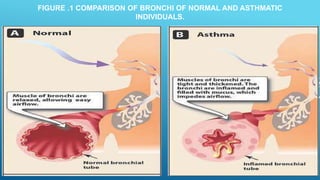
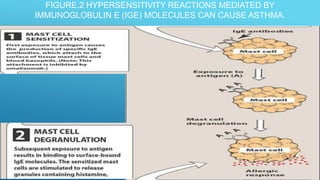
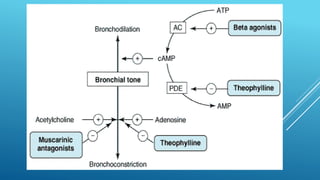
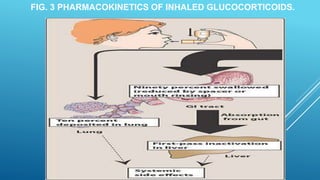
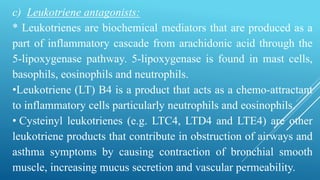
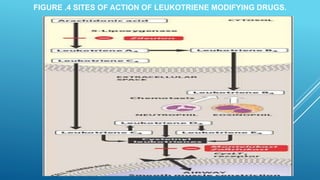
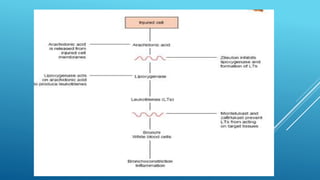
Bronchial asthma is a chronic inflammatory airway disease characterized by wheezing, breathlessness, and coughing. Allergens like dust or pollen can trigger an immune response releasing inflammatory mediators from mast cells that cause bronchospasm and obstruction. Asthma treatments include short-acting beta-2 agonists for acute symptoms, inhaled corticosteroids as primary treatment to reduce inflammation, and other drugs that dilate airways or block inflammatory pathways like leukotriene receptors. Managing asthma requires identifying and avoiding triggers while maintaining treatment to prevent symptoms and exacerbations.



























![Treatment of acute exacerbations of bronchial asthma:
# Mild acute attack: (dyspnea only with activity, peak expiratory
flow rate [PEF] > 70%), give inhaled short acting β2 agonist
alone which may need to be continued every 3-4 hours for one to
two days. If patient already taking inhaled corticosteroids, a 7-
day course of oral corticosteroids may be necessary.
# Moderate acute attack: (dyspnea interferes with usual activities,
PFF 40-69%), give inhaled short acting β2 agonist continuously
plus early administration of systemic corticosteroids.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/respiratory-tebfinal2-240225213616-609c872f/85/Respiratory-pharmacology-final-2-pptx-35-320.jpg)



