Embed presentation
Download to read offline

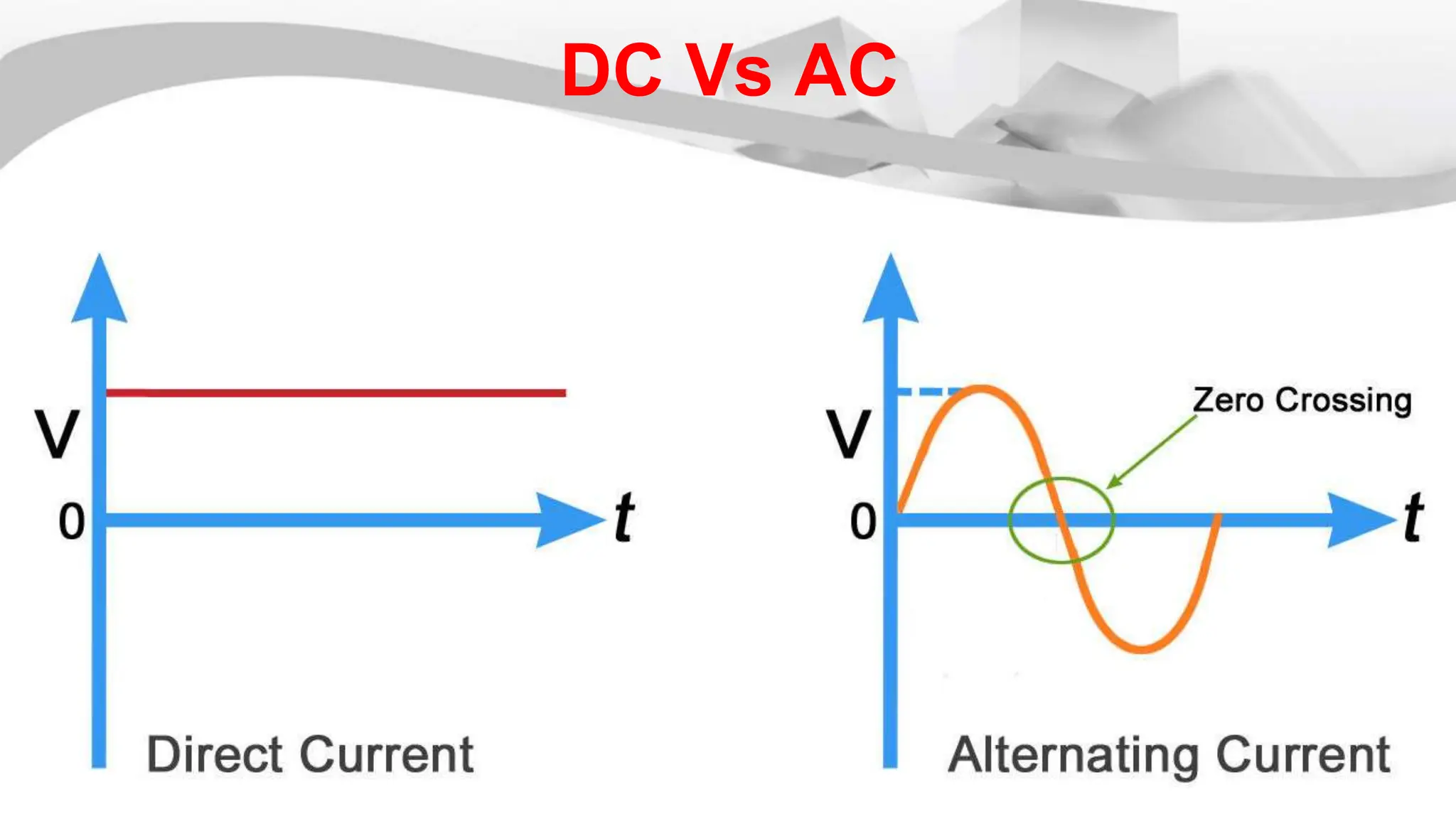
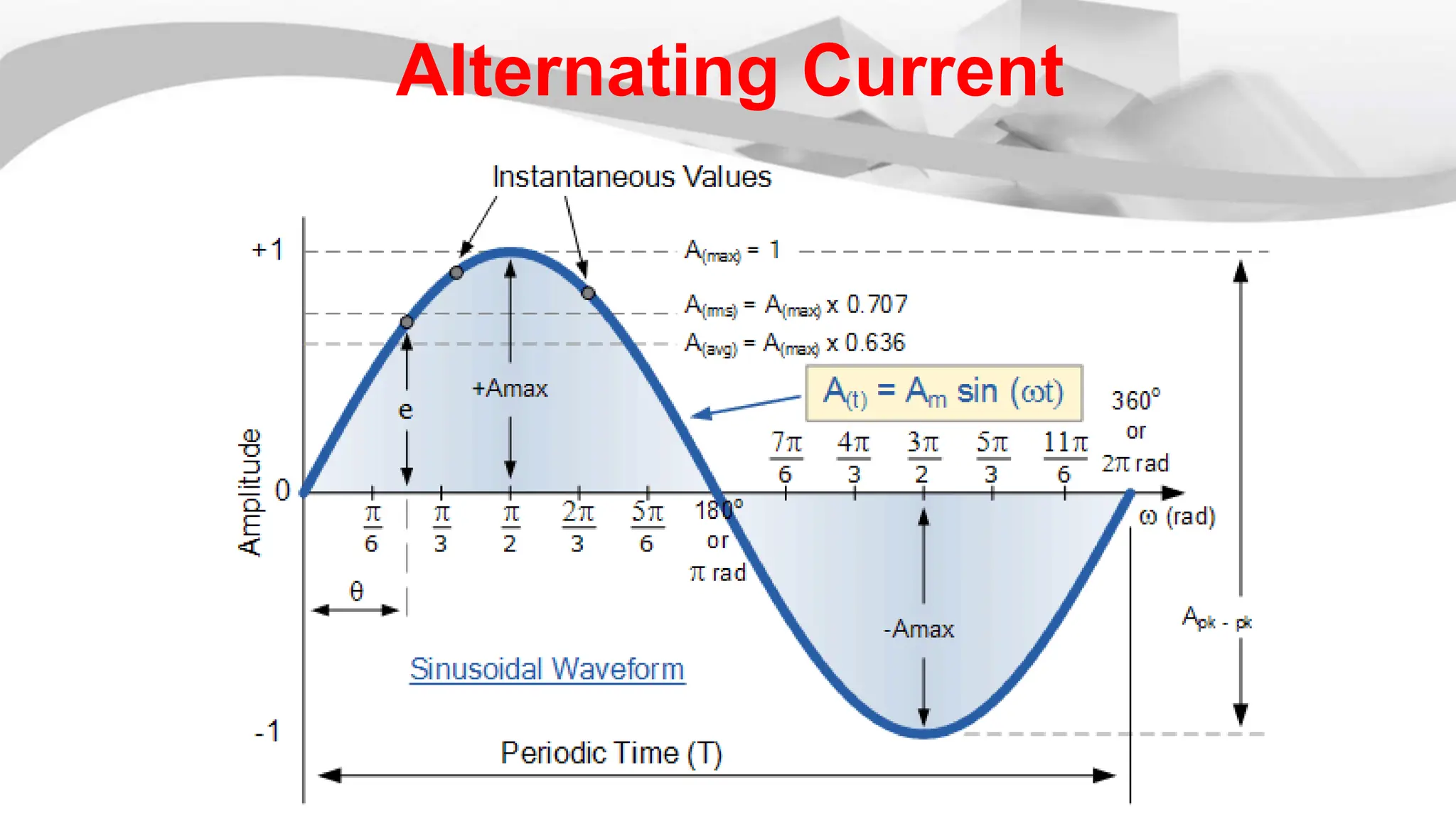
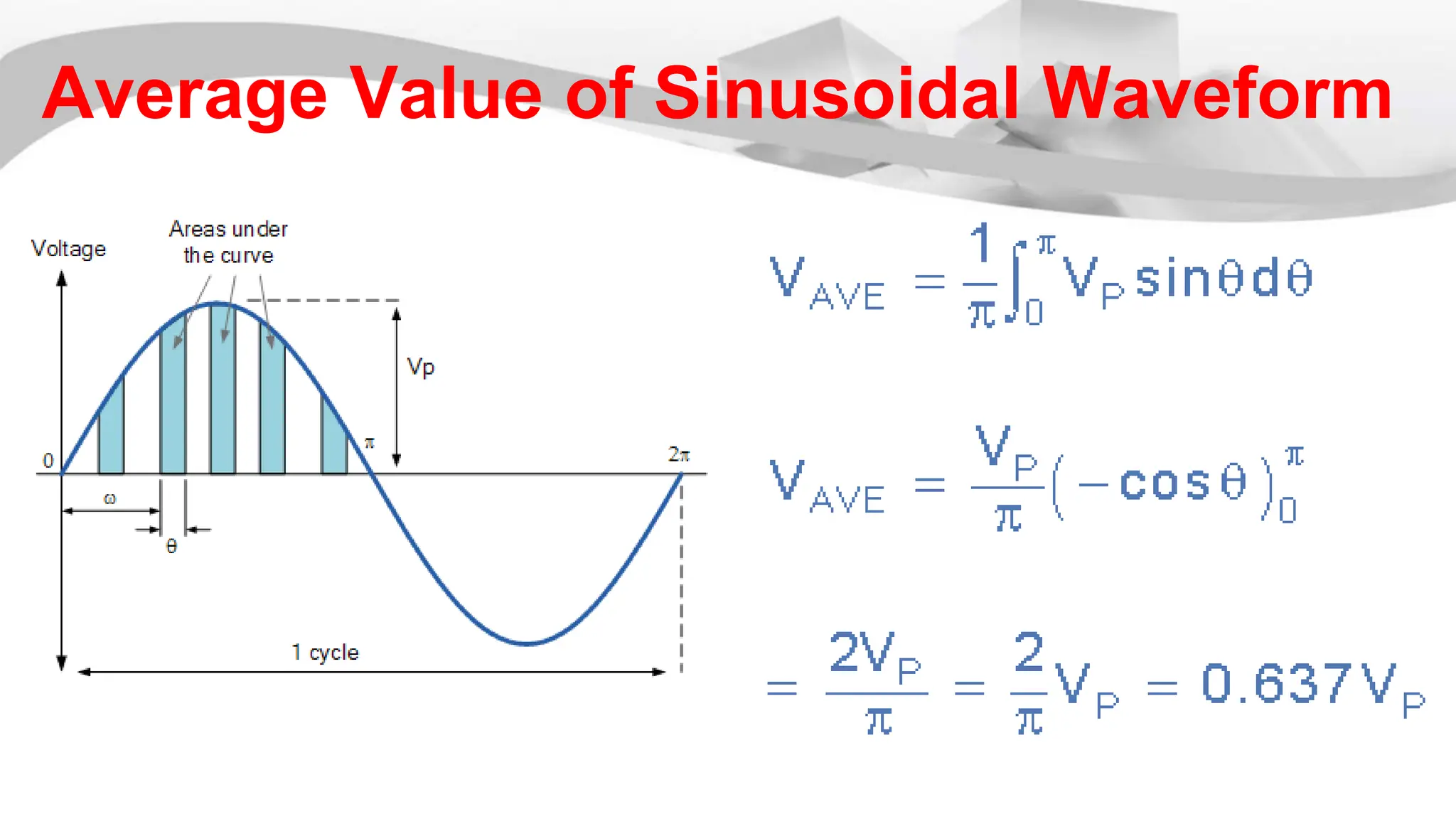
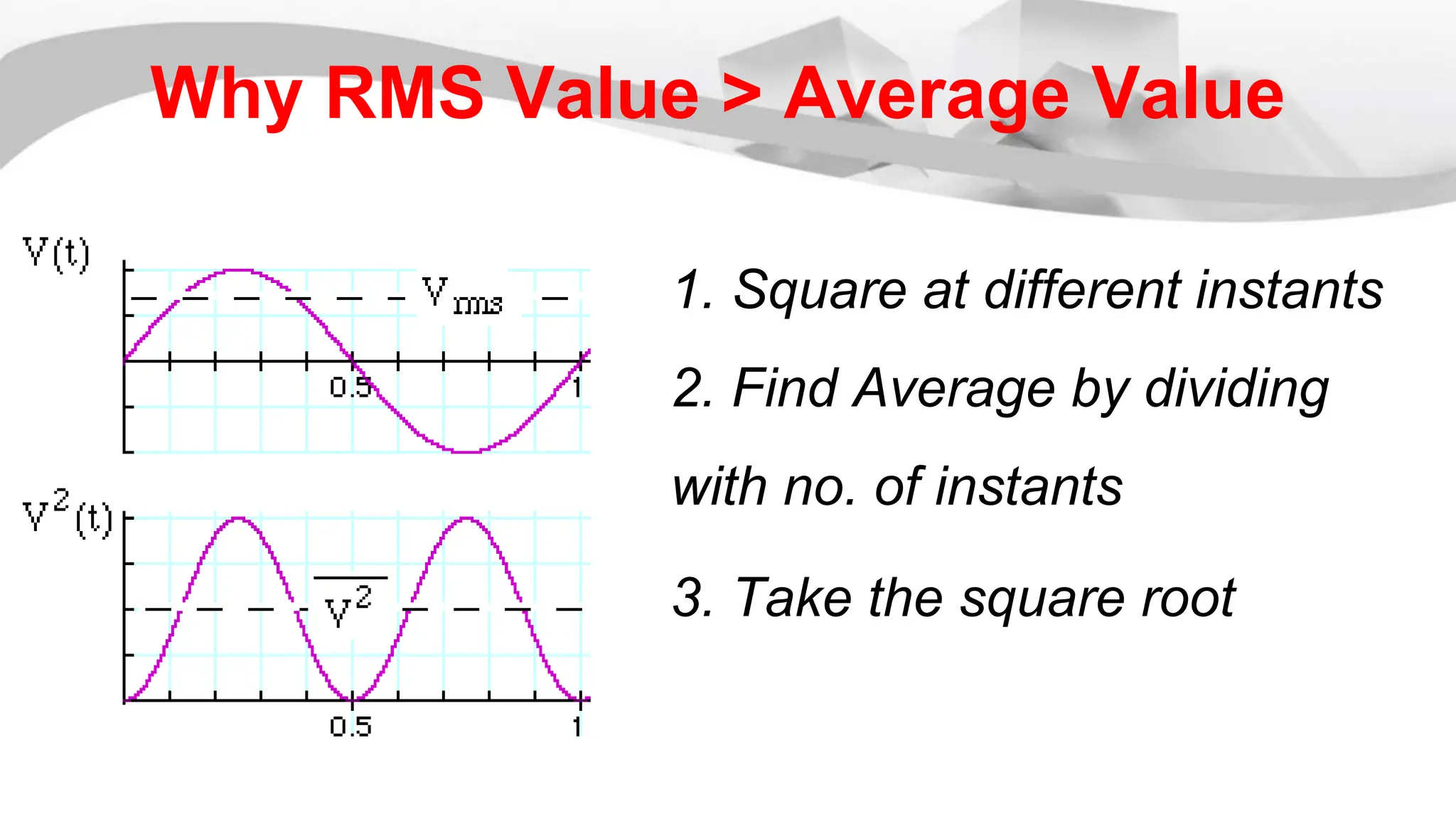
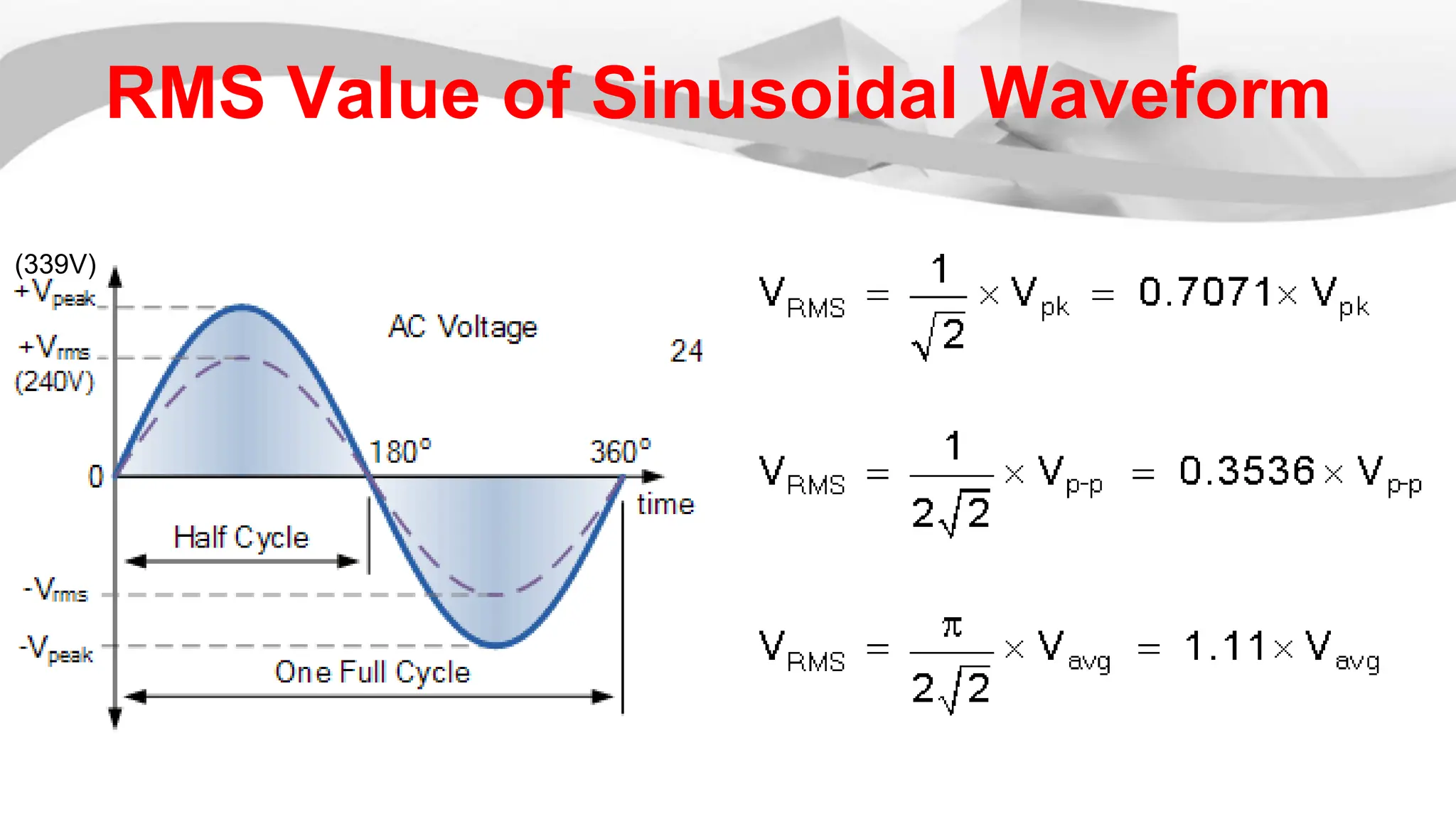
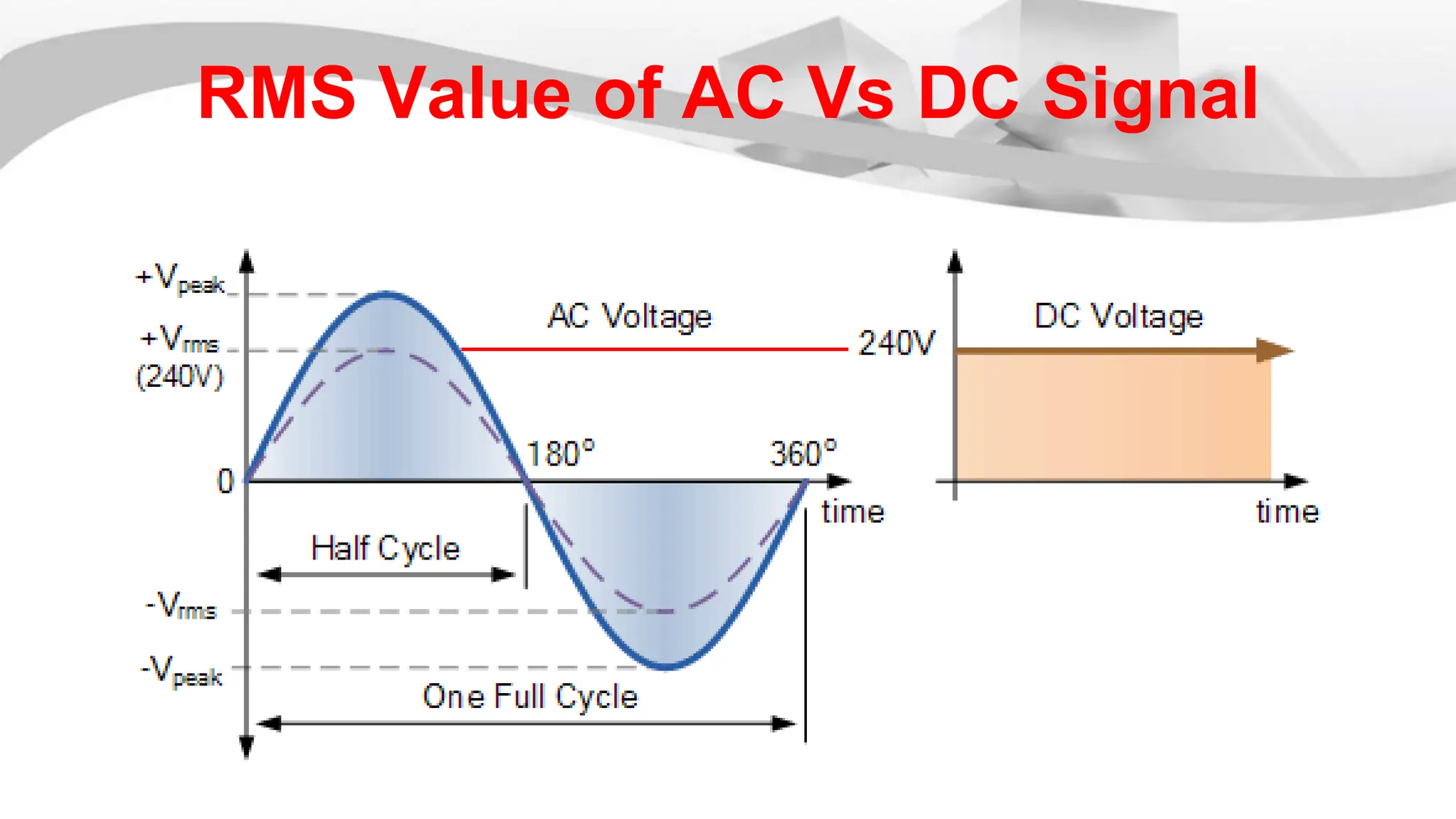
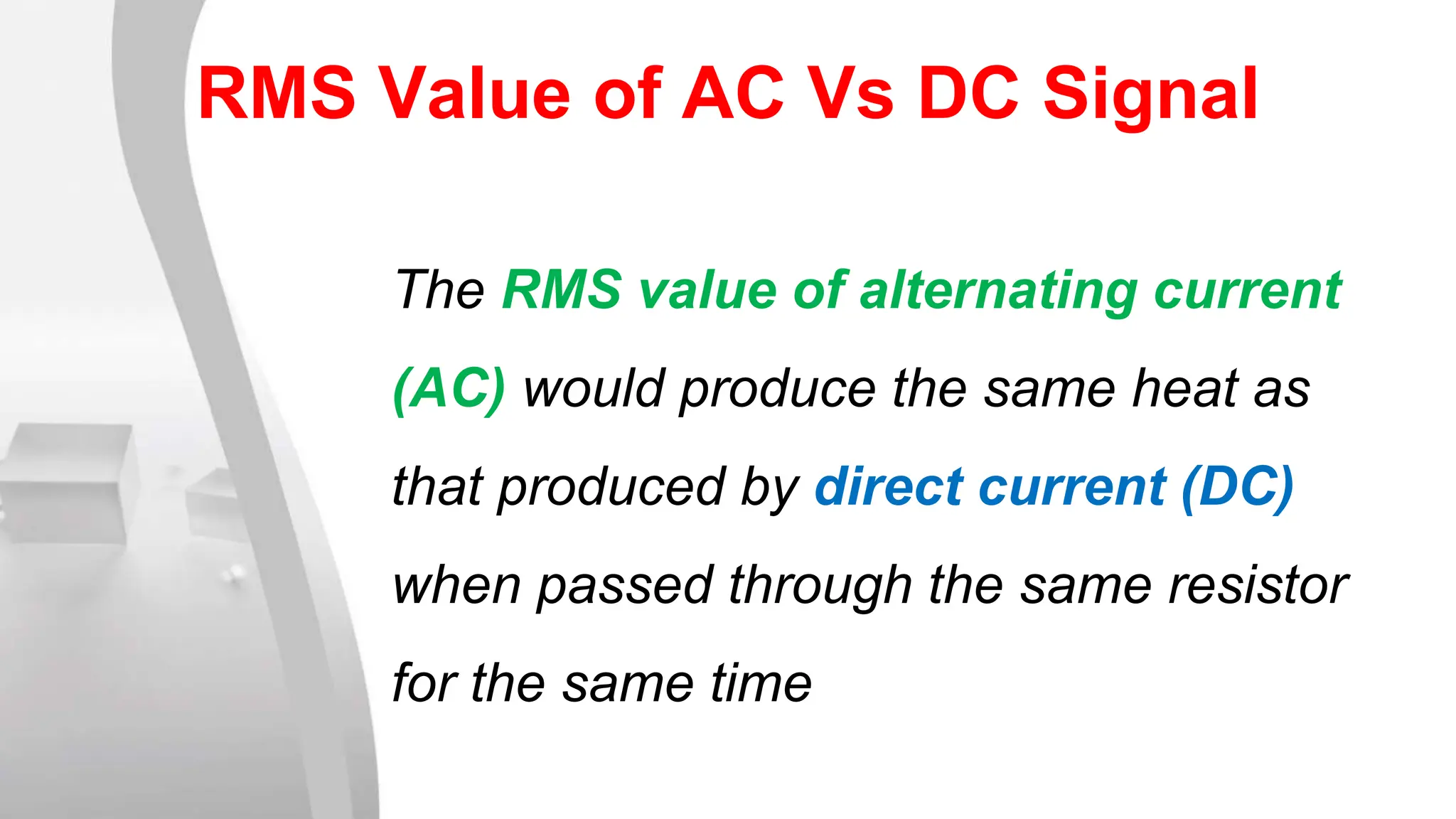

The root mean square (RMS) value is used for alternating current quantities because it provides a value that relates the power of an AC signal to what it would be if the same power was delivered by a DC signal through the same resistor over the same time period. The RMS value is calculated by squaring the instantaneous values of a sinusoidal waveform at different points, taking the average of the squared values, and then taking the square root of the average. This RMS value represents the equivalent DC voltage or current that would produce the same heating effect as the AC signal.








