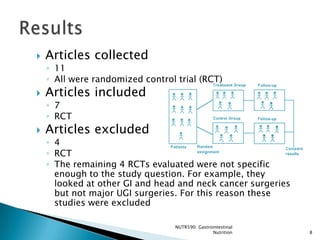
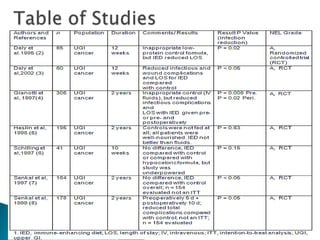
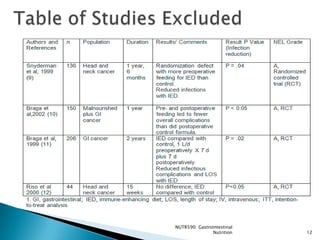
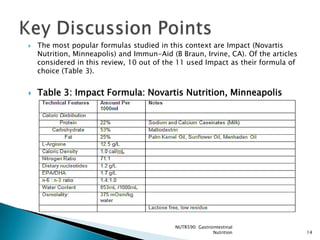
The document reviews evidence on the use of immunonutrition for patients undergoing major upper gastrointestinal cancer surgeries. It summarizes 7 randomized control trials that found immunonutrition containing arginine, omega-3 fatty acids, and nucleotides reduced postoperative infections compared to control solutions. However, studies had flaws like low feeding volumes. More recent research has found benefits of immunonutrition are greater when aggressive enteral feeding protocols are used to provide over 800mL per day. Overall, evidence suggests immunonutrition may decrease infection risk for patients with gastrointestinal cancer undergoing surgery.