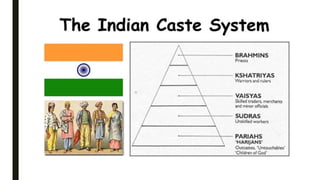
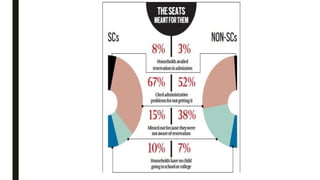
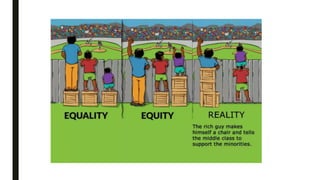
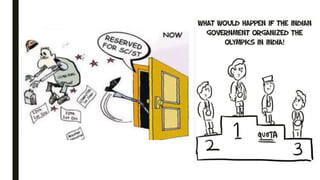
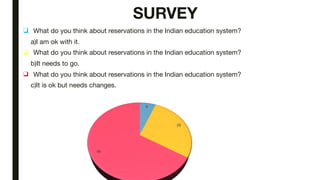
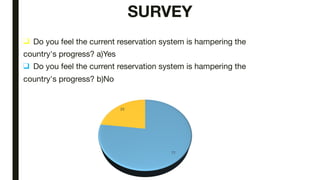
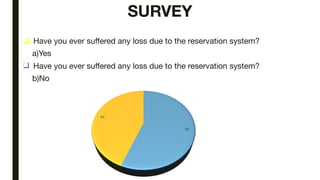
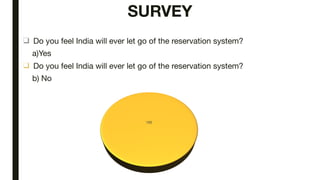
The document discusses India's reservation system which aims to promote access to education and employment for disadvantaged groups. It outlines the current reservation quotas of 45% for scheduled castes, scheduled tribes and other backward classes. While supporters see reservations as promoting social justice and representation, critics argue it hampers meritocracy and has created feelings of discrimination. The document examines various types of reservations including those based on caste, gender, religion and employment. It also discusses the pros and cons of the system as well as proposed solutions like tracking benefits and limiting reservations to the first two children in a family.