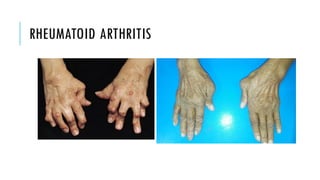
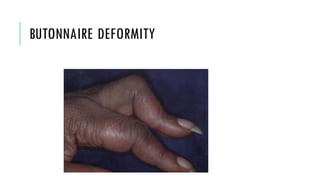
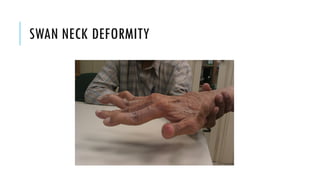
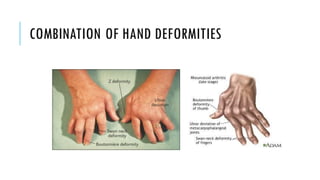
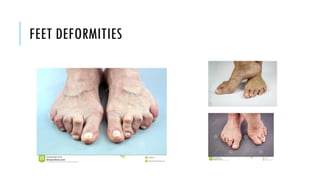
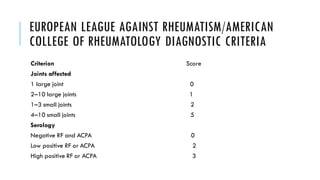
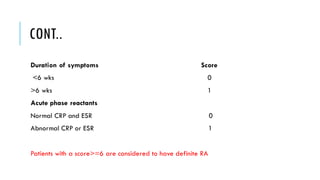
The document provides an overview of the musculoskeletal system, detailing the types of bones, their cell types, and the various joint categories. It introduces rheumatoid arthritis (RA) as a common autoimmune inflammatory condition, discussing its prevalence, clinical features, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment options, including DMARDs and biologics. RA's impact on quality of life and associated comorbidities, such as increased mortality, are highlighted, along with prognostic factors influencing disease progression.