In today’s digital world, Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are crucial for software to communicate smoothly. With more and more RESTful APIs being used, it’s vital for testers to ensure they work reliably.
Rest Assured, a Java library simplifies this process. It offers a specific language for writing clear and thorough tests. Rest Assured helps Java developers create strong test suites for checking API functionality, performance, and security. Its easy syntax speeds up testing, ensuring high-quality software.
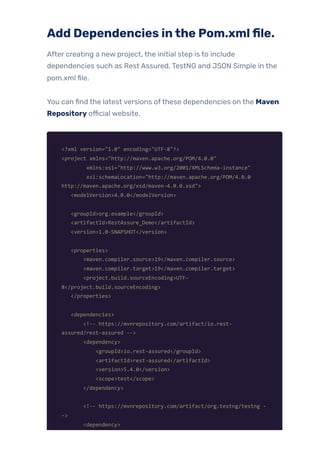
In this blog post, we’ll explore the significance of Rest Assured, explaining why it’s essential for both developers and testers. Additionally, we’ll offer a detailed guide on setting up a Maven project and provide a practical overview of its primary endpoints like GET and POST requests.