More Related Content
PPT
MBA 531 Week 1 Overview (Chapters 1 - 4) PPTX
PPT
PPT
IPPTChap001.international business slide PPT
Slides_01.ppt Globalization by Charles W. Hill PPTX
GE-5.-Lesson-2.-Structures-of-Globalization.pptx PPTX
International Business P1.pptx PPTX
Globalization-Chapter 1 :Charles W.L. Hill Similar to Rise of Globalization...................
PPT
Chap01 Globalization and its impacts in international business PPT
PPT
Globalization ( Chapter no. 1) PPTX
LESSON-1-IBAT-globalization and 5 emergence PPTX
GEC3-Contemporary World.pptx PPTX
GLOBAL-ECONOMY-CONTEMPORARY-GLOBALIZATION.pptx PPTX
CW_MODULE4.pptx globalization globalization PPTX
PPT
Chapter_1 IBM_wut.ppt presentation undergrade PPTX
PPTX
GLOBALIZATION AND ITS DISCONTENTS.pptx PPTX
LESSON 2 STRUCTURES OF GLOBALIZATION.pptx PPTX
Globalization by Islam El-Shafie PPT
PPT
PPT
PDF
Enhancing the Development Effectiveness of the Post-2015 Global Partnership f... PPTX
Chapter_1.Interntationsl_Business_Chapter1 PPT
PDF
Interrogating-Globalization in the Contemporary World Recently uploaded
PPT
Banking theory law & Practice Unit II.ppt DOCX
16 Best Sites To Buy Google Ads Accounts (Aged &.docx PDF
Maritime Routes and Trade in Ancient India India–Sri Lanka Exchanges in the I... PDF
How to Securely Purchase Verified PayPal Accounts in 2026 PPTX
Forks in the curve: whether and how to respond to monetary policy divergence PPTX
Size and Efficiency of Market in Industrial Economics.pptx PDF
2026-01-26 Valkea Presentation_FINAL DRAFT.pdf DOCX
SQHWYD Market Analysis: Crypto & Commodity Liquidity Cycles PDF
How to Secure a Verified Square Account: A Detailed Guide PDF
Beinsure Media Kit 2026 - advertising in B2B digital media platform focused o... DOCX
Sustainable Alpha Can ESG Portfolios Outperform Conventional Portfolios in Em... PDF
Geography Presentation about Economic activities of Ethiopia PDF
Where to Find Reliable Cash App Business Accounts Online in 2026 PDF
Ukraine Has Significant Untapped Trade Potential Within the Pan-Euro-Mediterr... PDF
Payeer Verification Guide for Freelancers & Online Sellers.pdf PDF
Wise Account Verification for eCommerce & Global Businesses DOCX
Case Studies and Learning Examples in Digital Banking Verification PDF
Economic Development Investment Program Investing in Growth.pdf PDF
Pre-Budget 2026 Expectations: Key Sectors to Benefit and Insights on India's ... DOCX
Why Verified Bybit Accounts Are a Smart Investment Choice.docx Rise of Globalization...................
- 1.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as
permitted in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
Chapter 1
The Rise of Globalization
Introduction to Global Business
- 2.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
1. Explain the characteristics of globalization and describe
how it functions.
2. Identify how major international institutions facilitate
globalization.
3. Evaluate the need for strong and transparent institutions
that can adapt to global competition.
4. Describe the key policy measures that make
globalization sustainable.
After studying this chapter, you should be able to:
- 3.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
5. Describe the role of information technology in bridging
the global digital divide.
6. Describe the validity of the anti-globalization argument.
7. Explain the case made to temporarily support those
people negatively affected by globalization.
After studying this chapter, you should be able to:
- 4.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
EXHIBIT 1.1 IMPACT OF THE GLOBAL CREDIT CRISIS
- 5.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
What Is Globalization?
• Globalization is the socioeconomic reform process of
eliminating trade, investment, cultural, information
technology, and political barriers across countries.
• It can lead to increased economic growth and geopolitical
integration and interdependence among nations of the
world.
• It is no longer simply another word for “Westernization” or
“Americanization.”
- 6.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
Emerging Economies
• Emerging economies
– Are implementing more open trade and free-market policies to
“compete with everyone from everywhere for everything”
– Are becoming the world’s center of economic gravity through
innovation, research, and development
• BRIC economies
– Brazil, Russia, India, and China
- 7.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
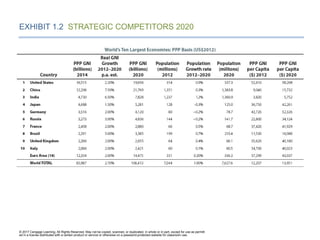
EXHIBIT 1.2 STRATEGIC COMPETITORS 2020
- 8.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
• Decoupling
– A global shift in which
industrialized country-
dependent developing
economies grow based on
their own underlying
economic strengths rather
than those of highly-
developed countries
• Multipolar world
– A world economy in which
the engines of growth are
comprised of both
industrialized (e.g., the
United States) and emerging
market economies (e.g.,
BRIC countries)
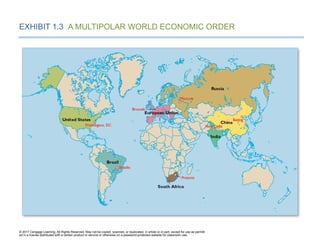
Decoupling and the Move to a Multipolar World
Economic Order
- 9.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
EXHIBIT 1.3 A MULTIPOLAR WORLD ECONOMIC ORDER
- 10.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
Key International Institutions That
Facilitate Globalization
• The International Monetary Fund (IMF)
• The World Bank
• The World Trade Organization (WTO)
- 11.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
The International Monetary Fund
• International Monetary Fund’s role in global financial
stability:
– Provides a forum for cooperation on international monetary
problems
– Facilitates international trade that promotes job creation, economic
growth, and poverty reduction
– Promotes exchange rate stability and an open system of
international payments
– Lends countries foreign exchange to help address balance of
payment problems
- 12.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
The World Bank
• World Bank’s initial role was to aid the reconstruction of
Europe after World War II.
• Current focus areas:
– Global integration through trade liberalization
– Analysis and national trading policy advice
– Agreements supporting international standards in financial
systems
– Information and knowledge transfer to developing countries to
support sustainable development
– Eradicating communicable diseases
- 13.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
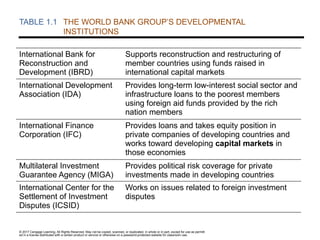
TABLE 1.1 THE WORLD BANK GROUP’S DEVELOPMENTAL
INSTITUTIONS
International Bank for
Reconstruction and
Development (IBRD)
Supports reconstruction and restructuring of
member countries using funds raised in
international capital markets
International Development
Association (IDA)
Provides long-term low-interest social sector and
infrastructure loans to the poorest members
using foreign aid funds provided by the rich
nation members
International Finance
Corporation (IFC)
Provides loans and takes equity position in
private companies of developing countries and
works toward developing capital markets in
those economies
Multilateral Investment
Guarantee Agency (MIGA)
Provides political risk coverage for private
investments made in developing countries
International Center for the
Settlement of Investment
Disputes (ICSID)
Works on issues related to foreign investment
disputes
- 14.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
The World Trade Organization
• The WTO began trading in 1948 under the General
Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT).
– Liberalized trade by lowering and/or removing trade barriers such
as tariffs, quotas, and subsidies
• WTO promotes global trade by:
– Administering trade agreements
– Acting as a forum for trade negotiations
– Settling trade disputes
– Reviewing national trade policies
– Providing developing countries with technical assistance and
training programs
– Cooperating with the IMF and the World Bank
- 15.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
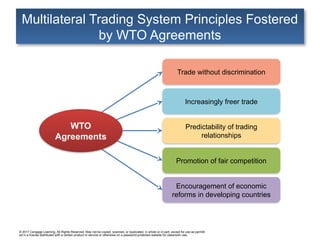
Multilateral Trading System Principles Fostered
by WTO Agreements
Trade without discrimination
Increasingly freer trade
Promotion of fair competition
Encouragement of economic
reforms in developing countries
WTO
Agreements
Predictability of trading
relationships
- 16.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
Institutional Structure and
Its Impact on Globalization
• What is institutional structure?
– Institutions are the rules, enforcement mechanisms, and
organizations that support market transactions.
• Impact of globalization:
– Demand for transparency, openness, and disclosure from political
institutions
– Need for adaptive institutions that provide societal stability and
incentives for private investment
– Increasing expectations of accountability and responsibility for
those who govern
– Importance of independent judiciary and free press
- 17.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
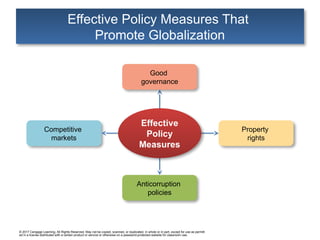
Effective Policy Measures That
Promote Globalization
Good
governance
Competitive
markets
Anticorruption
policies
Effective
Policy
Measures
Property
rights
- 18.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
Impact of Information Technology
on Globalization
The Digital
Generation
Expanding the
Global Use of
Information
Technology
The Digital
Divide Myth
“Leapfrogging”
into the
Internet and
Cell Phone
Era
- 19.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
The Globalization Controversy
• Arguments against globalization:
– Job losses and income stagnation
– Loss of local control over economic policies and developments
– Disappearance of old industries
– Related erosion of communities
- 20.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
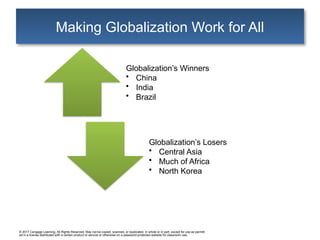
Making Globalization Work for All
Globalization’s Winners
• China
• India
• Brazil
Globalization’s Losers
• Central Asia
• Much of Africa
• North Korea
- 21.
© 2017 CengageLearning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part, except for use as permitt
ed in a license distributed with a certain product or service or otherwise on a password-protected website for classroom use.
globalization
emerging economies
decoupling
multipolar world
international monetary
system
economic reforms
capital markets
liberalization of the trading
system
institutions
adaptive institutions
accountability
transparency
antitrust laws
digital era
bandwidth
the web
digital divide
sustainable development
Key Terms