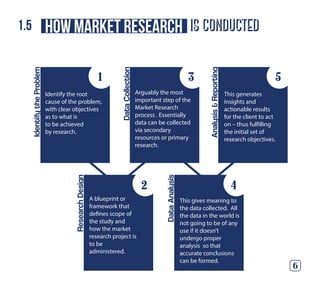
This document provides an overview of market research, including definitions, types, methods, and purposes. It begins with an introduction to market research, defining it as the systematic collection and analysis of information about individuals or organizations. Sections then discuss the role of market research in marketing decision making, who uses market research, and why it is conducted. The document outlines common types of qualitative and quantitative market research, such as focus groups, surveys, and social media research. It also explores specific methods like mystery shopping and sampling.