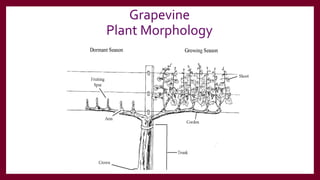
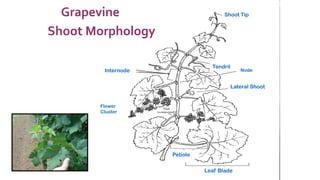
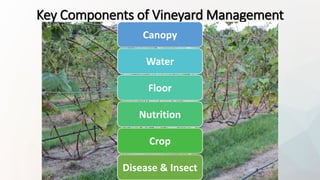
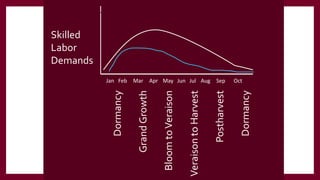
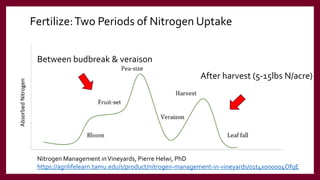
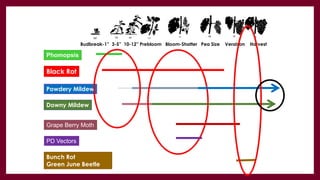
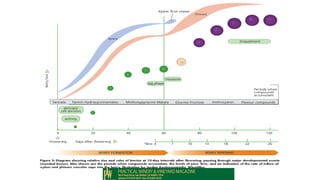
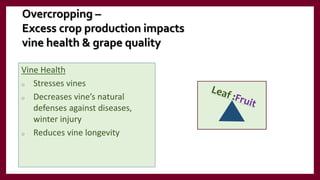
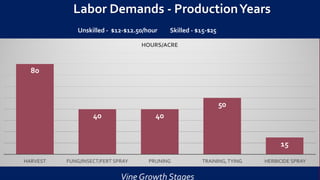
This document provides information and guidance for starting a vineyard in the Rio Grande Valley region. It discusses vineyard establishment, including site selection criteria, planting considerations, trellis system installation, and labor needs. Key vineyard management practices like canopy management, disease and pest control, irrigation, and pruning are covered. The document outlines the multi-year vineyard development process and seasonal labor demands. Maintaining vineyard uniformity, balanced vine growth, and quality fruit are emphasized as important for success.