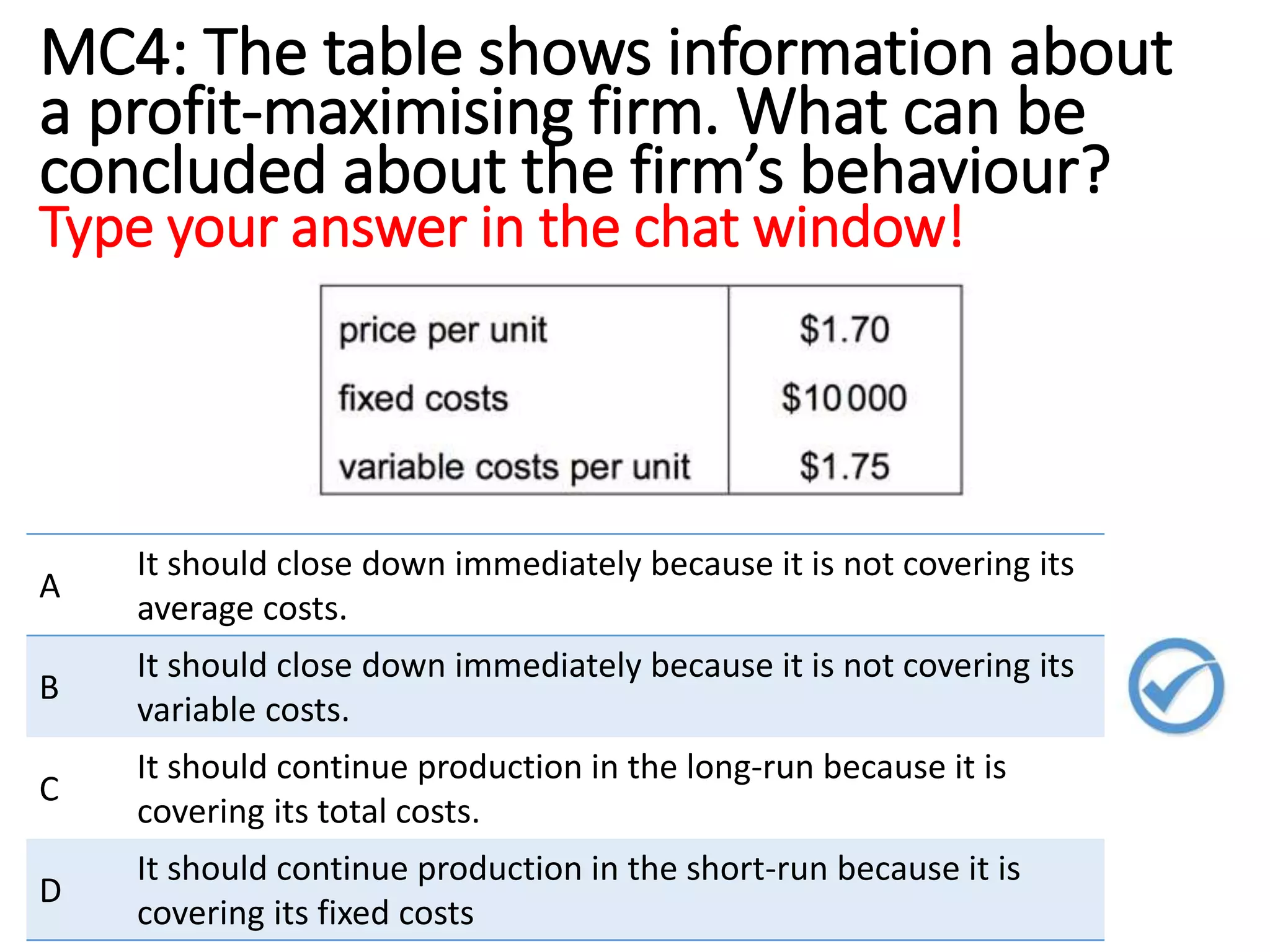
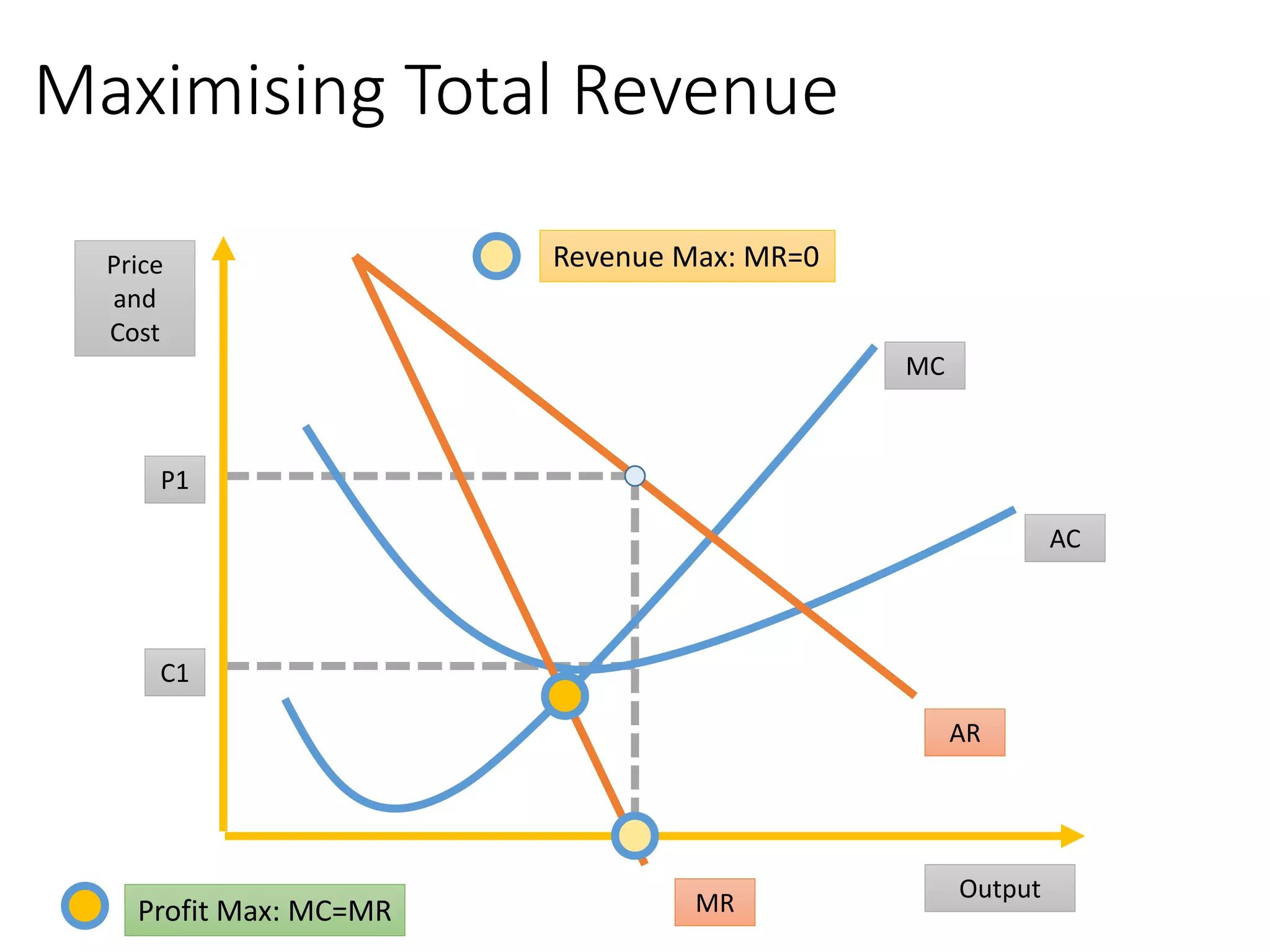
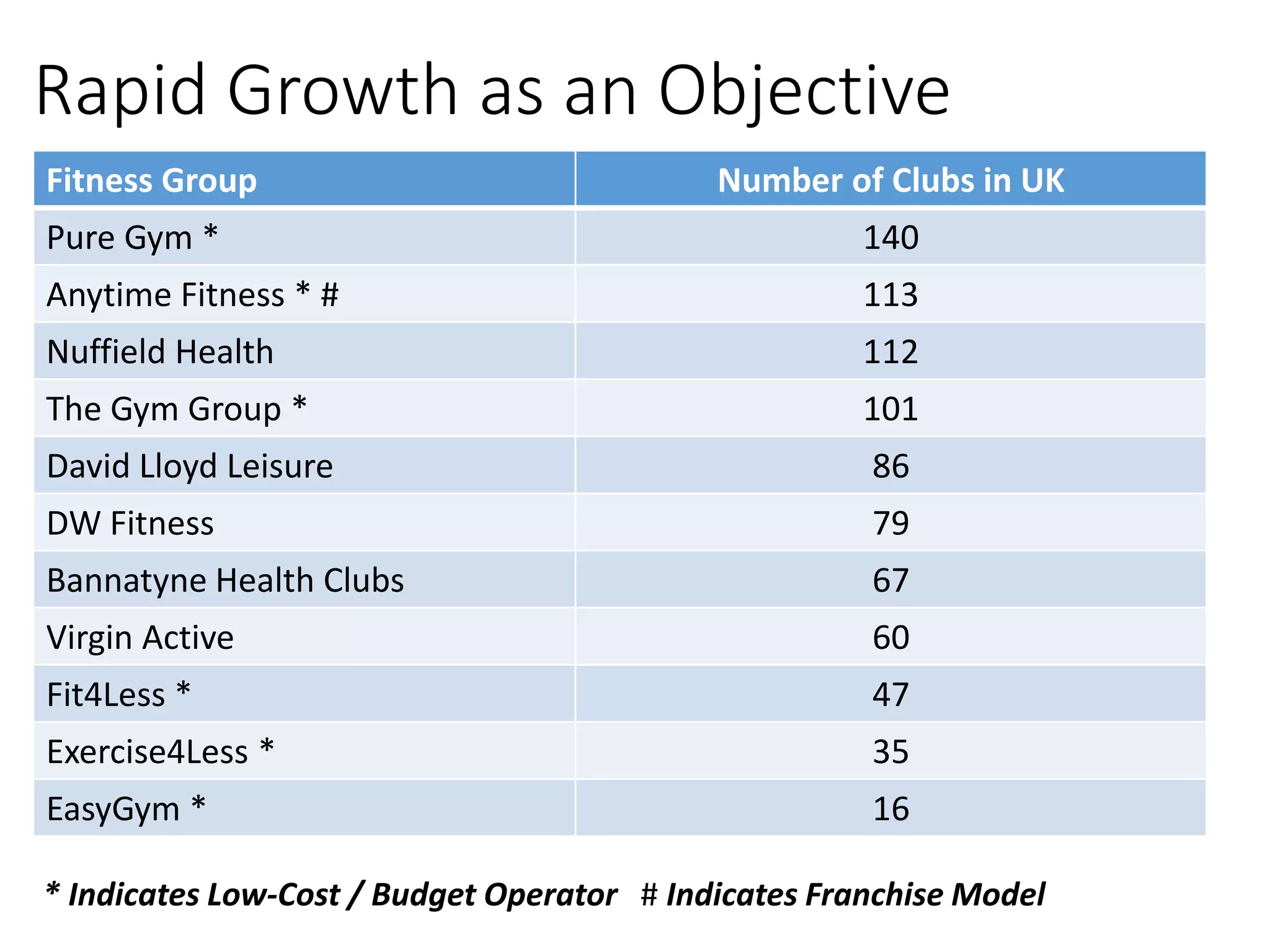
The document discusses different business objectives that firms may have beyond pure profit maximization, including revenue or sales maximization, business growth, and survival. Objectives can vary depending on factors like firm size, ownership structure, and whether the firm is a social enterprise or state-owned. Maximizing profit involves producing where marginal cost equals marginal revenue, while revenue is maximized where marginal revenue is zero. Some firms may simply aim to satisfy minimum profitability levels through a "satisficing" approach rather than precisely maximizing objectives.