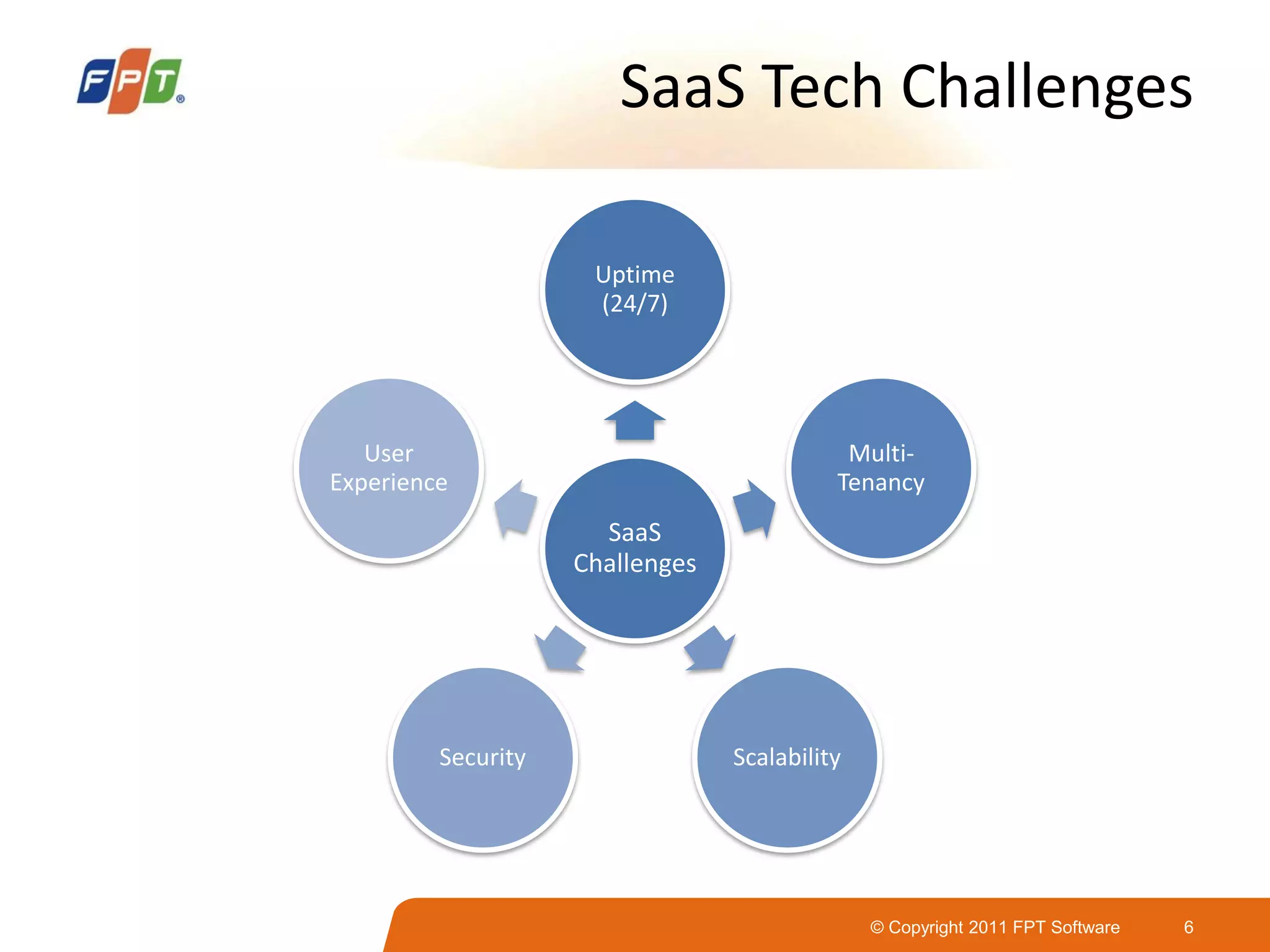
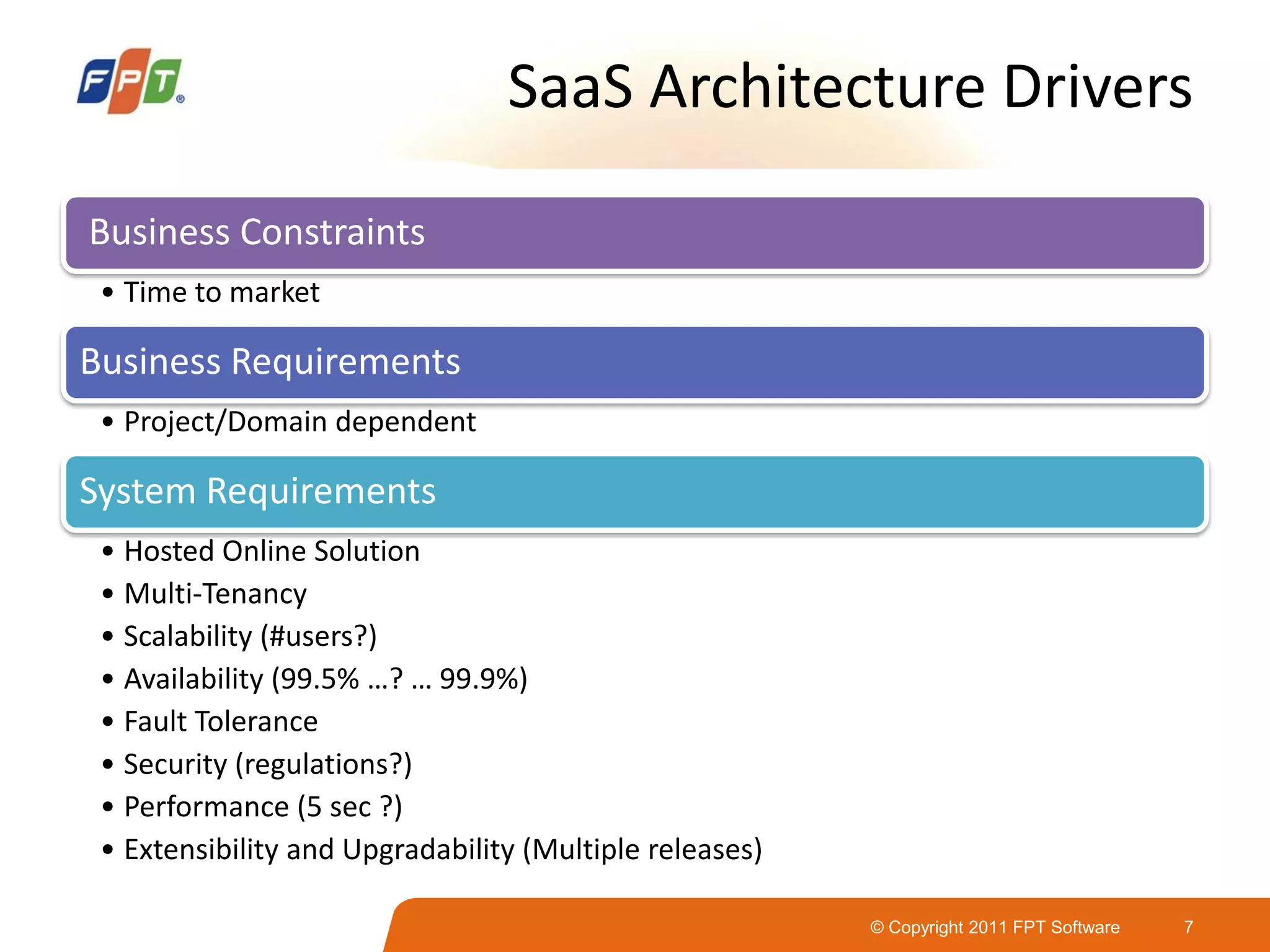
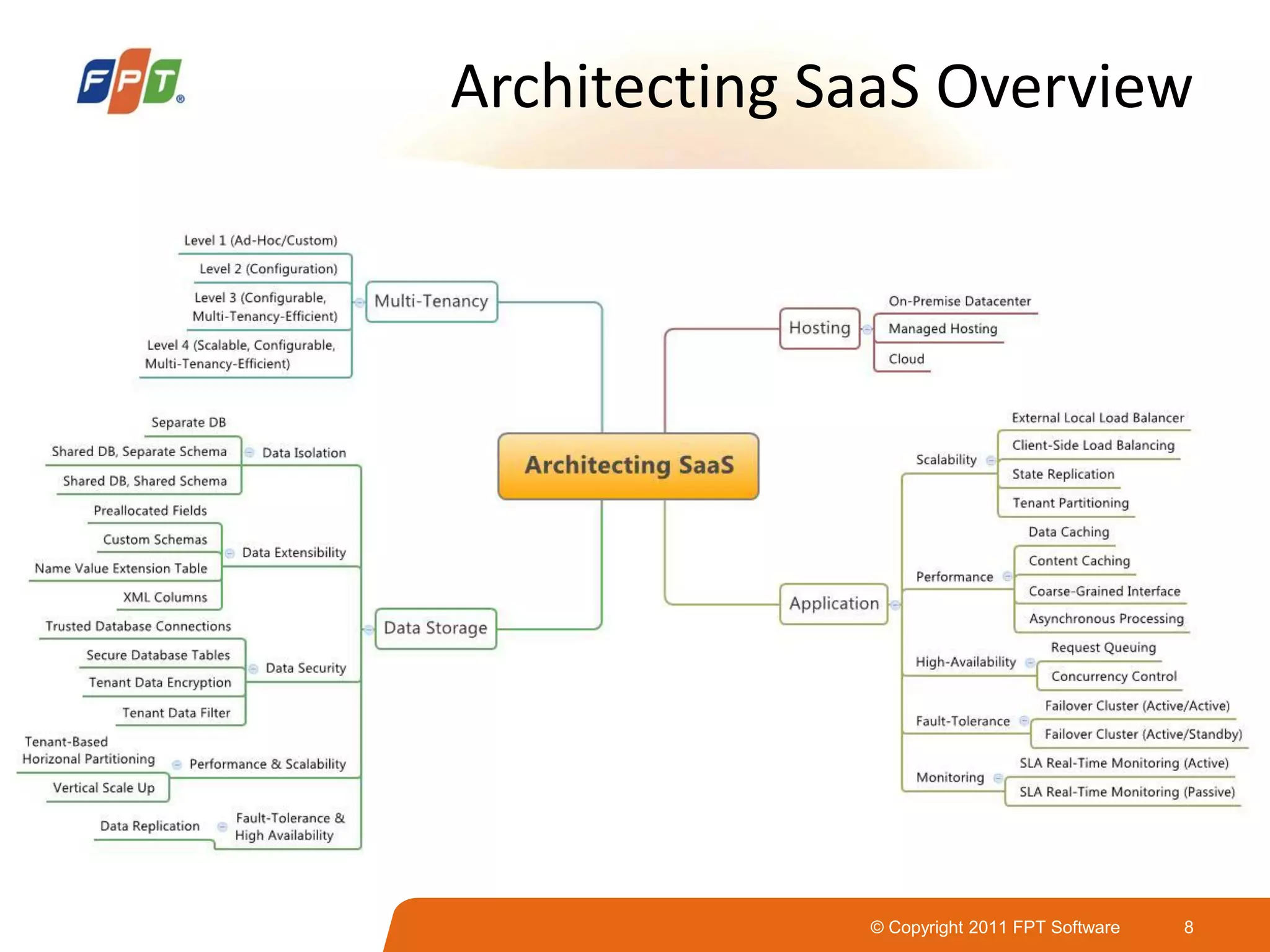
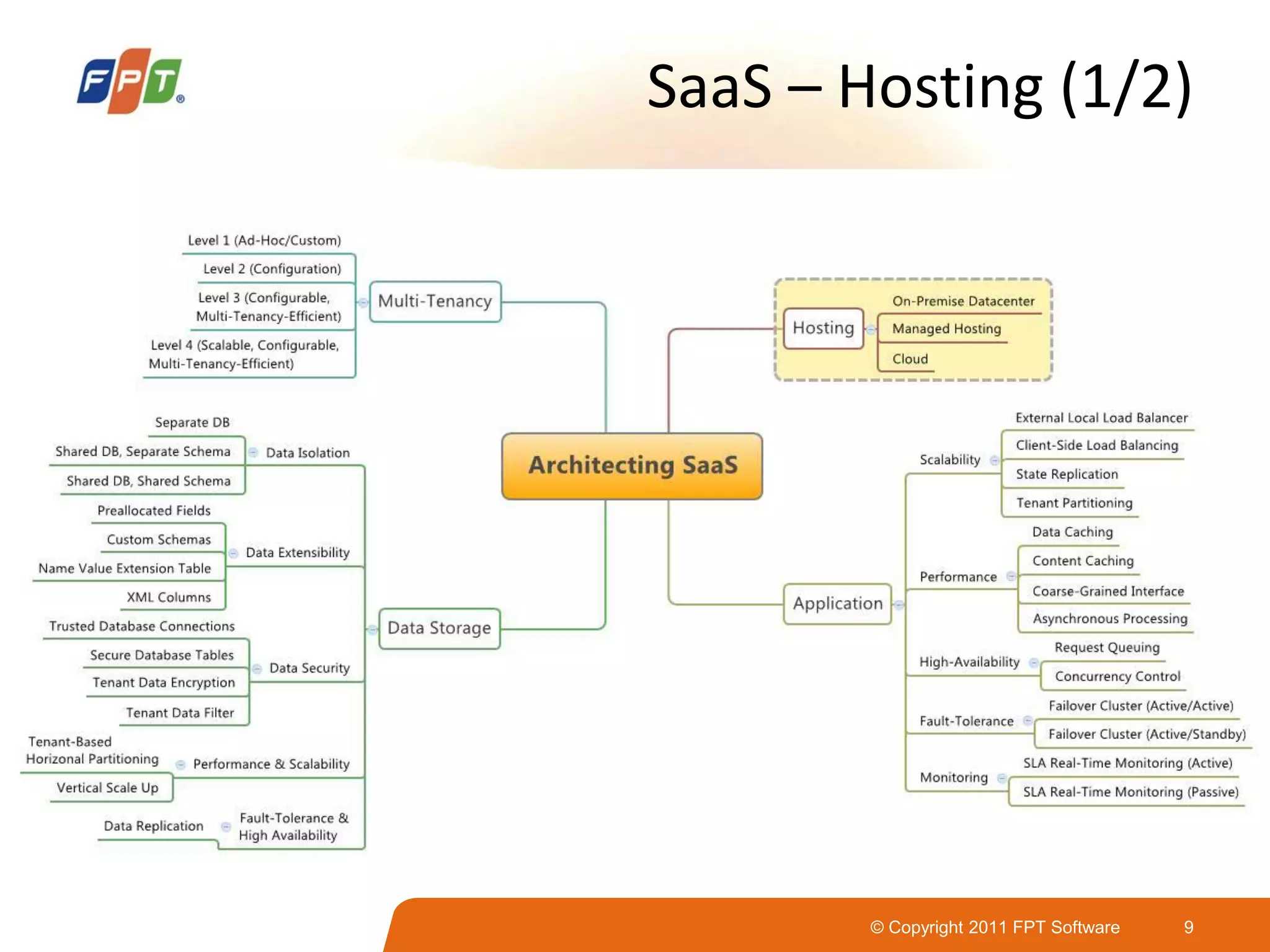
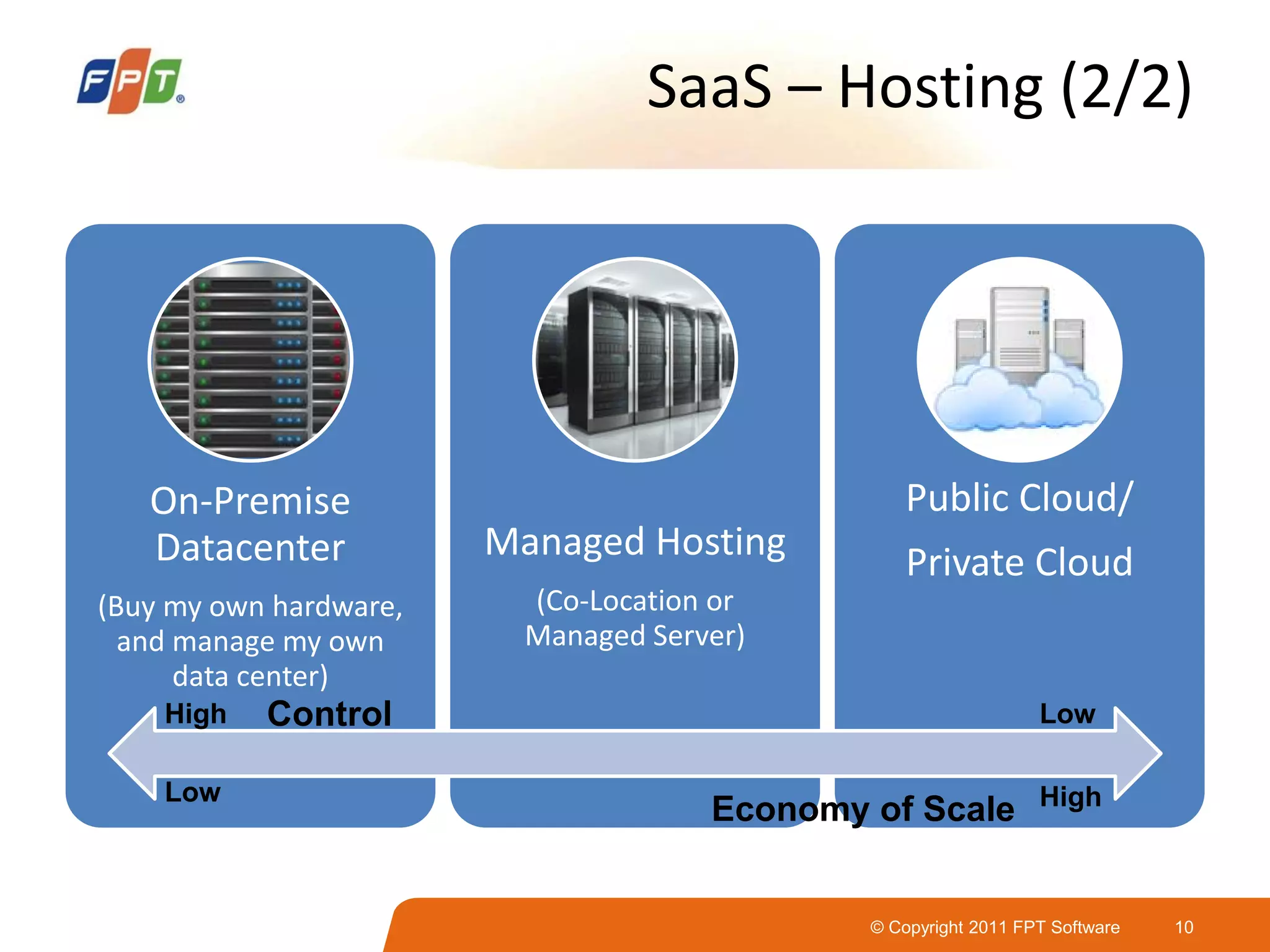
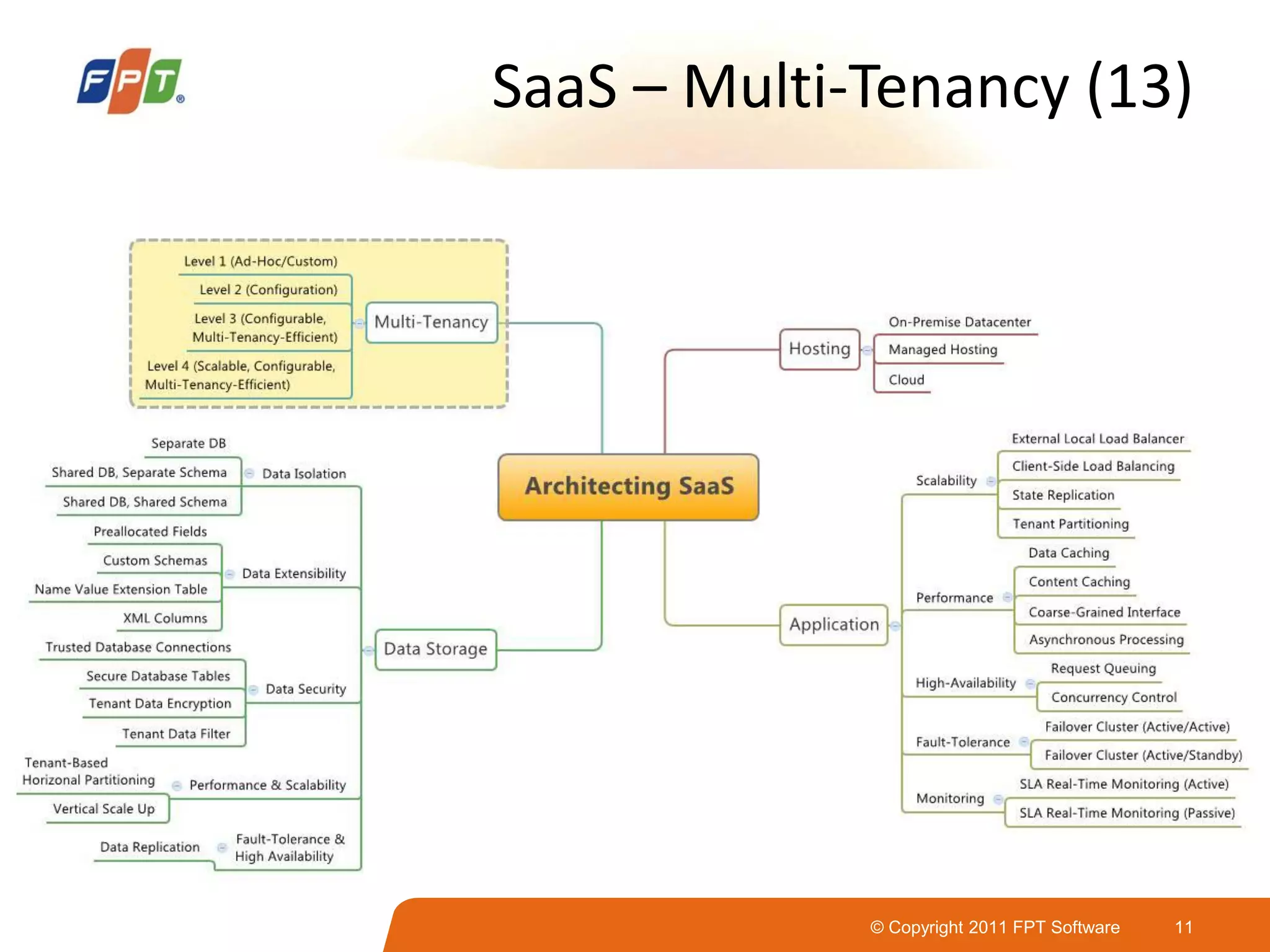
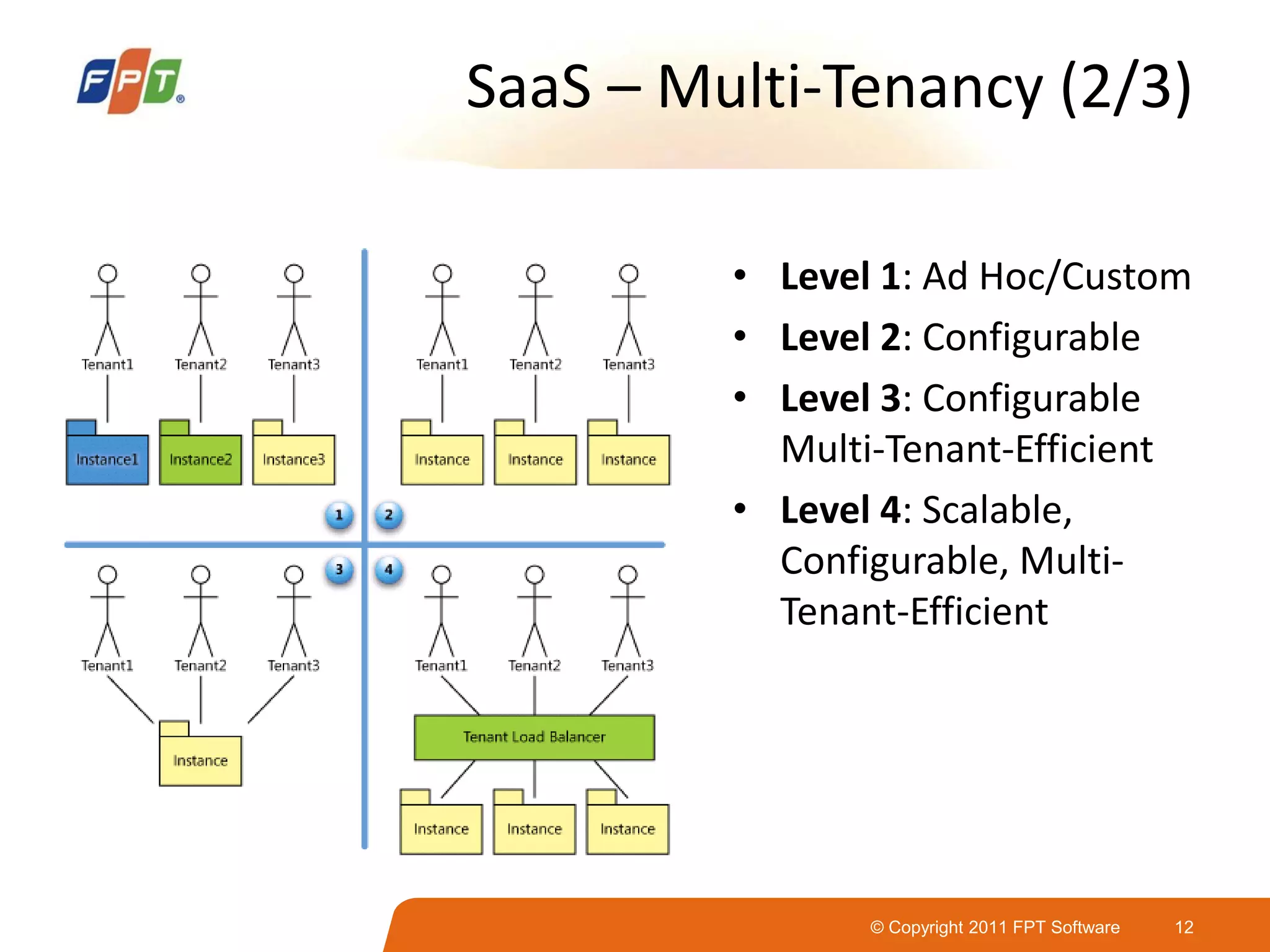
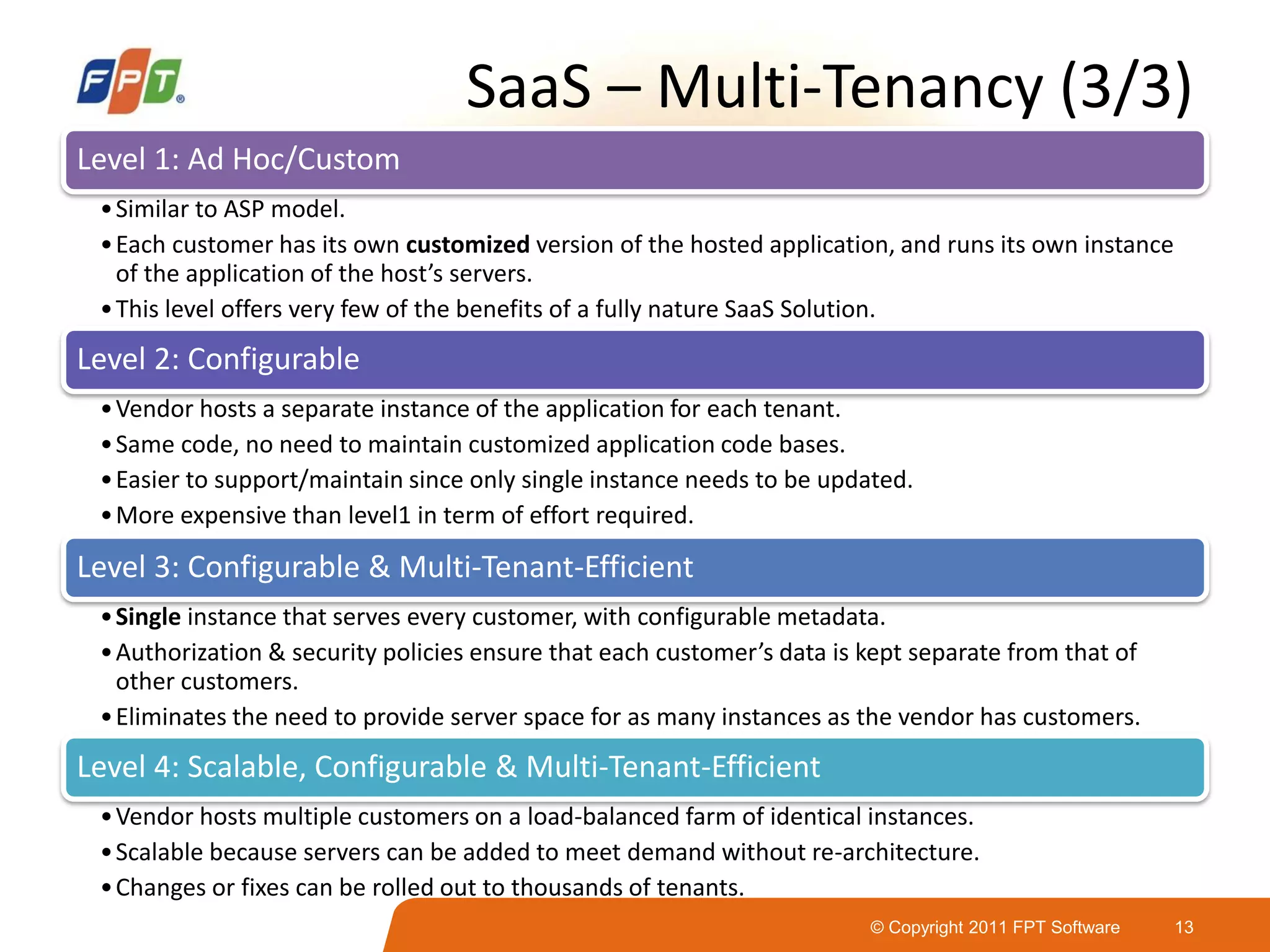
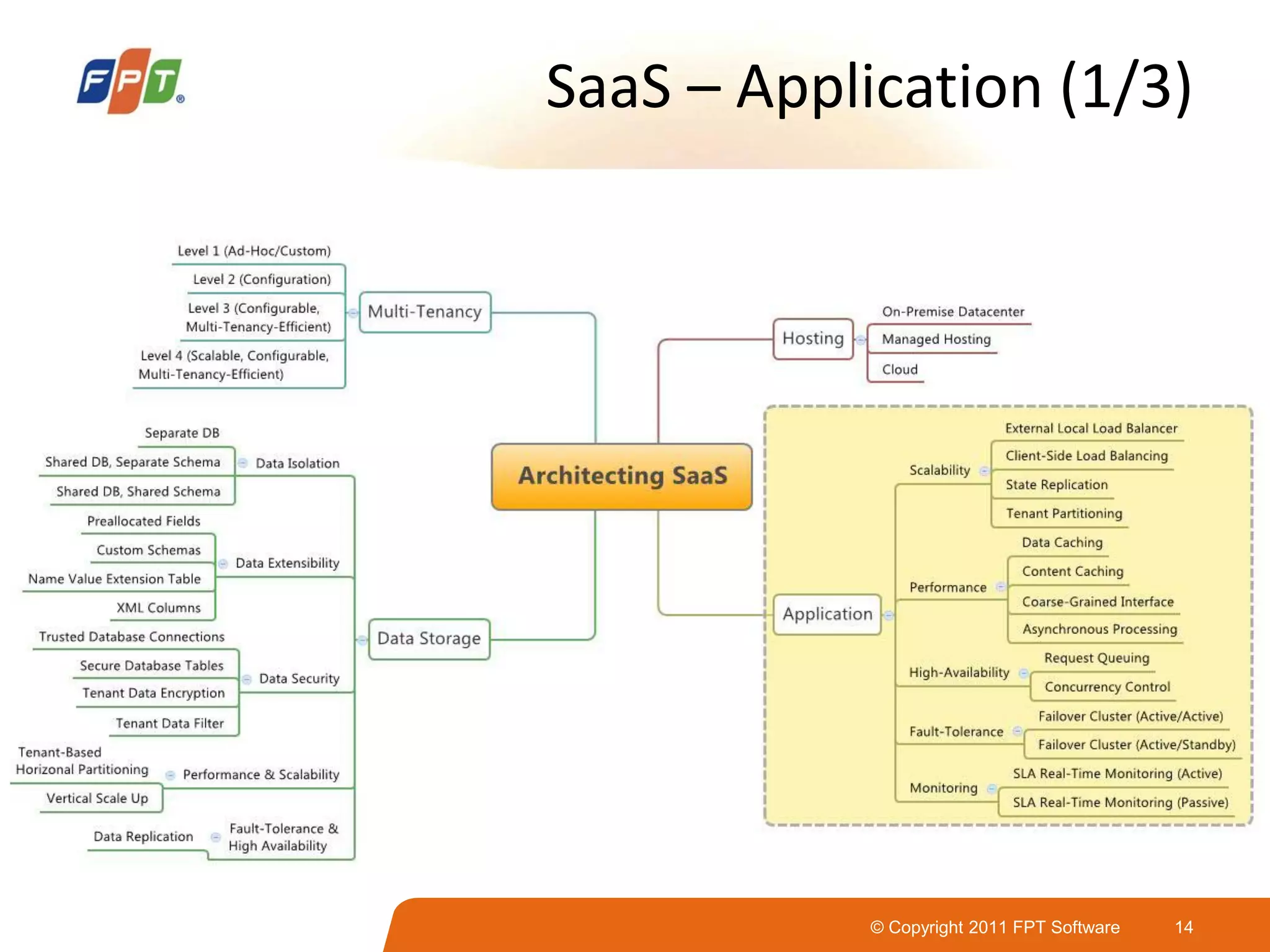
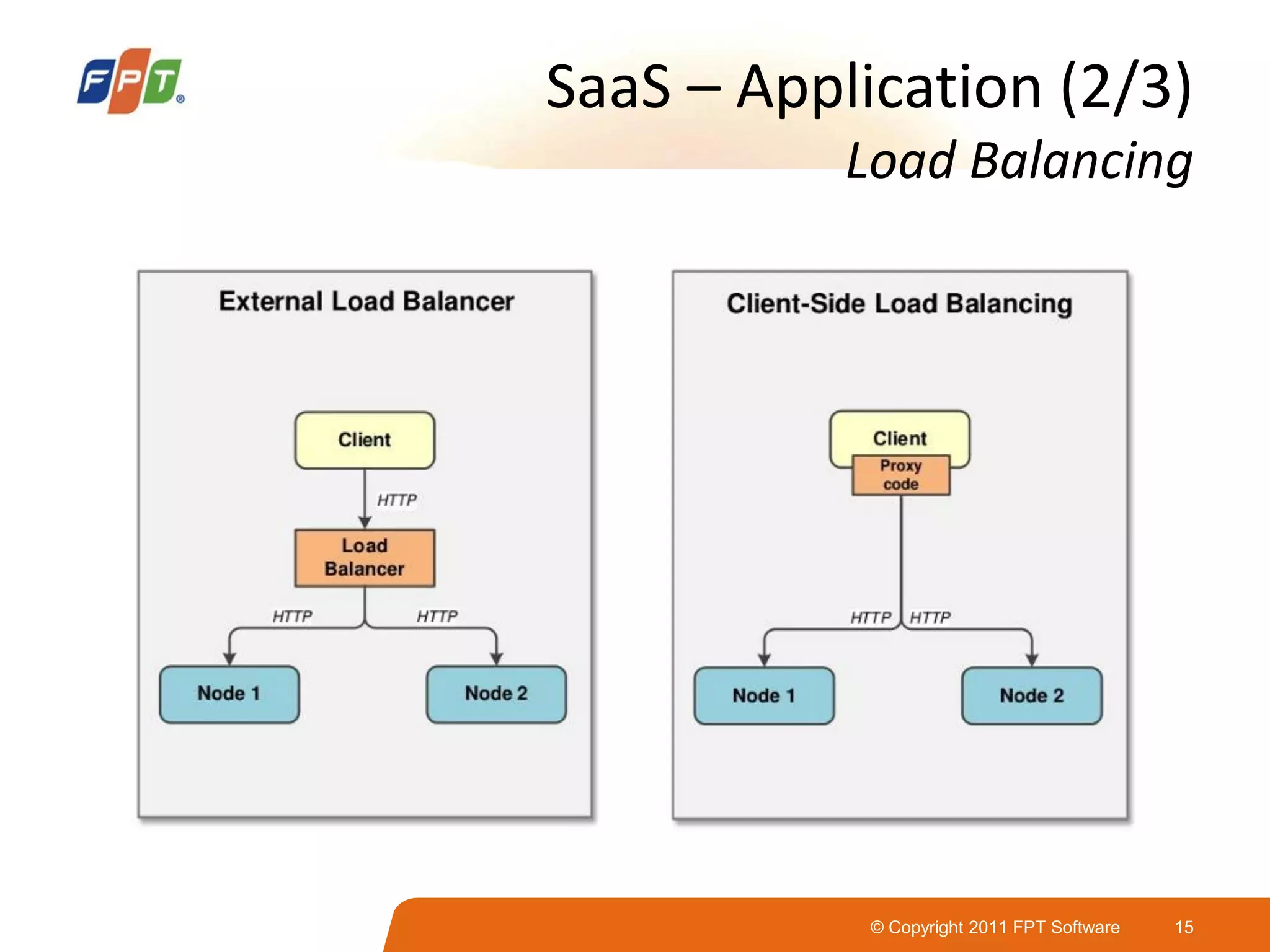
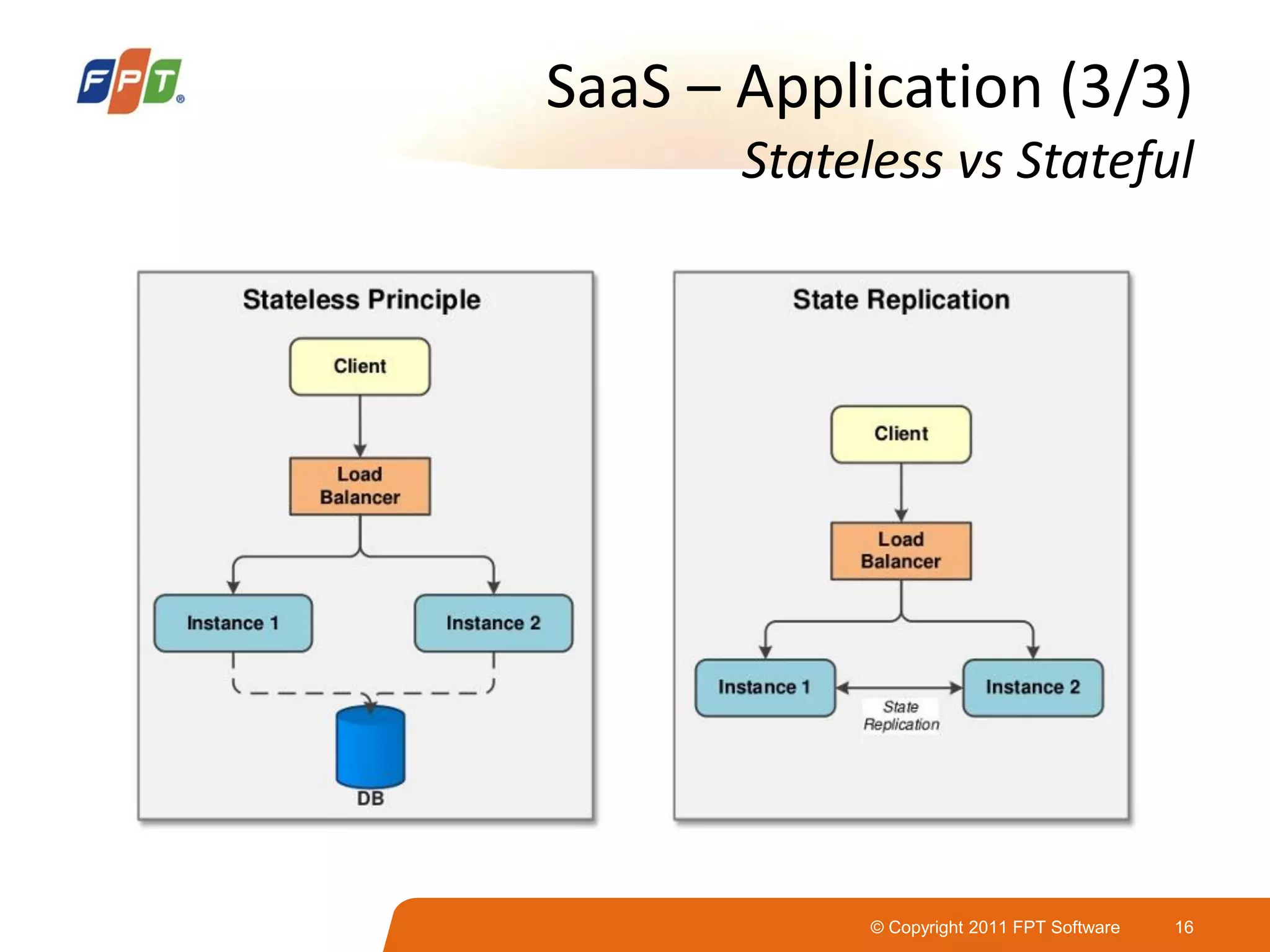
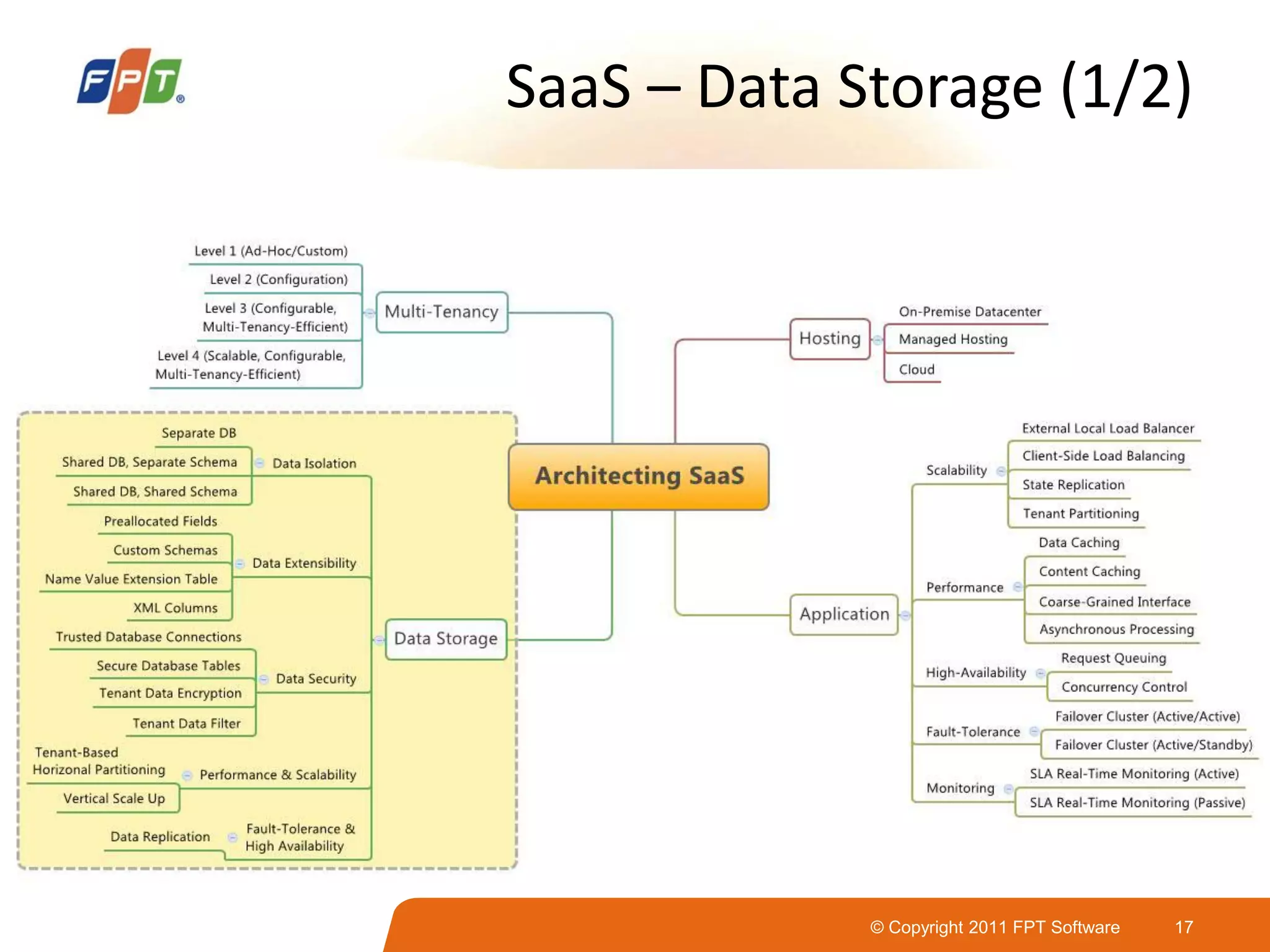
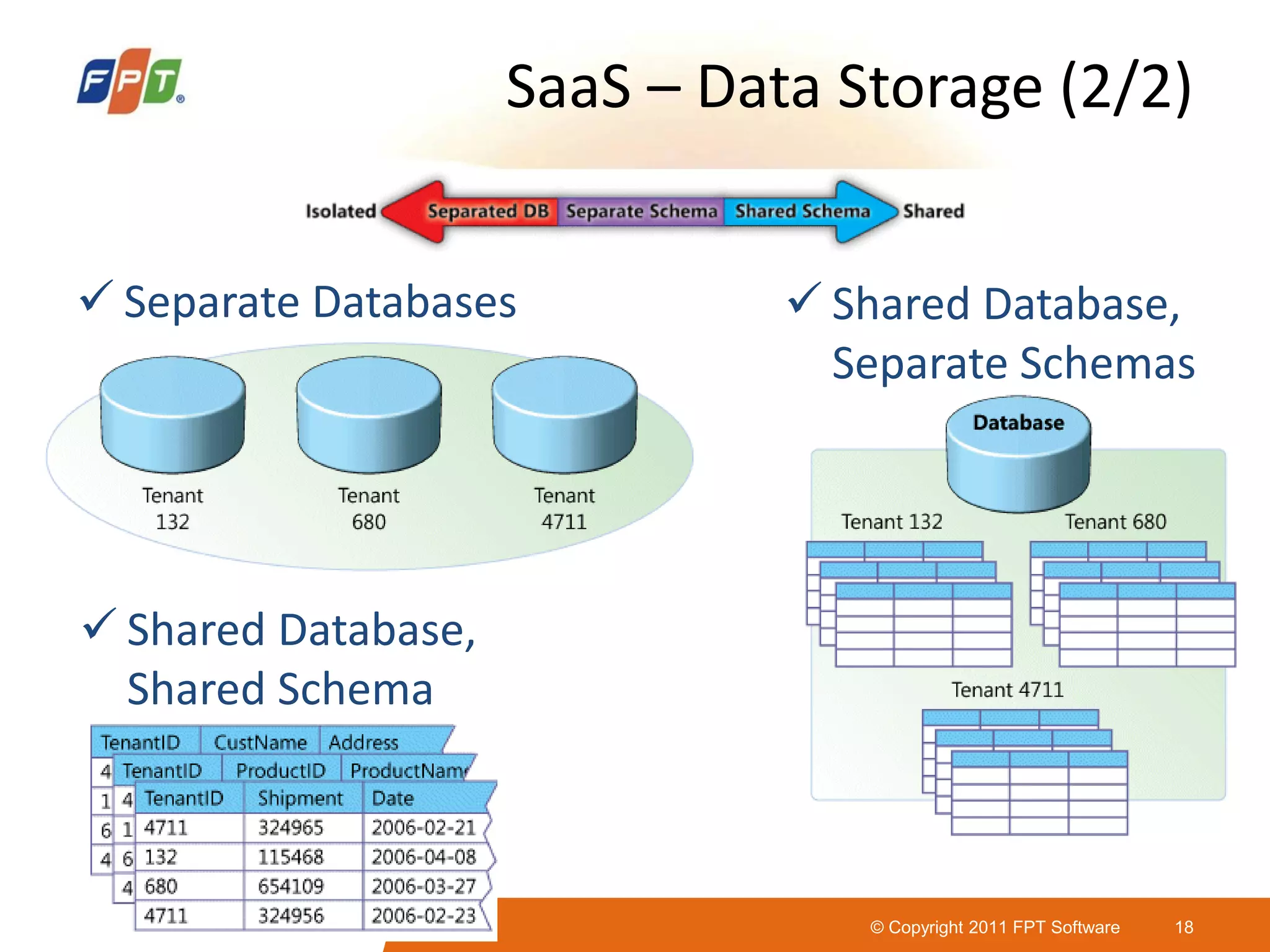
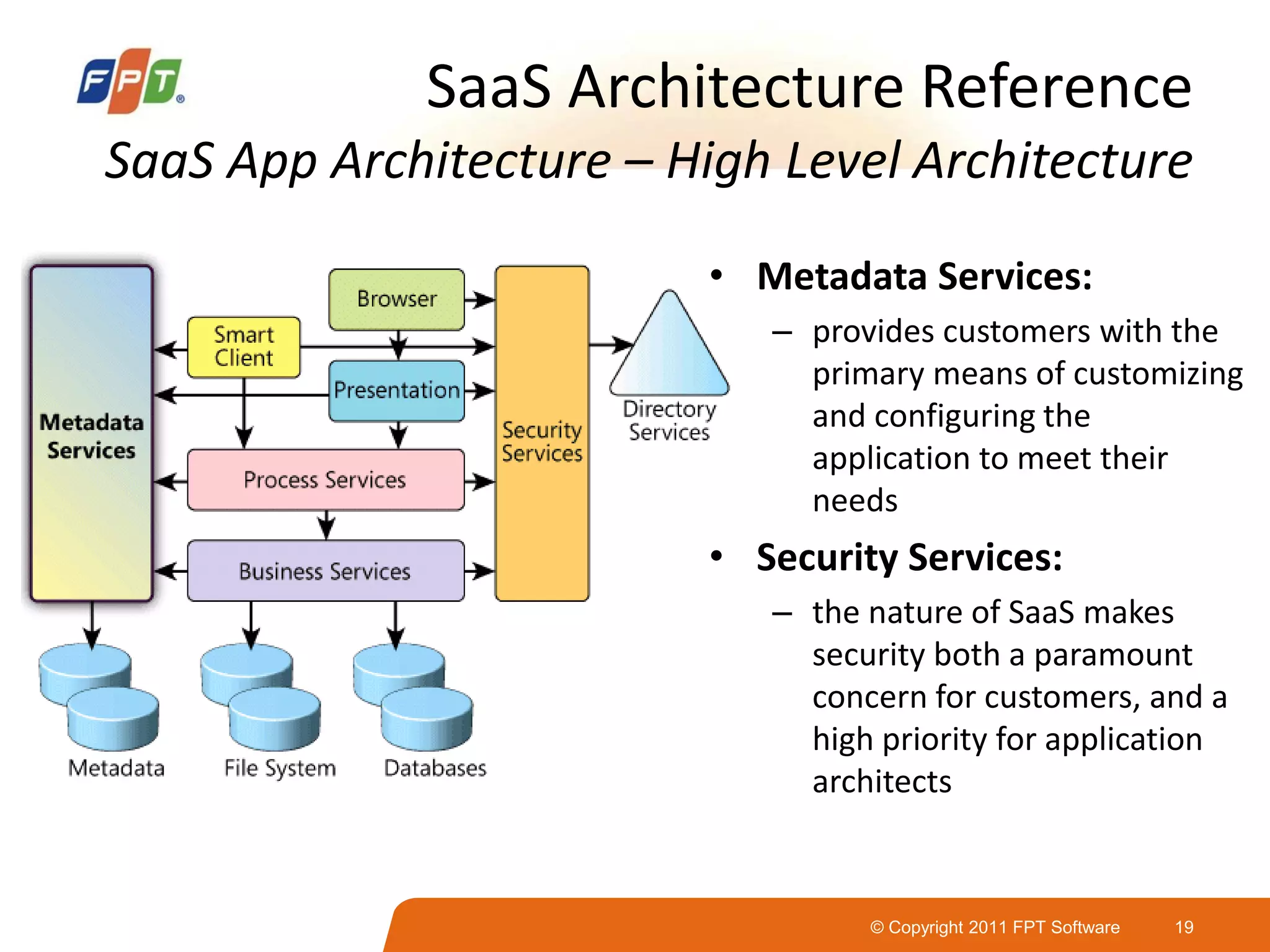
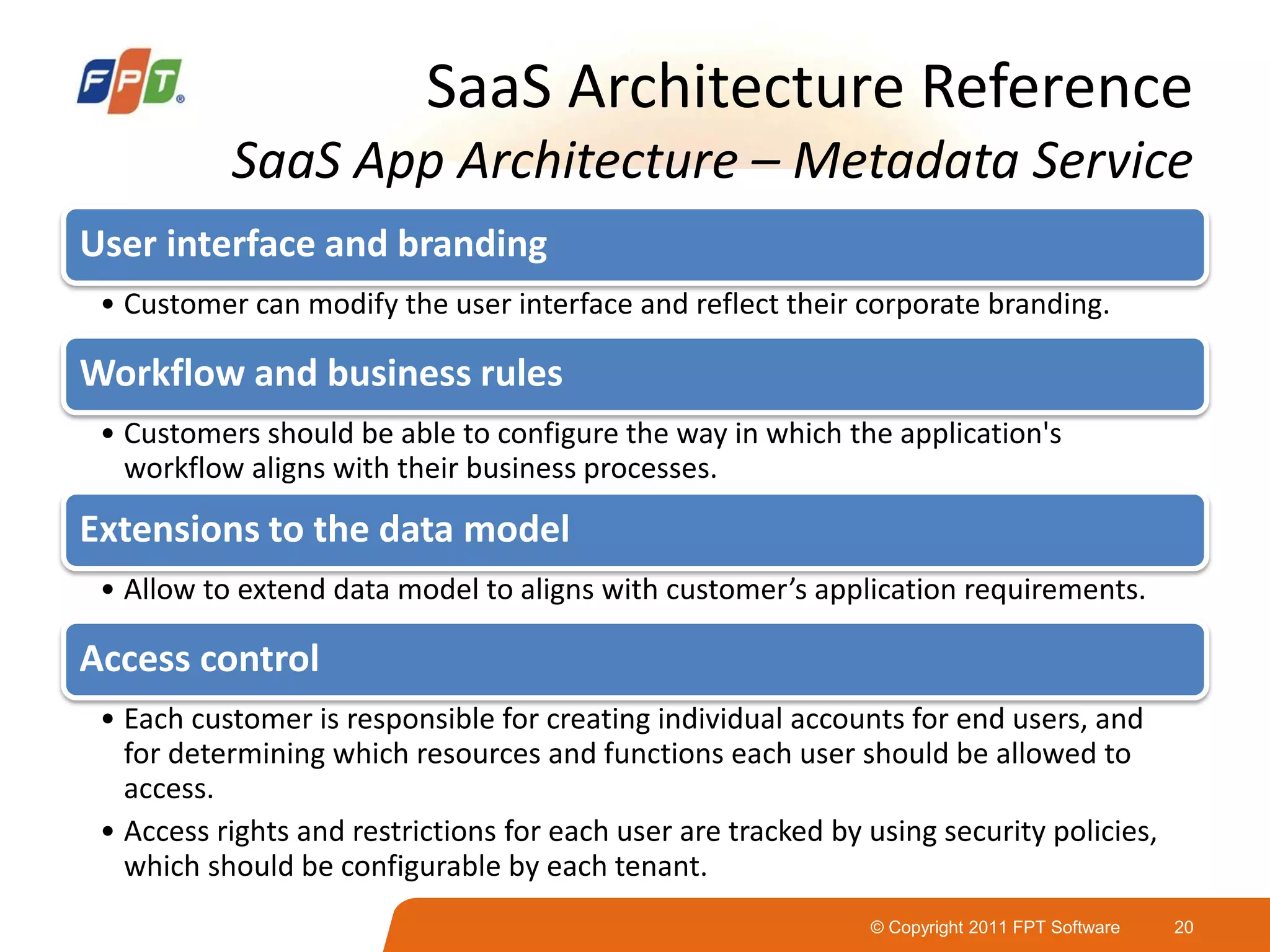
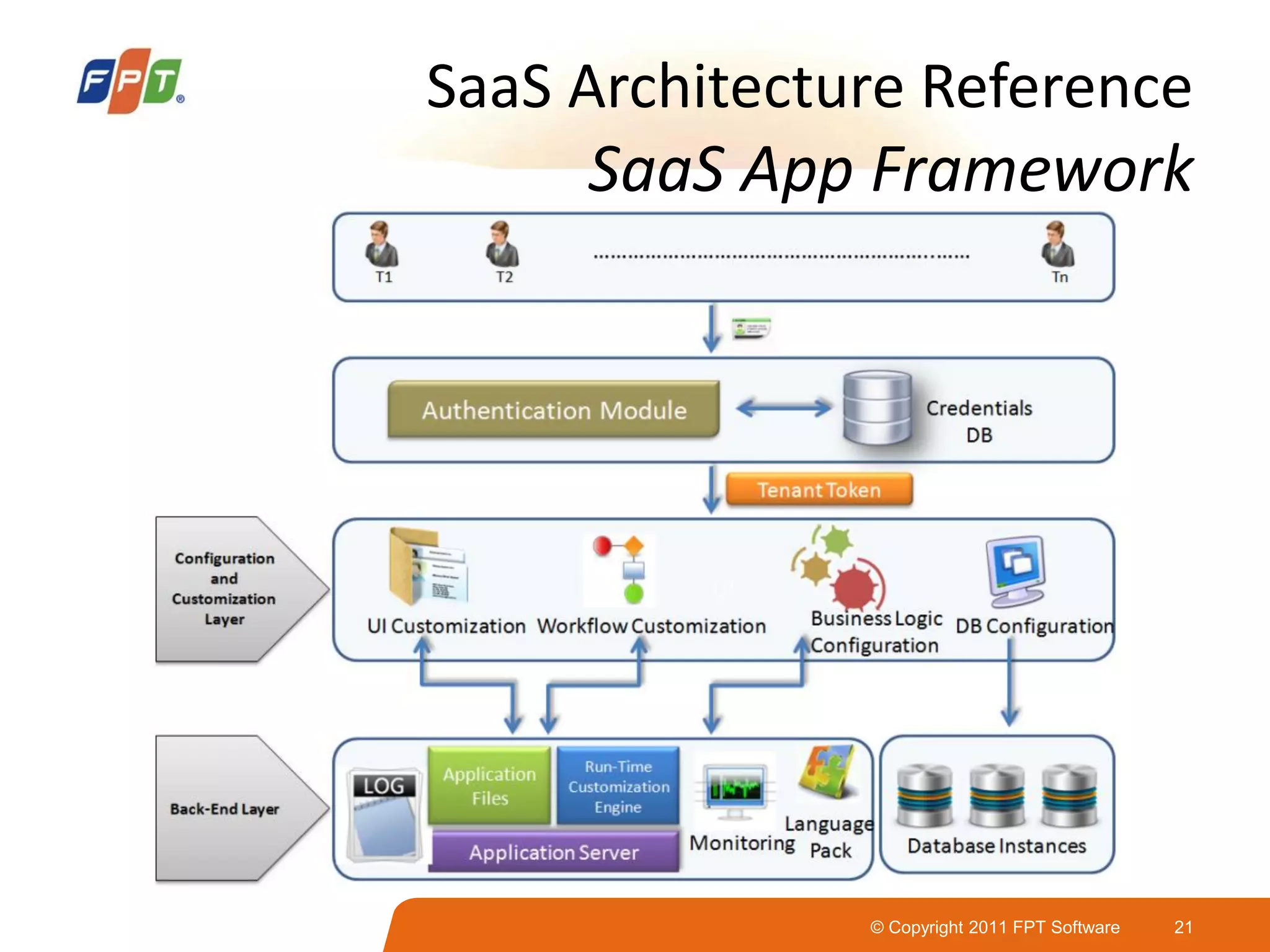
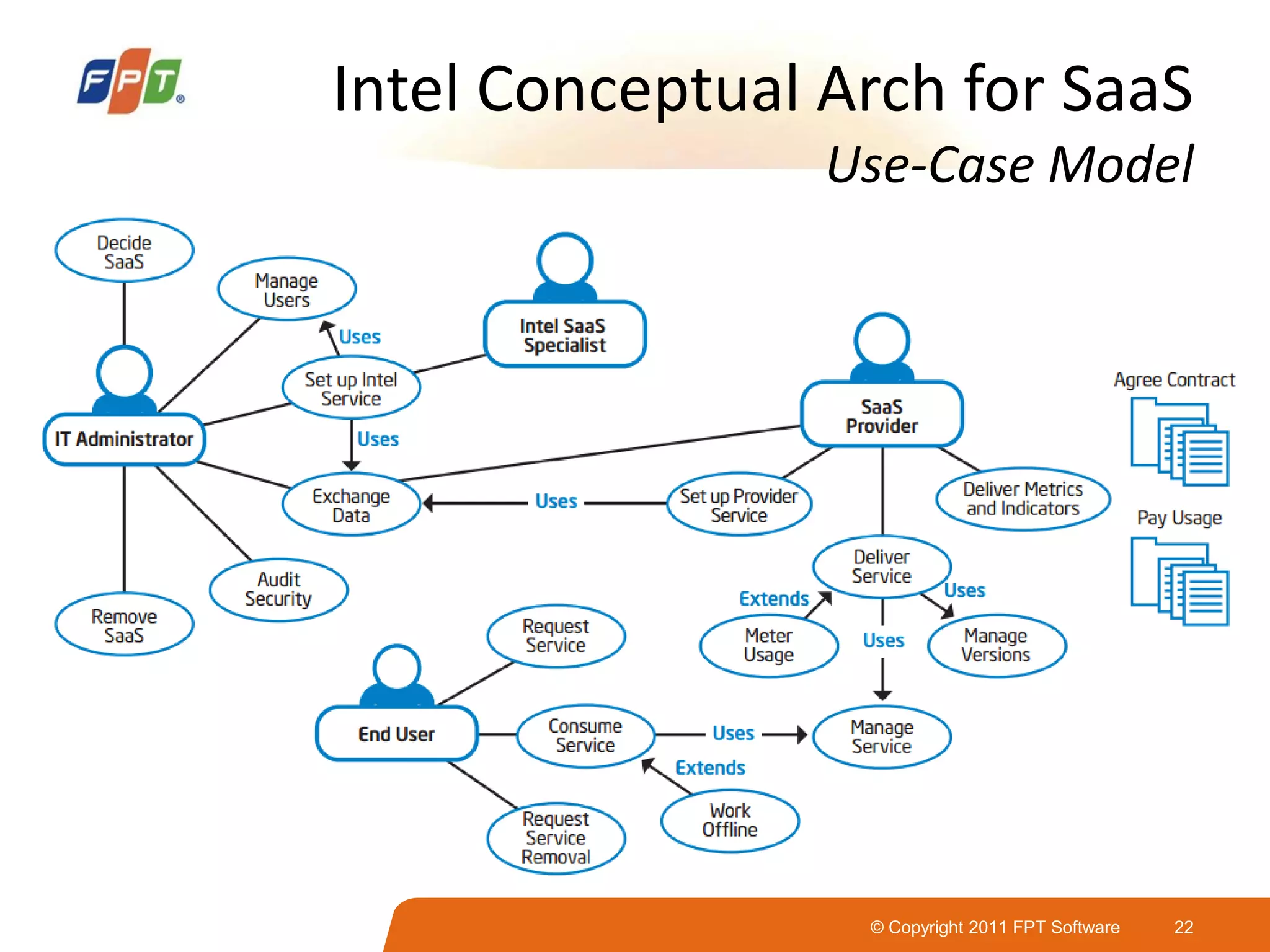
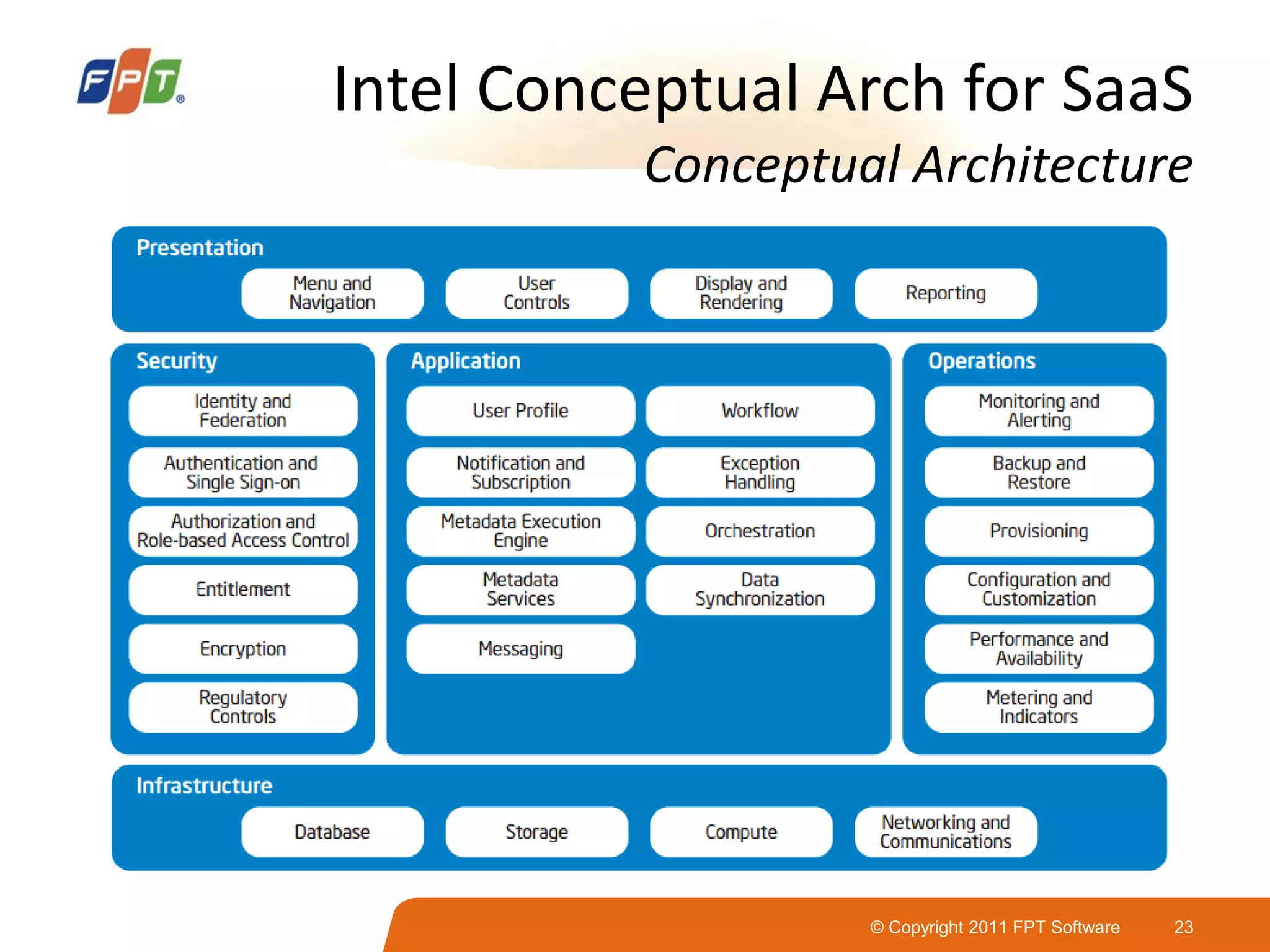
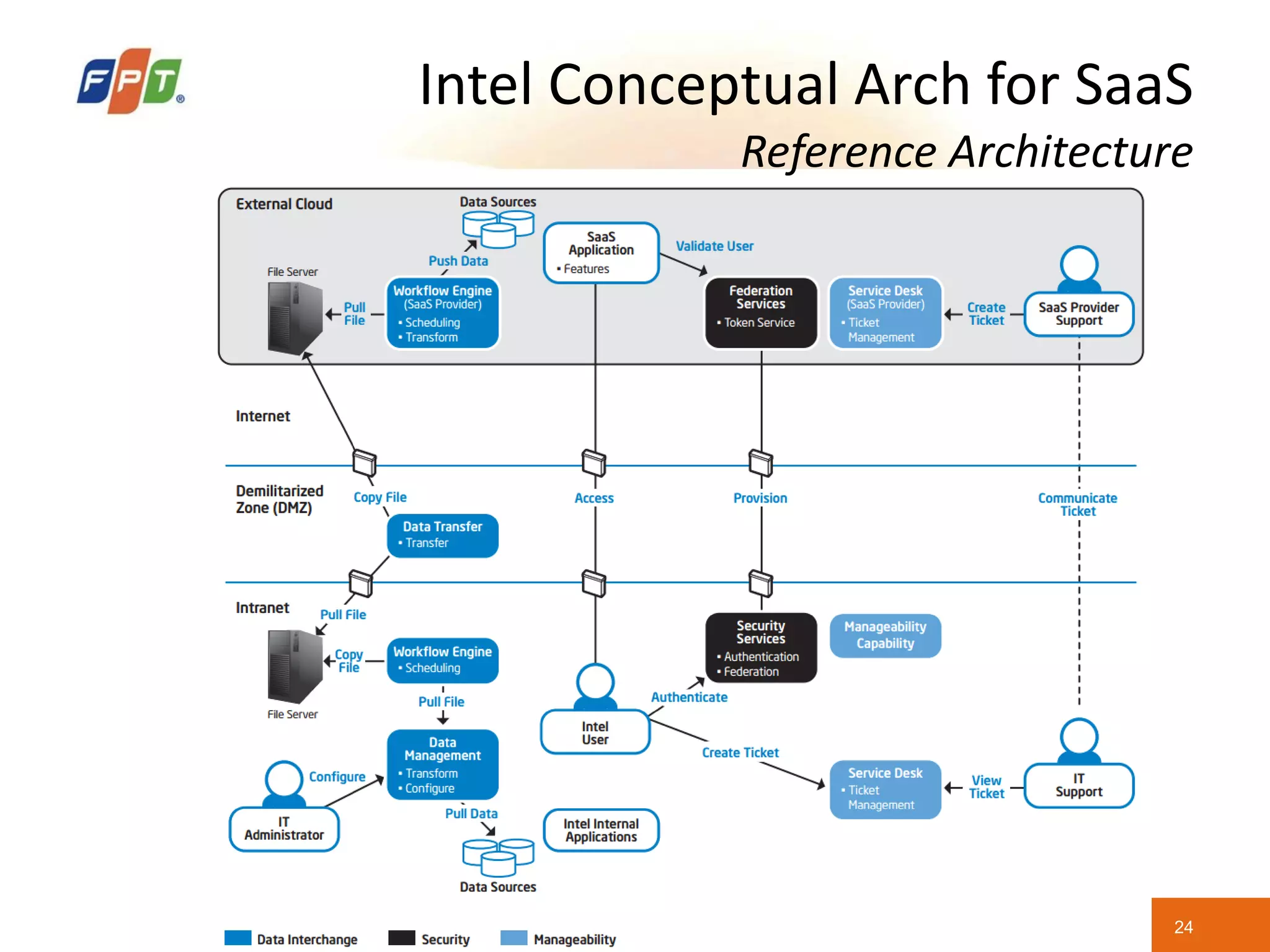
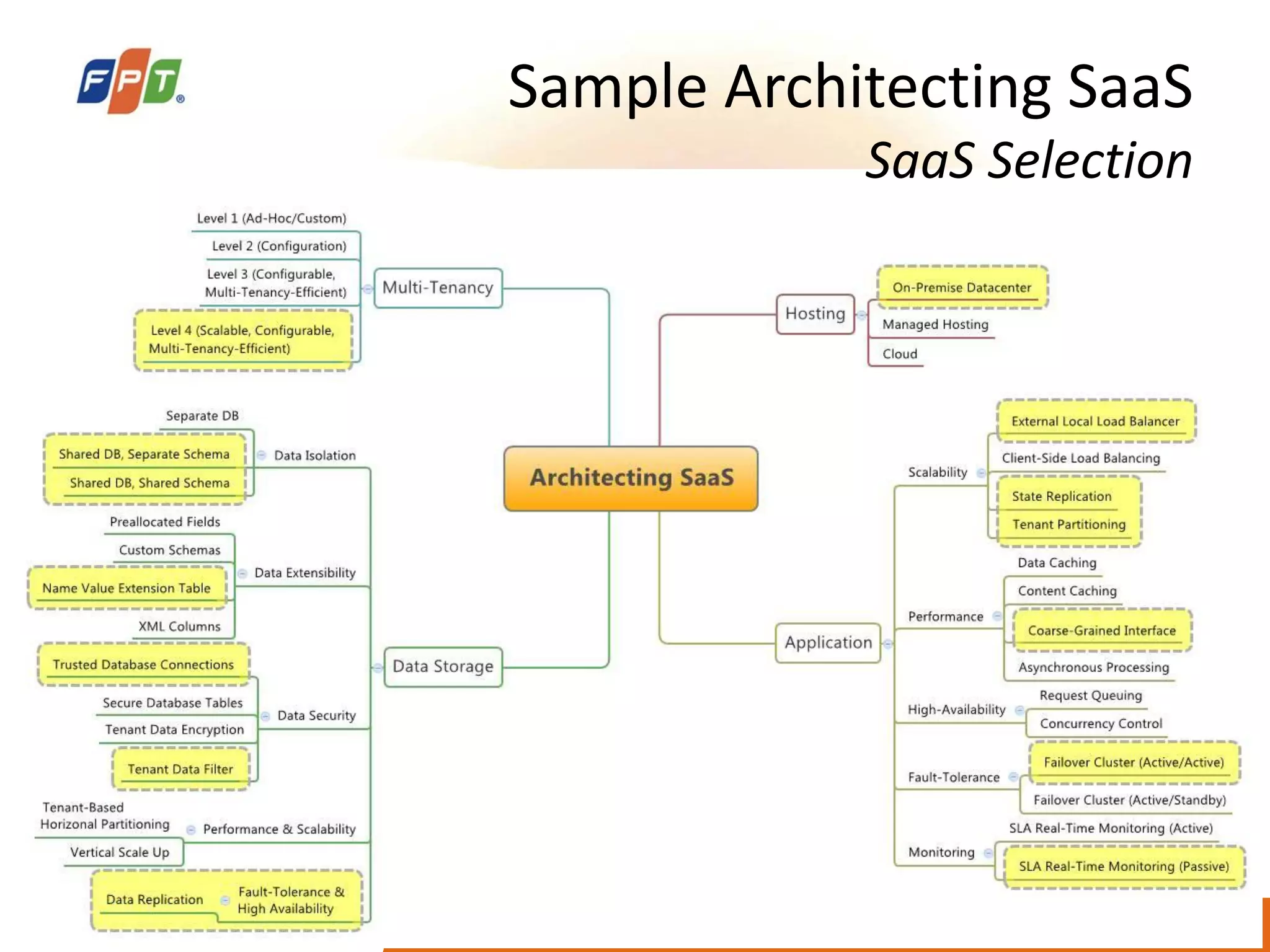
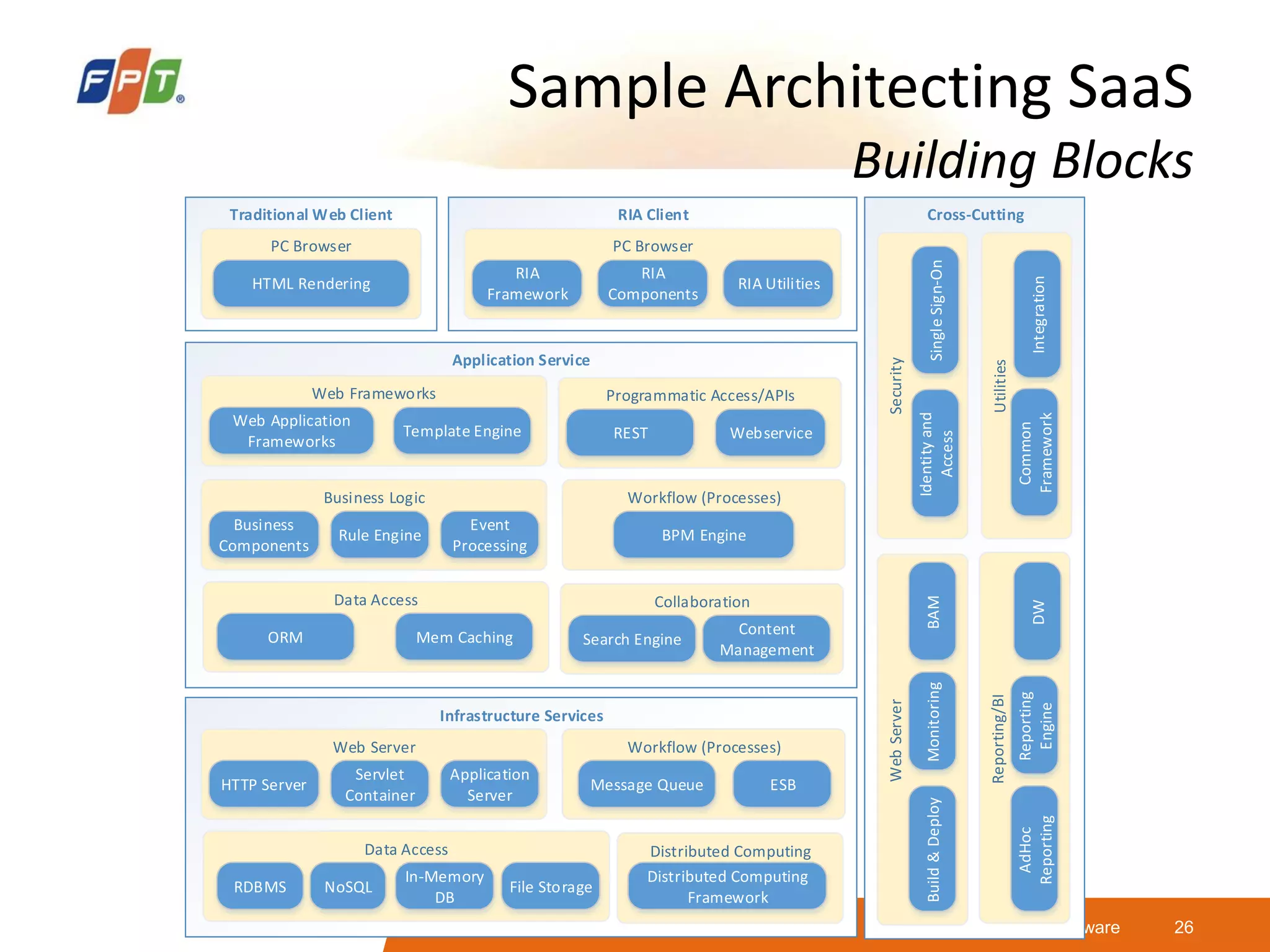
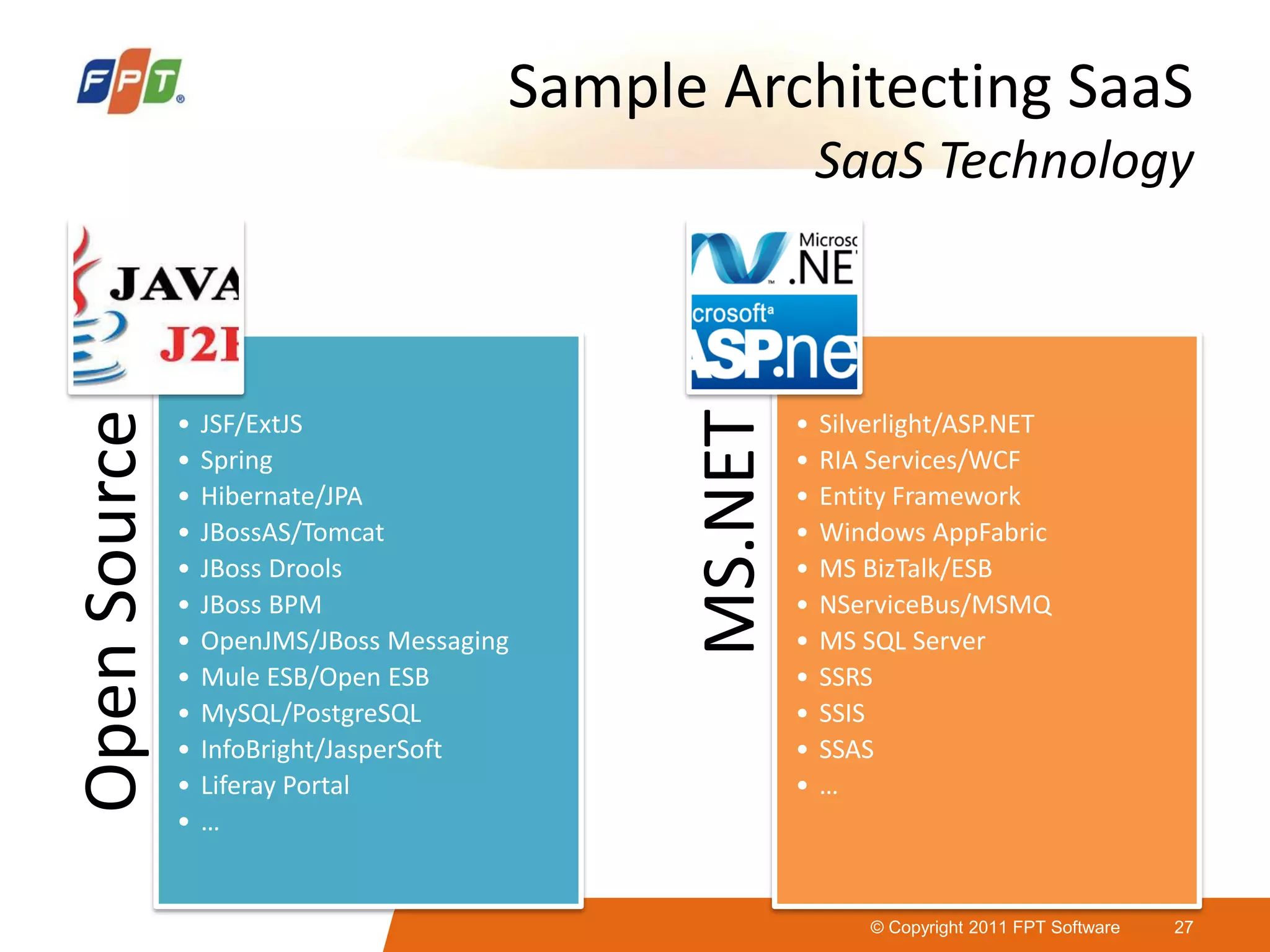
This document provides an overview of software as a service (SaaS) architecture. It discusses SaaS characteristics and challenges, outlines common SaaS architecture stacks, and describes key considerations for architecting multi-tenant SaaS applications including hosting, application structure, data storage, and security services. Examples of SaaS reference architectures and conceptual models are also presented.