Drugs Used in Asthma and COPD
Subject: Pharmacology Word Count Target: ~3001 words Target Audience: 2nd Prof MBBS peers
🔷 Outline
Introduction
Overview of Asthma and COPD
Pathophysiological Differences
Drug Classifications
Bronchodilators
Anti-inflammatory agents
Combination therapies
Mucolytics and adjuncts
Drugs Used in Asthma (Stepwise approach)
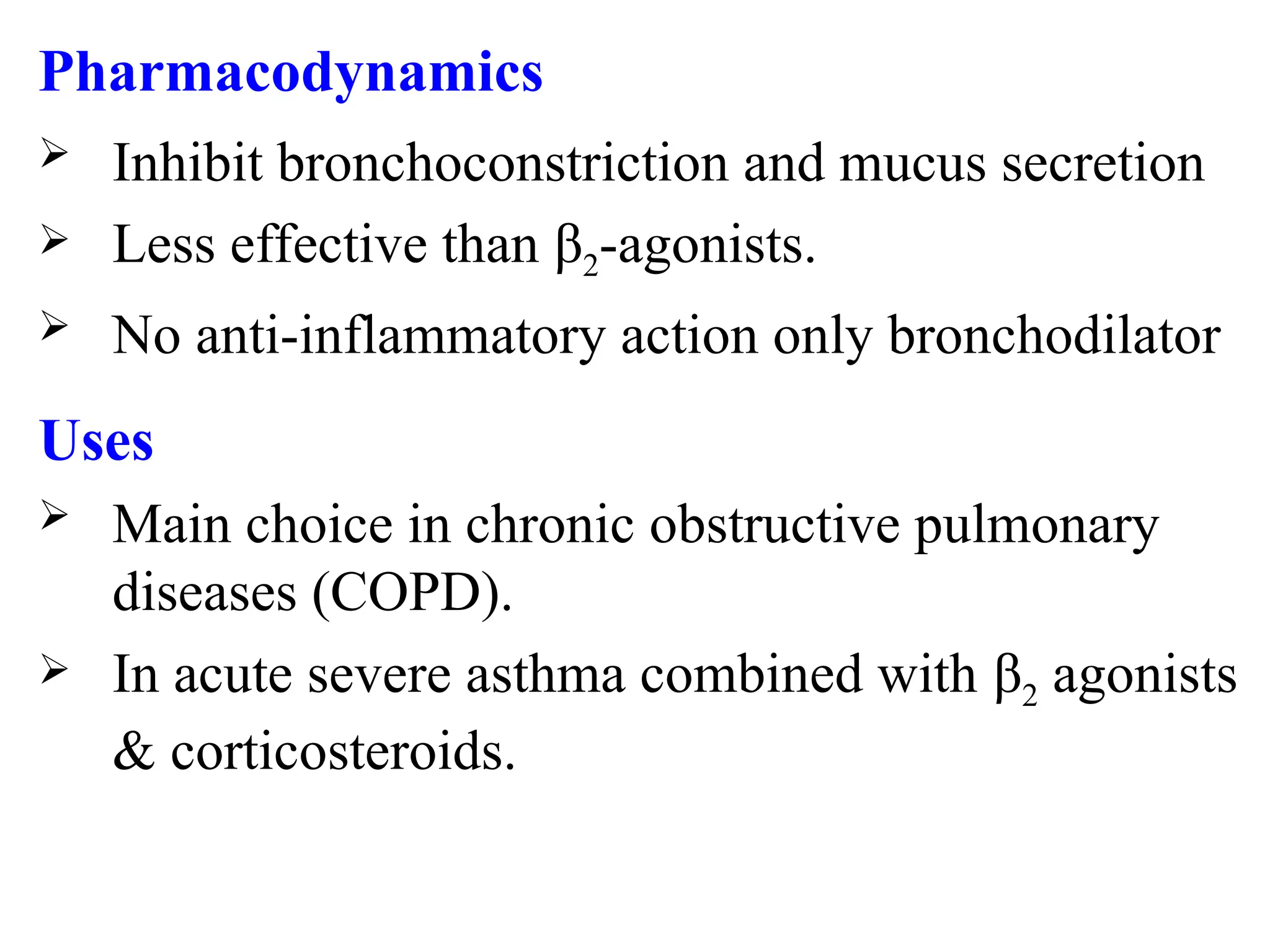
Drugs Used in COPD (GOLD guidelines)
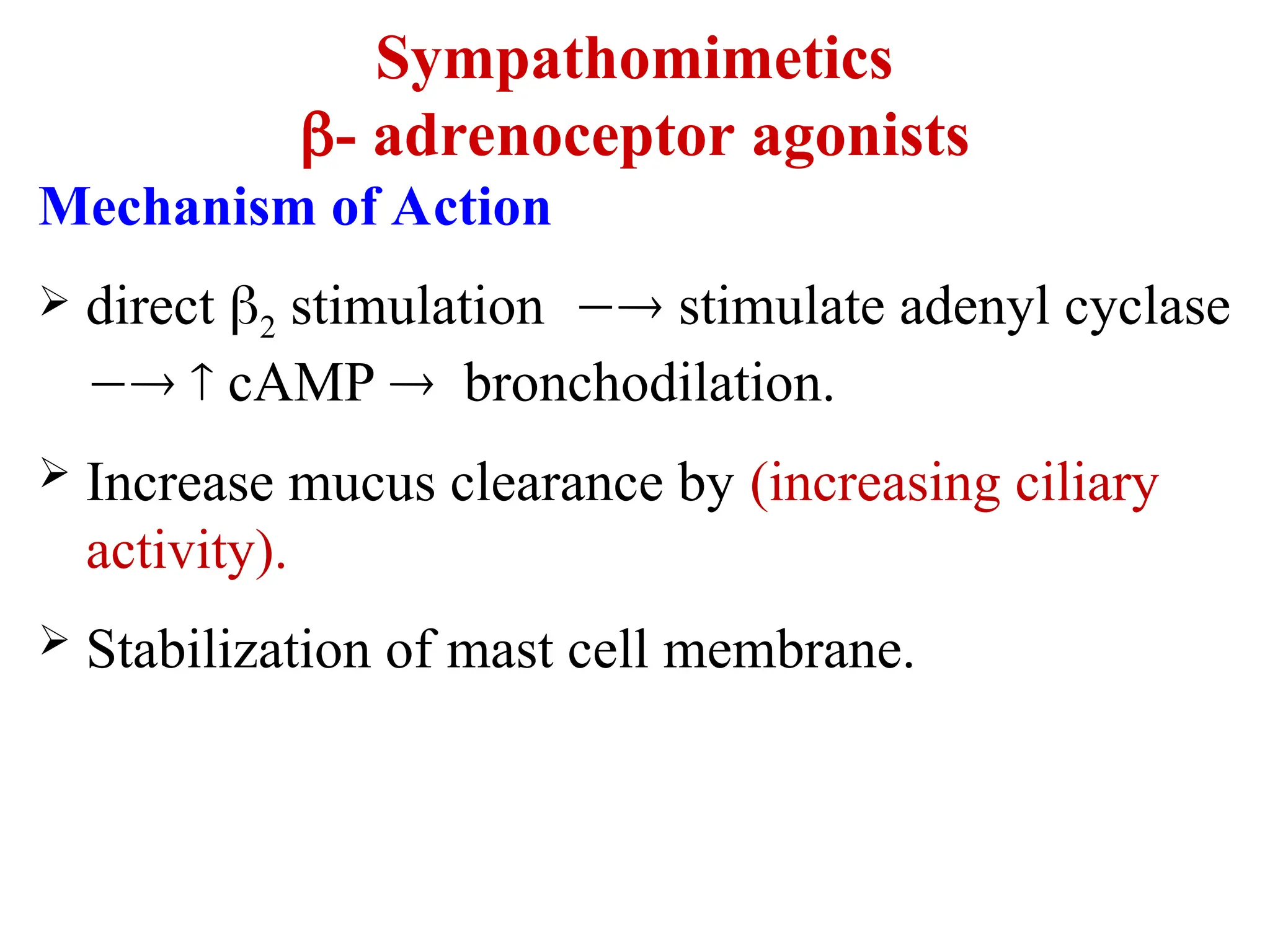
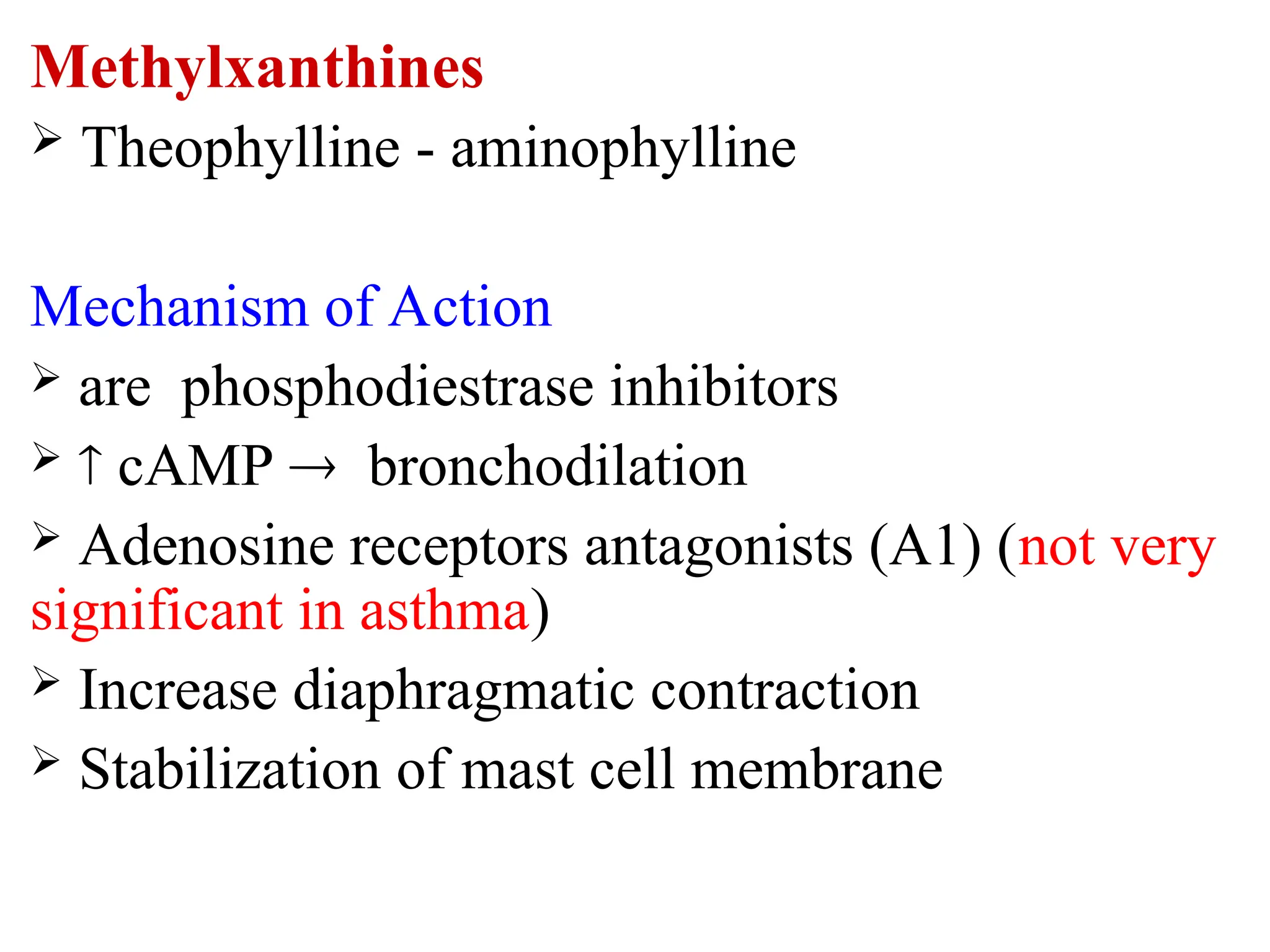
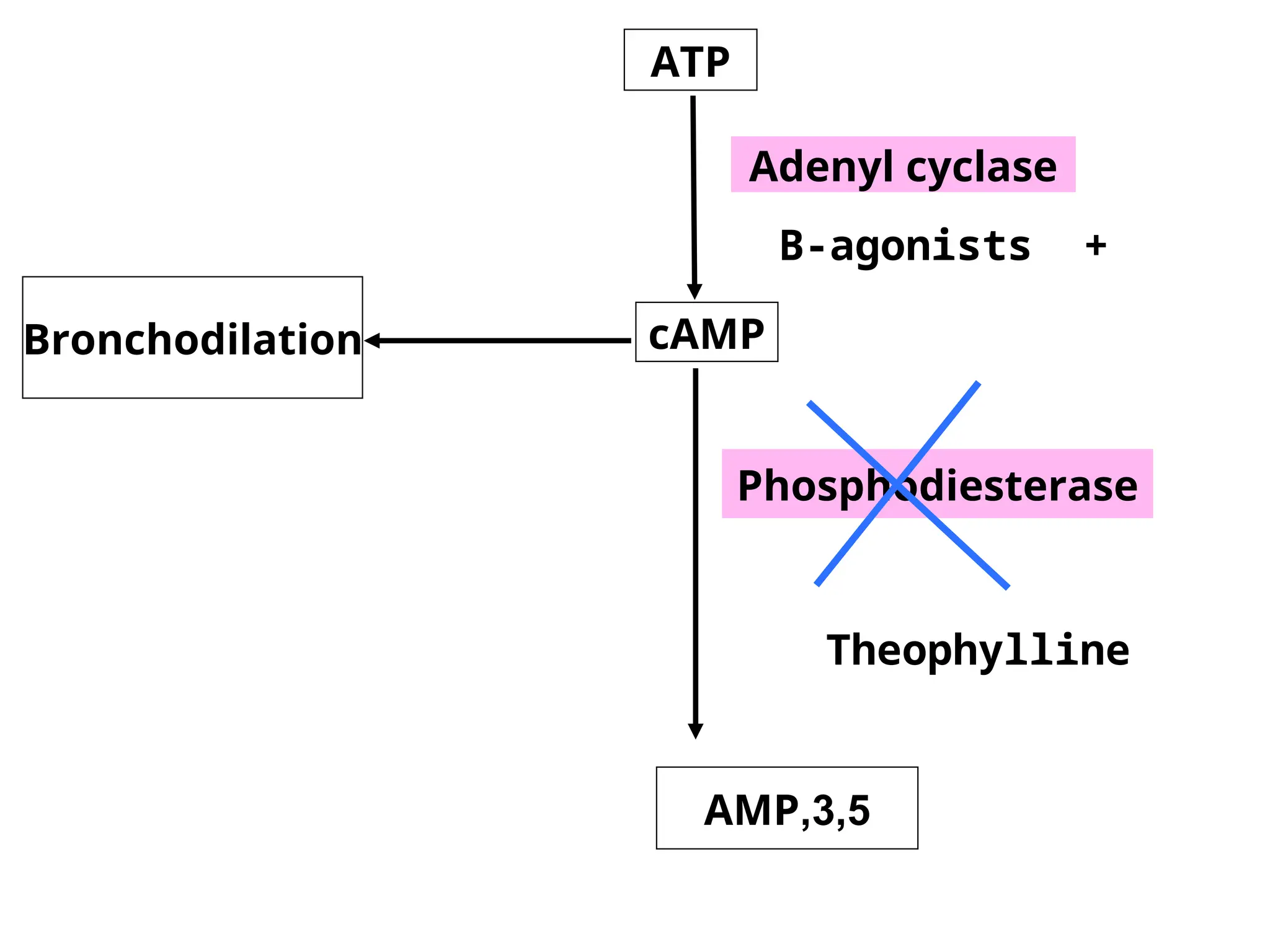
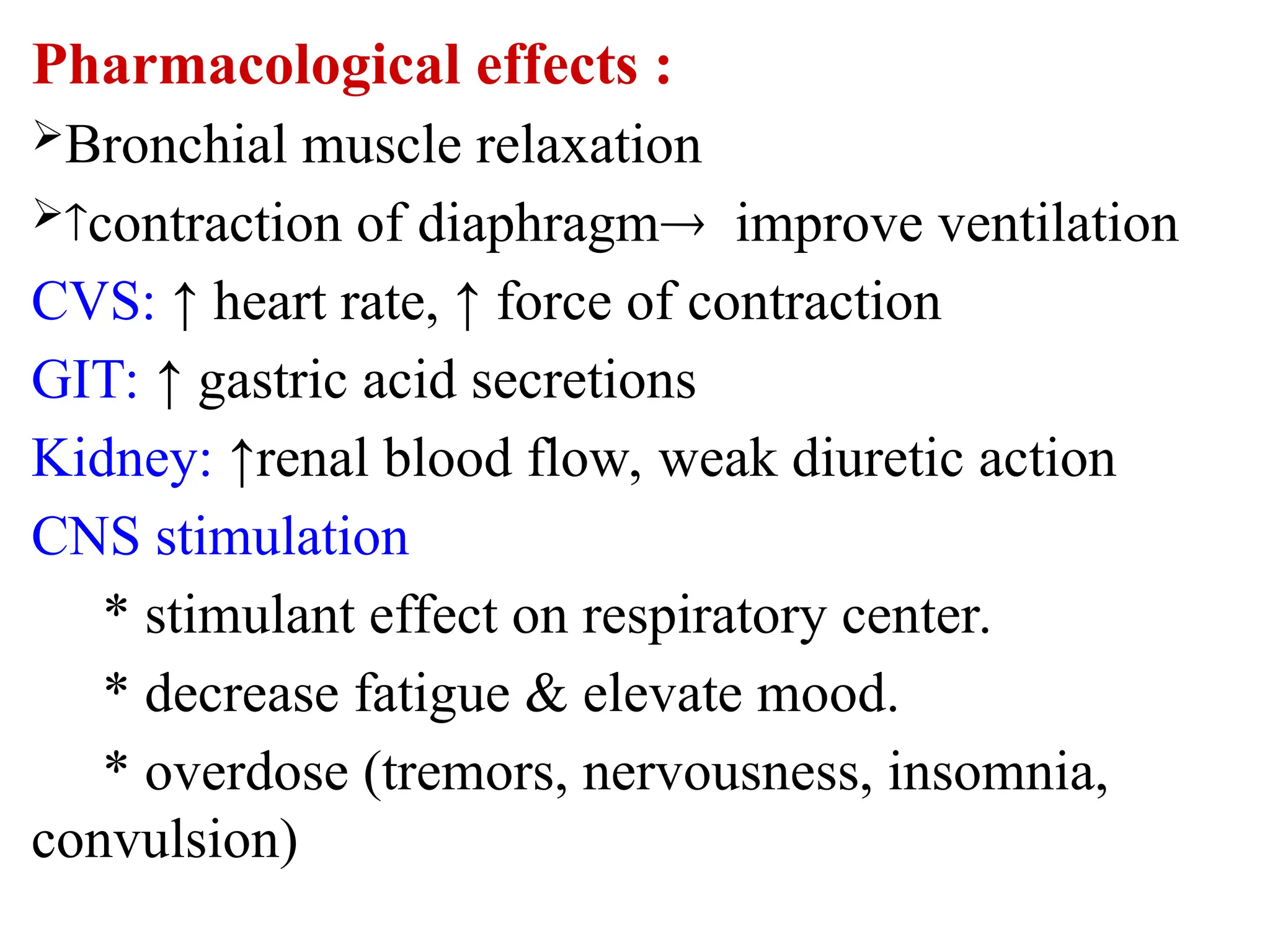
Mechanisms of Action
Comparative Pharmacology
Recent Advances
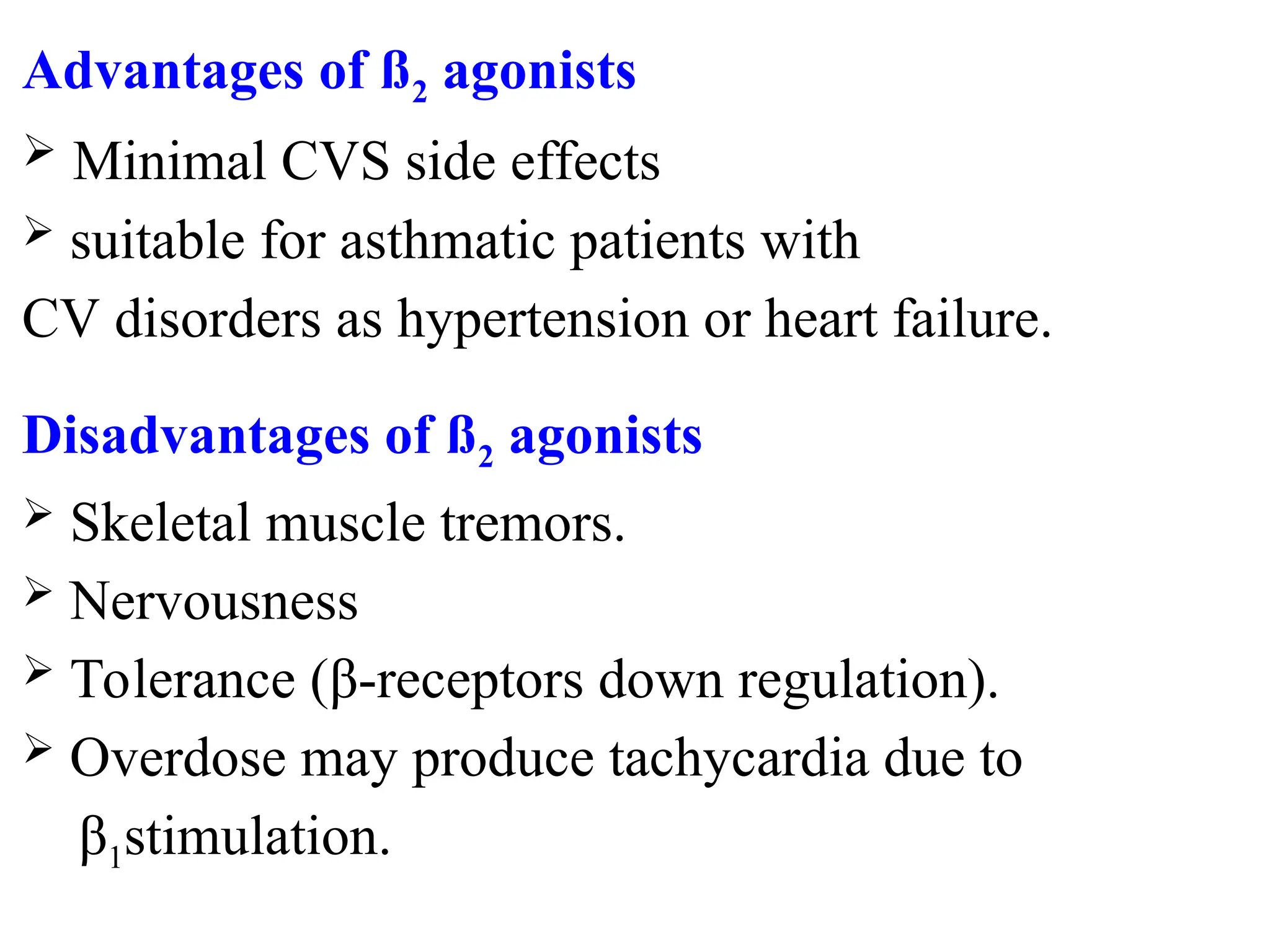
Adverse Effects and Contraindications
Conclusion
🔹 1. Introduction
Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are prevalent respiratory disorders marked by airflow limitation and chronic inflammation—but they differ in etiology, reversibility, and treatment response. Pharmacological management aims to relieve symptoms, improve quality of life, and minimize exacerbations. The drugs employed in these conditions span multiple classes, from bronchodilators to targeted biologics.
🔹 2. Overview of Asthma and COPD
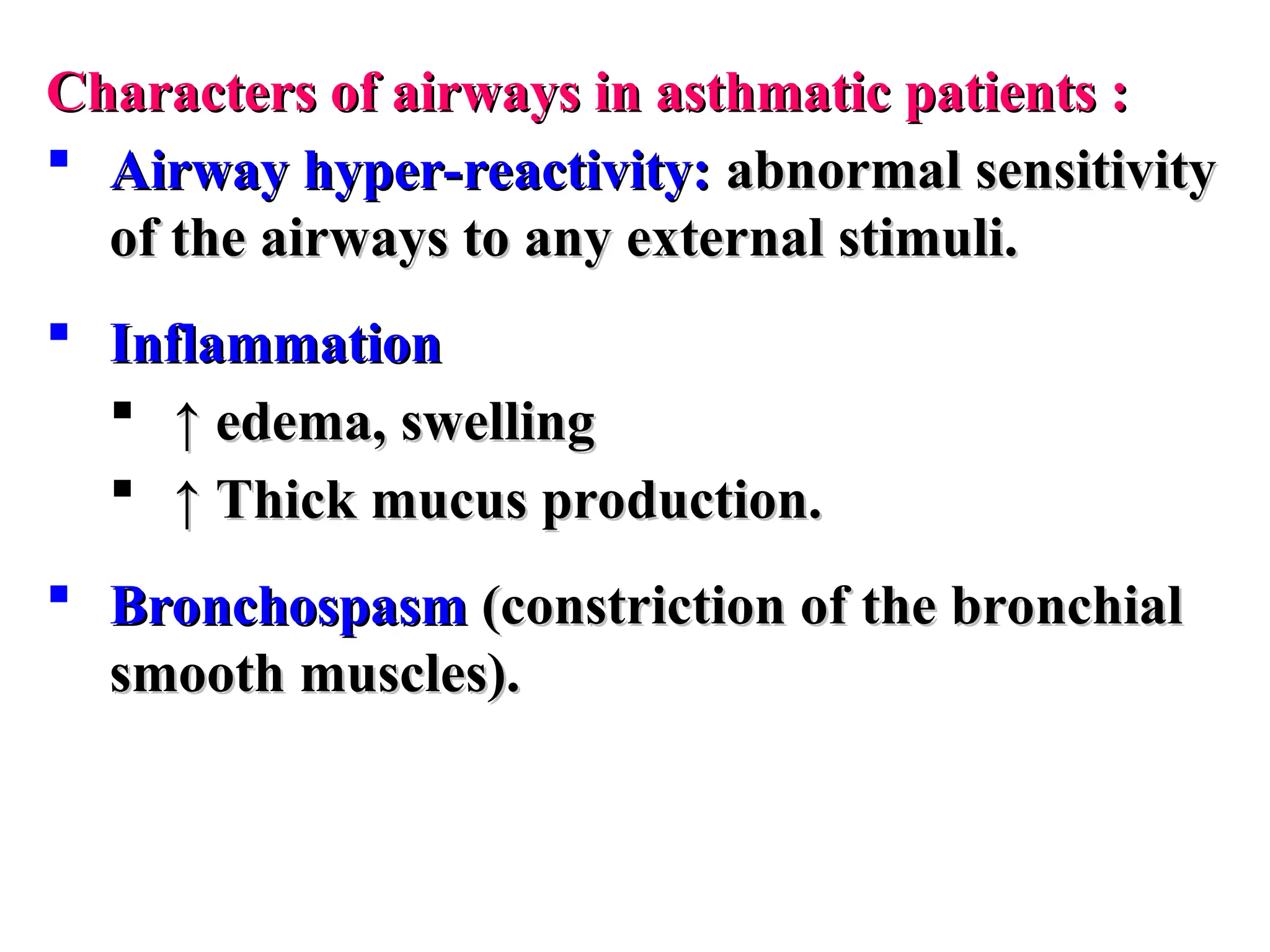
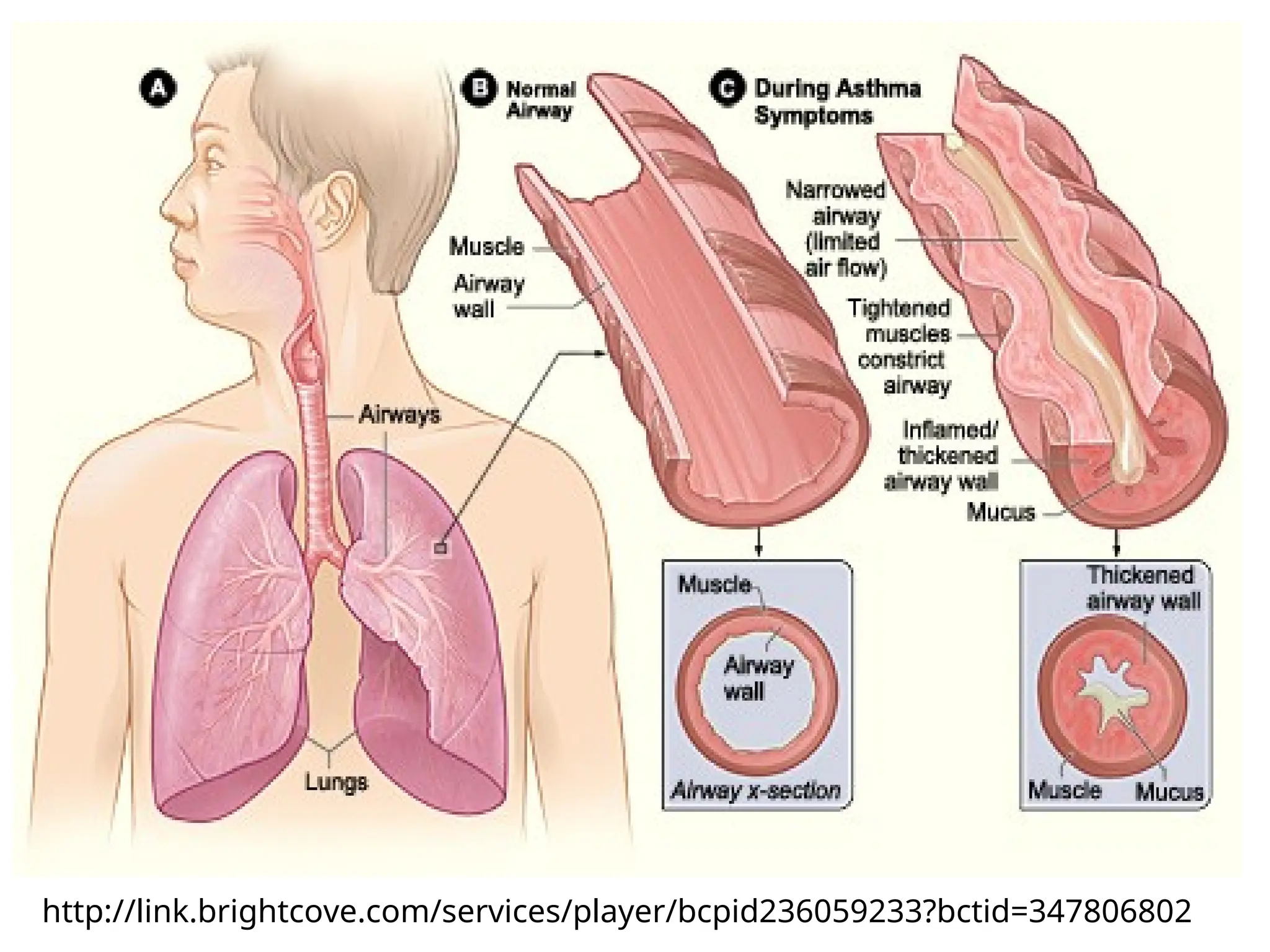
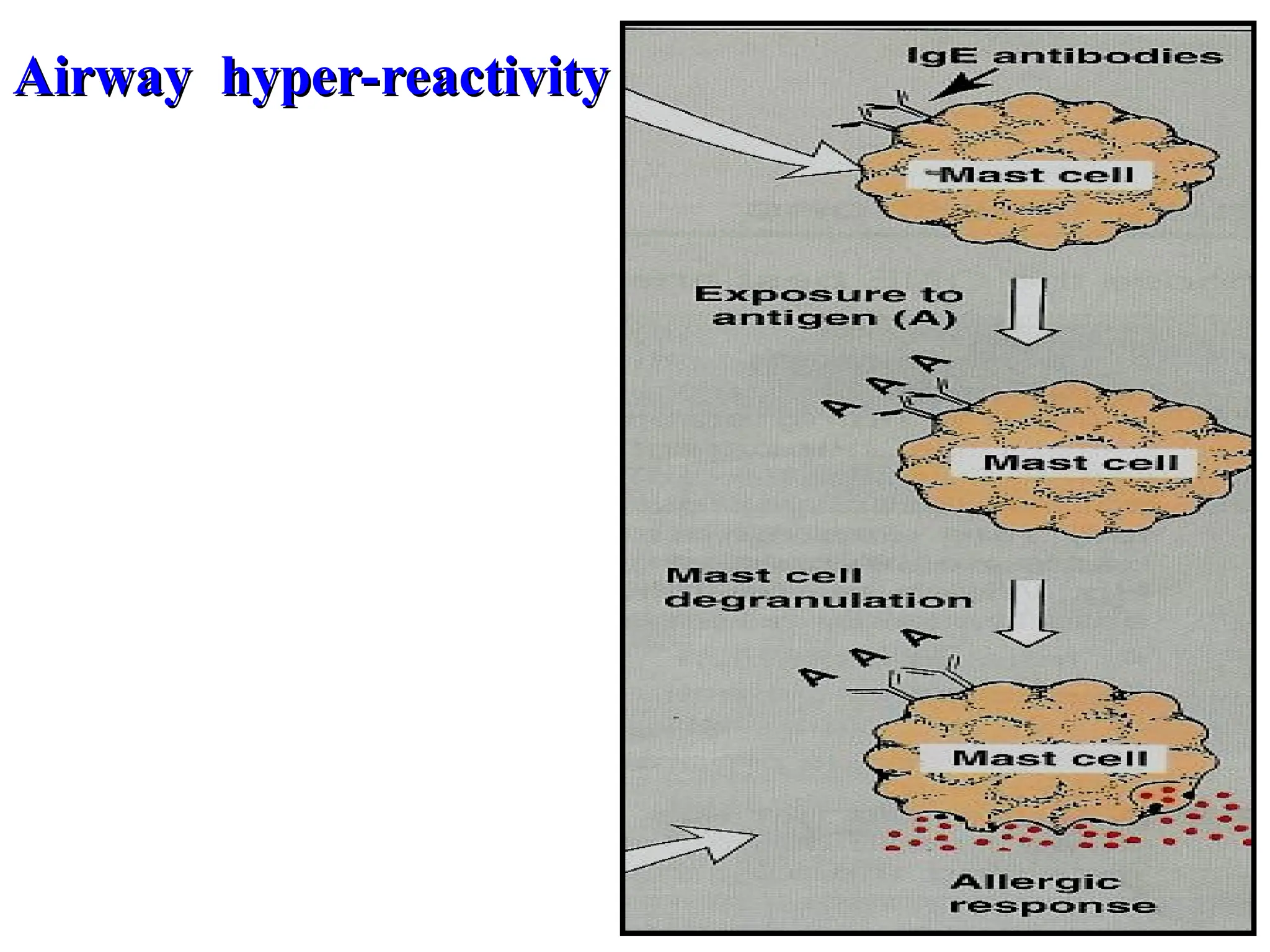
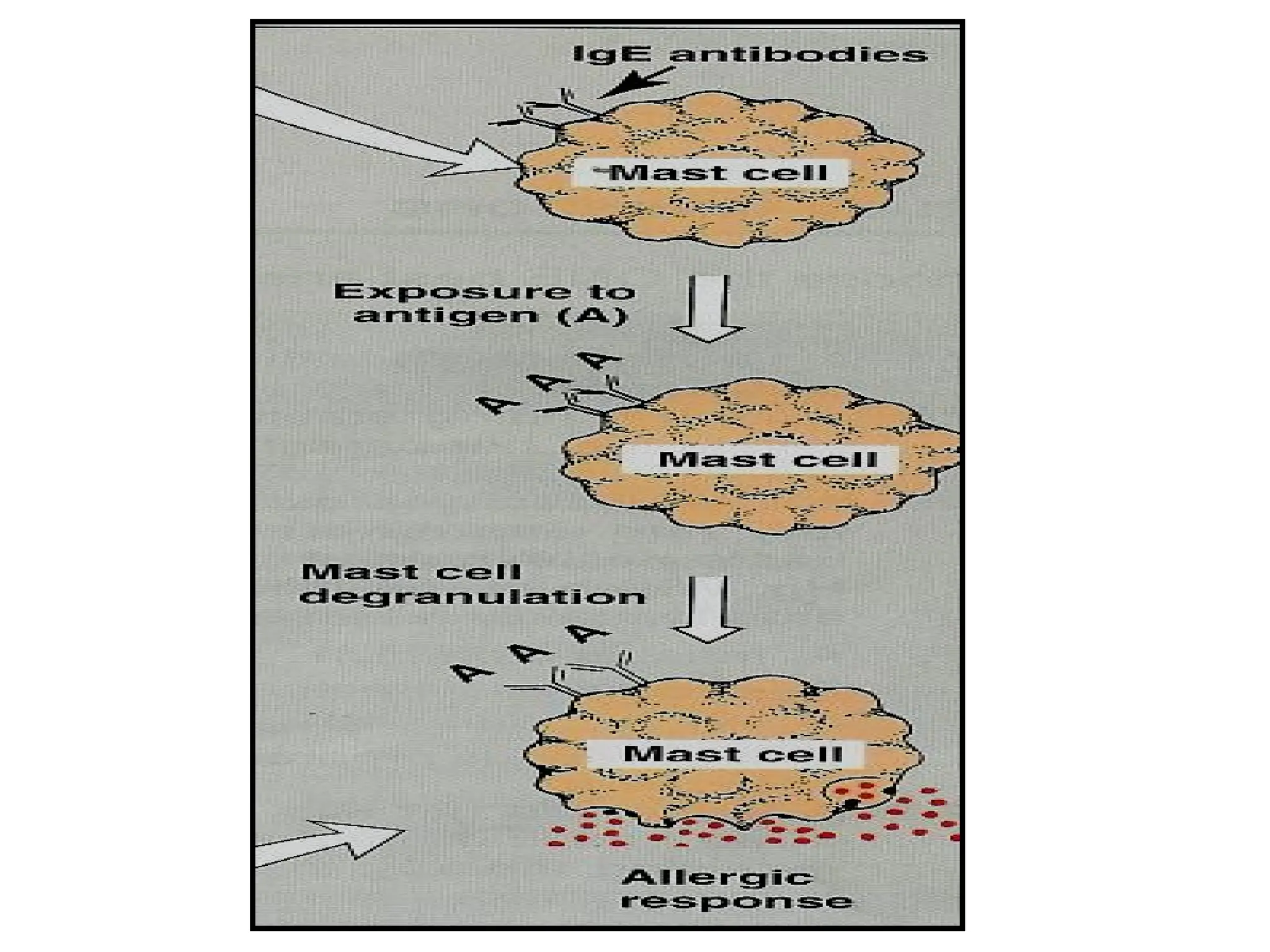
Asthma is a reversible, episodic inflammatory airway disease with hyperresponsiveness to triggers like allergens or cold air.
COPD, often caused by long-term smoking, is marked by irreversible airflow limitation due to chronic bronchitis or emphysema.
Understanding this distinction guides therapeutic strategy: anti-inflammatory control in asthma, symptom relief and exacerbation prevention in COPD.
🔹 3. Pathophysiological Differences
Feature Asthma COPD
Inflammation Eosinophilic, mast cell–dominant Neutrophilic, macrophages
Reversibility Fully reversible Partially or non-reversible
Onset Early life Midlife/later
Structural changes Airway remodeling Alveolar destruction
🔹 4. Drug Classifications
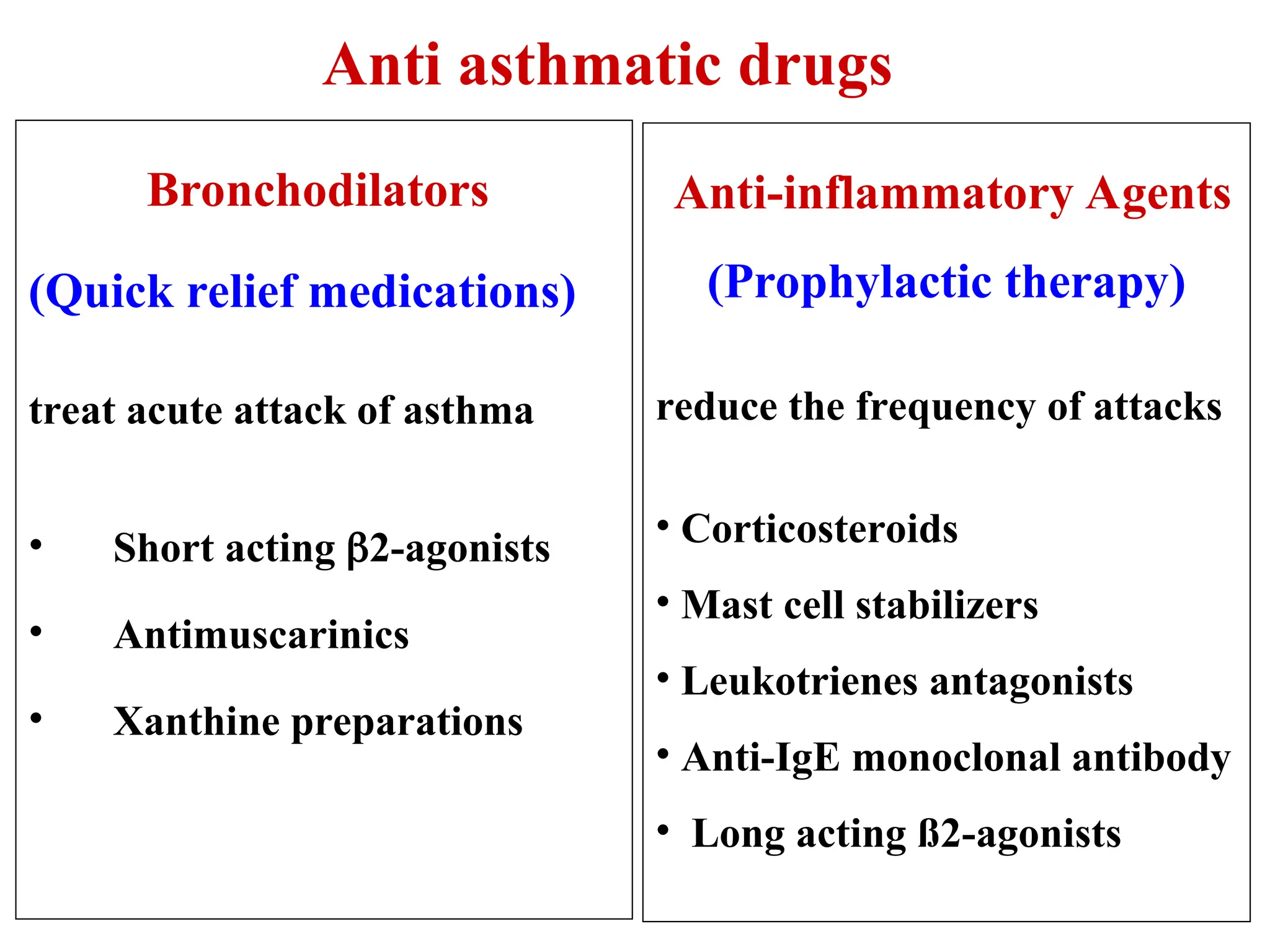
A. Bronchodilators
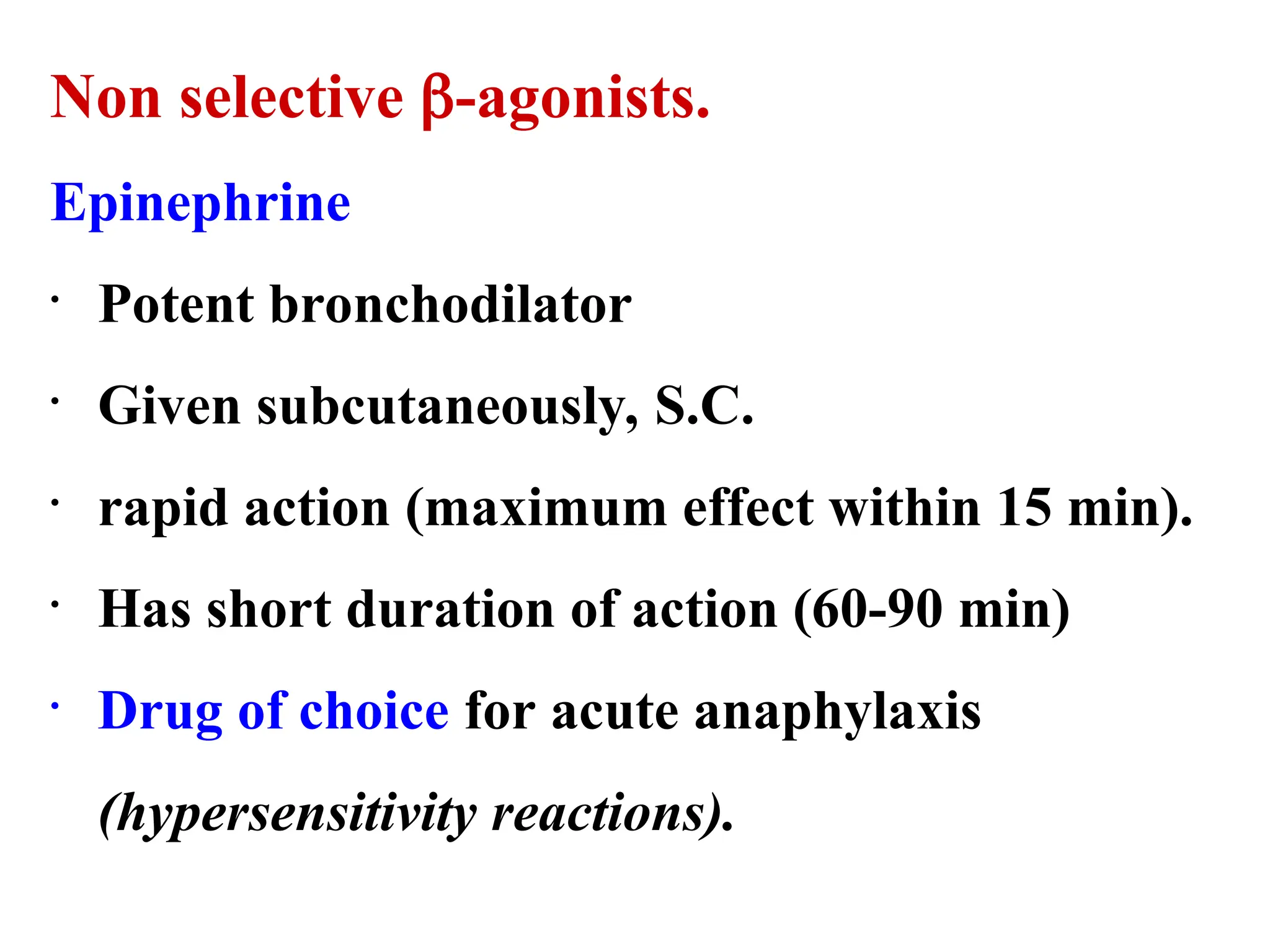
β2-Agonists:
Short-acting (SABA): Salbutamol
Long-acting (LABA): Salmeterol, Formoterol
Anticholinergics (Muscarinic antagonists):
Short-acting (SAMA): Ipratropium
Long-acting (LAMA): Tiotropium
Methylxanthines: Theophylline (rarely used now)
B. Anti-inflammatory Agents
Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS): Budesonide, Fluticasone
Systemic corticosteroids: Prednisolone (short courses during exacerbation)
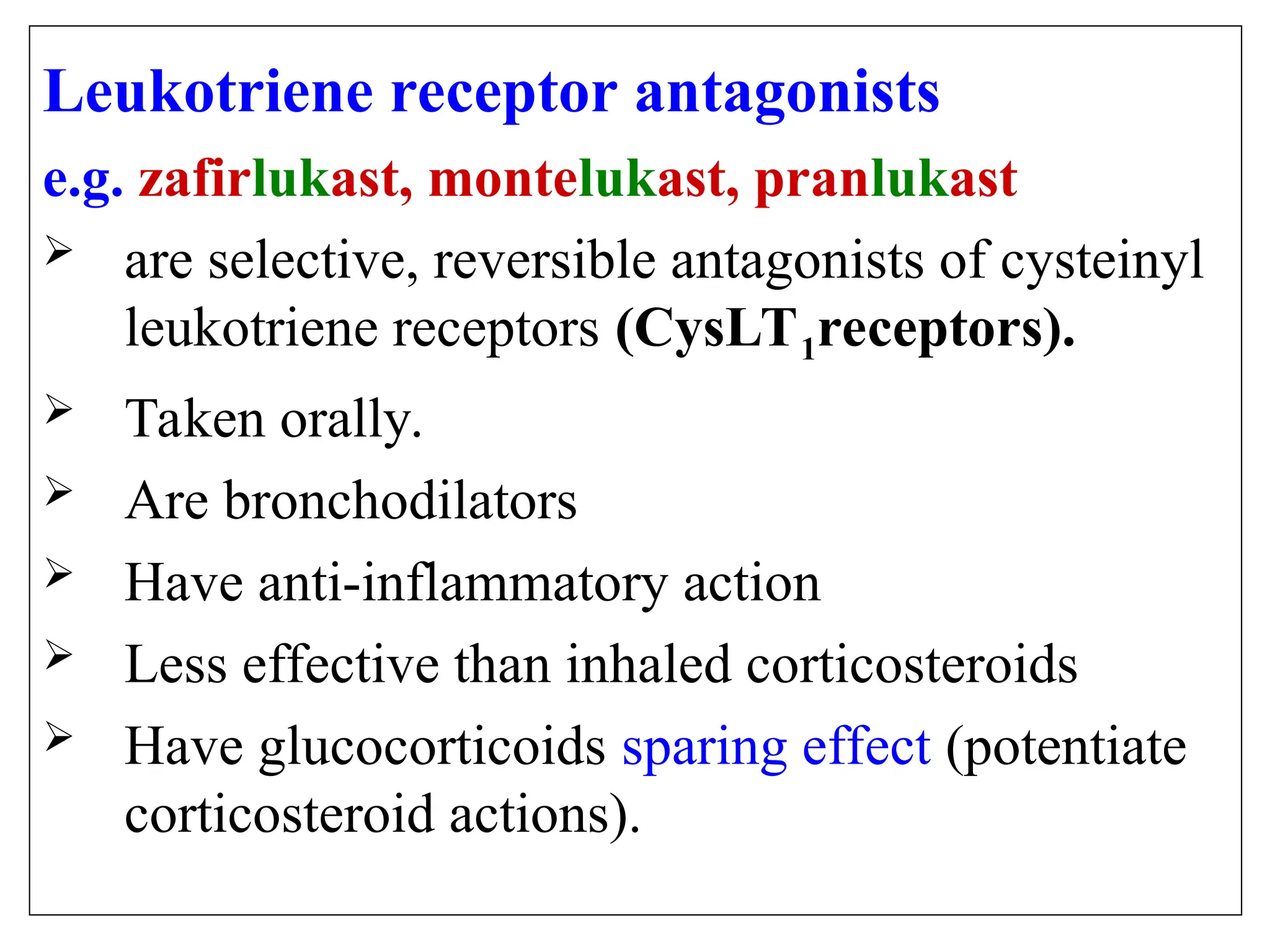
Leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs): Montelukast
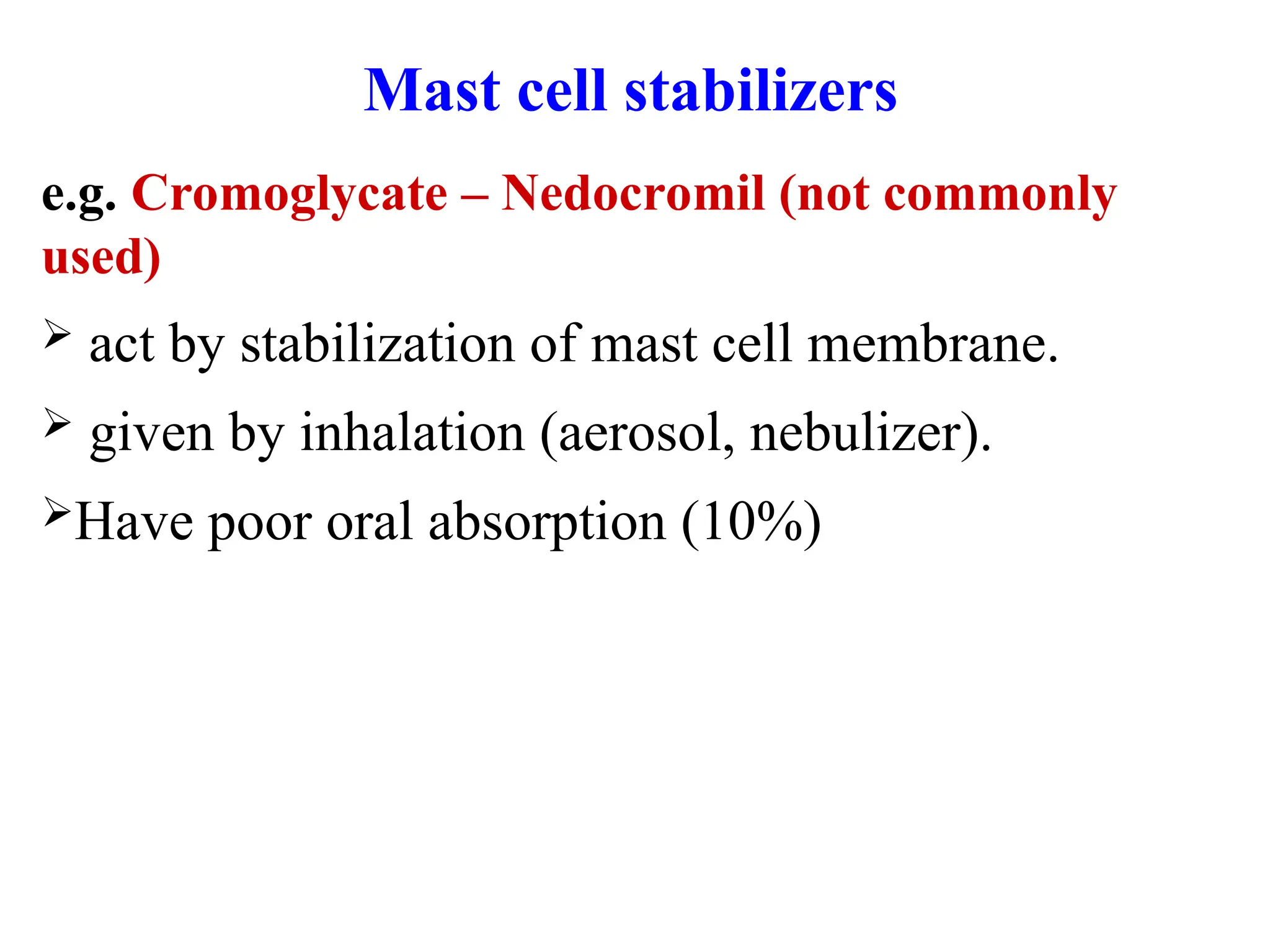
Mast cell stabilizers: Cromolyn sodium
Biologics (Asthma):
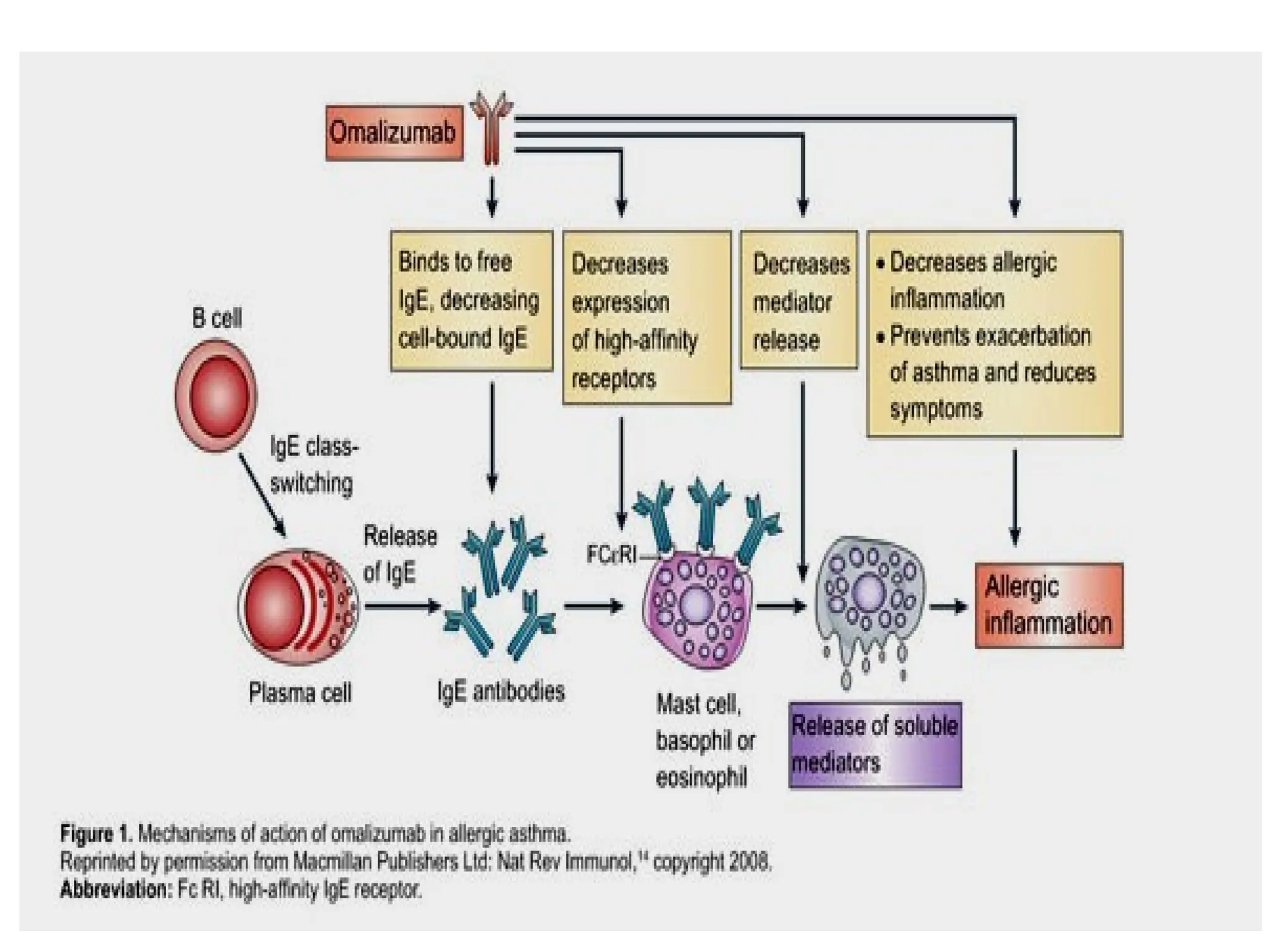
Anti-IgE: Omalizumab
Anti-IL-5: Mepolizumab, Reslizumab
Anti-IL-4Rα: Dupilumab
C. Combination Inhalers
LABA + ICS
LABA + LAMA
LABA + LAMA + ICS
D. Adjunctive Therapies
Roflumilast: PDE-4 inhibitor (in COPD)
Antibiotics: In infectious exacerbations
Mucolytics: N-acetylcysteine (especially in COPD)
🔹 5. Drugs in Asthma (GINA Guidelines Approach)
Stepwise treatment tailored to severity:
Step Treatment Notes
1 Low-dose ICS-formoterol (as needed) Preferred even in mild asthma
2 Daily low-dose ICS OR PRN ICS-formoterol Maintenance
3 Low-dose ICS-LABA Add LTRA if needed
4 Medium-dose ICS-LABA Consider referral
5 High-dose ICS-LABA + biologics Omalizumab, Mepolizumab if severe
🌬 Acute Asthma Exacerbation Treatment:
Nebulized salbuta